Abstract
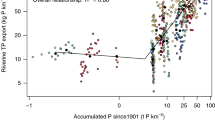
Phosphorus (P) plays a crucial role in both agricultural production and water quality. There has been growing recognition of the importance of “legacy” P (surplus P that has accumulated in watersheds over time) for understanding contemporary water quality outcomes; however, little is known about how different watersheds respond to cumulative pressures from surplus P. The “buffering capacity” concept describes the ability of watersheds to attenuate P loading to surface waters by retaining P inputs over time. To explore the role of various watershed characteristics in buffering capacity, we used historic P data to calculate indices describing long- and short-term buffering for 16 large watersheds in southern Quebec, Canada, across a 30-year time span (1981–2011). We examined the correlation between these buffering capacity indicators and a set of key geochemical, hydrological, landscape and socio-ecological variables that we hypothesized could influence P buffering dynamics. Both short- and long-term buffering metrics were most strongly correlated with hydrological characteristics. Riverine TP flux across the watersheds was most strongly correlated with long-term buffering, which could represent a dominant influence of legacy P on contemporary riverine P flux. However, short- and long-term watershed buffering indices were not correlated with each other, suggesting distinctly different timescales and mechanisms of buffering. Combining estimates of long-term P accumulation along with biophysical characteristics of the watershed (including hydrology) explained a much greater share of the variation in riverine TP flux (R2 = 0.69) than biophysical characteristics alone (R2 = 0.36). Our findings reinforce the need to consider P buffering capacity and legacy P accumulation to help guide decision making around regional water quality targets across human-dominated landscapes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander RB, Smith RA, Schwarz GE, Boyer EW, Nolan JV, Brakebill JW. 2007. Differences in phosphorus and nitrogen delivery to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River Basin. Environ Sci Technol 42:822–30.
Allan JD. 2004. Landscapes and riverscapes: the influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Systemat 35:257–84.
Barry C, Foy R. 2016. Assessing the success of regional measures for lowering agricultural nutrient pollution in headwater streams. J Environ Qual 45:1329–43.
Beaudet P, Grenier M, Giroux M, Girard V. 2003. Description statistique des propriétés chimiques des sols minéraux du Québec: Basée sur les analyses de sols effectuées de 1995 a 2001. Ministere de l’Agriculture, des Pêcheries et de l’Alimentation du Québec and Institut de recherche et de développement en agroenvironnement Inc.
Bennett EM, Carpenter SR, Caraco NF. 2001. Human impact on erodable phosphorus and eutrophication: a global perspective increasing accumulation of phosphorus in soil threatens rivers, lakes, and coastal oceans with eutrophication. Bioscience 51:227–34.
Borbor-Cordova MJ, Boyer EW, McDowell WH, Hall CA. 2006. Nitrogen and phosphorus budgets for a tropical watershed impacted by agricultural land use: Guayas, Ecuador. Biogeochemistry 79:135–61.
Boutin D. 2005. Reconciling farm support and environmental protection: trends and prospects. In: 6th biennial conference of the Canadian society for ecological economics.
Carpenter SR. 2005. Eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems: bistability and soil phosphorus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10002–5.
Childers DL, Corman J, Edwards M, Elser JJ. 2011. Sustainability challenges of phosphorus and food: solutions from closing the human phosphorus cycle. Bioscience 61:117–24.
Dobermann A, Cassman K. 2002. Plant nutrient management for enhanced productivity in intensive grain production systems of the United States and Asia. Progress in Plant Nutrition: Plenary Lectures of the XIV International Plant Nutrition Colloquium: Springer, p 153–175.
Doody DG, Withers PJ, Dils RM, McDowell RW, Smith V, McElarney YR, Dunbar M, Daly D. 2016. Optimizing land use for the delivery of catchment ecosystem services. Front Ecol Environ 14:325–32.
Environment CCot, Development S. 2001. Report of the Commissioner of the Environment and Sustainable Development to the House of Commons: The Commissioner.
ESRI. 2012. ArcGIS 10.1. Redlands, CA: Environmental Systems Research Institute.
Fraterrigo JM, Downing JA. 2008. The influence of land use on lake nutrients varies with watershed transport capacity. Ecosystems 11:1021–34.
Gentry L, David M, Royer T, Mitchell C, Starks K. 2007. Phosphorus transport pathways to streams in tile-drained agricultural watersheds. J Environ Qual 36:408–15.
Gordon LJ, Peterson GD, Bennett EM. 2008. Agricultural modifications of hydrological flows create ecological surprises. Trends Ecol Evol 23:211–19.
Goyette JO, Bennett EM, Howarth RW, Maranger R. 2016. Changes in anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs to the St. Lawrence sub-basin over 110 years and impacts on riverine export. Global Biogeochem Cycles 30:1000–14.
Hong B, Swaney DP, Mörth C-M, Smedberg E, Hägg HE, Humborg C, Howarth RW, Bouraoui F. 2012. Evaluating regional variation of net anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs (NANI/NAPI), major drivers, nutrient retention pattern and management implications in the multinational areas of Baltic Sea basin. Ecol Model 227:117–35.
Jarvie HP, Sharpley AN, Spears B, Buda AR, May L, Kleinman PJ. 2013. Water quality remediation faces unprecedented challenges from “legacy phosphorus”. Environ Sci Technol 47:8997–8.
Jutras P. 1967. Extent of agricultural drainage needs in Quebec. Can Agric Eng 9:117–25.
King KW, Williams MR, Johnson LT, Smith DR, LaBarge GA, Fausey NR. 2017. Phosphorus availability in western lake erie basin drainage waters: legacy evidence across spatial scales. J Environ Qual 46:466–9.
Kleinman P, Sharpley A, Buda A, McDowell R, Allen A. 2011. Soil controls of phosphorus in runoff: management barriers and opportunities. Can J Soil Sci 91:329–38.
Lee CJ, Hirsch RM, Schwarz GE, Holtschlag DJ, Preston SD, Crawford CG, Vecchia AV. 2016. An evaluation of methods for estimating decadal stream loads. J Hydrol 542:185–203.
Lehner B, Grill G. 2013. Global river hydrography and network routing: baseline data and new approaches to study the world’s large river systems. Hydrol Process 27:2171–86.
Lim KJ, Engel BA, Tang Z, Choi J, Kim KS, Muthukrishnan S, Tripathy D. 2005. Automated web gis based hydrograph analysis tool, WHAT1. Wiley Online Library.
MacDonald GK, Bennett EM. 2009. Phosphorus accumulation in Saint Lawrence River watershed soils: a century-long perspective. Ecosystems 12:621–35.
Mailhot A, Rousseau A, Salvano E, Turcotte R, Villeneuve J. 2002. Évaluation de l’impact de l’assainissement urbain sur la qualité des eaux du bassin versant de la rivière Chaudière à l’aide du système de modélisation intégrée GIBSI. Revue des sciences de l’eau/J Water Sci 15:149–72.
McDowell R, Monaghan R, Morton J. 2003. Soil phosphorus concentrations to minimise potential P loss to surface waters in Southland. N Z J Agric Res 46:239–53.
McGarigal K, Cushman SA, Ene E. 2012. FRAGSTATS 4.0: Spatial pattern analysis program for categorical and continuous maps. Amherst, Massachusetts, USA: University of Massachusetts.
Meals DW, Dressing SA, Davenport TE. 2010. Lag time in water quality response to best management practices: a review. J Environ Qual 39:85–96.
Metson GS, Lin J, Harrison JA, Compton JE. 2017. Linking terrestrial phosphorus inputs to riverine export across the United States. Water Res 124:177–91.
Montpetit É, Coleman WD. 1999. Policy communities and policy divergence in Canada: agro-environmental policy development in Quebec and Ontario. Can J Polit Sci 32:691–714.
Motew M, Chen X, Booth EG, Carpenter SR, Pinkas P, Zipper SC, Loheide SP, Donner SD, Tsuruta K, Vadas PA. 2017. The influence of legacy P on lake water quality in a Midwestern agricultural watershed. Ecosystems: 1–15.
Osborne LL, Kovacic DA. 1993. Riparian vegetated buffer strips in water-quality restoration and stream management. Freshw Biol 29:243–58.
Painchaud J. 1997. La qualité de l’eau des rivières du Québec: état et tendances: Ministère de l’environnement et de la faune.
Preston SD, Alexander RB, Schwarz GE, Crawford CG. 2011. Factors affecting stream nutrient loads: a synthesis of regional SPARROW model results for the continental United States. JAWRA J Am Water Resour Assoc 47:891–915.
Qiu J, Turner MG. 2015. Importance of landscape heterogeneity in sustaining hydrologic ecosystem services in an agricultural watershed. Ecosphere 6:1–19.
R Core Team. 2016. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Raudsepp-Hearne C, Peterson GD, Bennett E. 2010. Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:5242–7.
Reed T, Carpenter SR. 2002. Comparisons of P-yield, riparian buffer strips, and land cover in six agricultural watersheds. Ecosystems 5:568–77.
Rowe H, Withers PJ, Baas P, Chan NI, Doody D, Holiman J, Jacobs B, Li H, MacDonald GK, McDowell R. 2016. Integrating legacy soil phosphorus into sustainable nutrient management strategies for future food, bioenergy and water security. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 104:393–412.
Russell MJ, Weller DE, Jordan TE, Sigwart KJ, Sullivan KJ. 2008. Net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs: spatial and temporal variability in the Chesapeake Bay region. Biogeochemistry 88:285–304.
Scheffer M, Carpenter S, Foley JA, Folke C, Walker B. 2001. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 413:591.
Sharpley A, Jarvie HP, Buda A, May L, Spears B, Kleinman P. 2013. Phosphorus legacy: overcoming the effects of past management practices to mitigate future water quality impairment. J Environ Qual 42:1308–26.
Soil Landscapes of Canada Working Group. 2010. Soil Landscapes of Canada version 3.2. Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada.
van Bochove E, Thériault G, Denault J-T, Dechmi F, Allaire SE, Rousseau AN. 2012. Risk of phosphorus desorption from Canadian agricultural land: 25-year temporal trend. J Environ Qual 41:1402–12.
Vaz MR, Edwards A, Shand C, Cresser M. 1993. Phosphorus fractions in soil solution: influence of soil acidity and fertiliser additions. Plant Soil 148:175–83.
Vitousek PM, Naylor R, Crews T, David M, Drinkwater L, Holland E, Johnes P, Katzenberger J, Martinelli L, Matson P. 2009. Nutrient imbalances in agricultural development. Science 324:1519–20.
Walker W. 1999. Simplified procedures for eutrophication assessment and prediction: user manual. United States Army Corps of Engineers. Instruction Report W-96-2.
Withers PJ, Neal C, Jarvie HP, Doody DG. 2014. Agriculture and eutrophication: where do we go from here? Sustainability 6:5853–75.
Acknowledgements
We thank Helen Jarvie and Donnacha Doody for comments on previous drafts. We thank Guillaume Larocque at the Québec Centre for Biodiversity Science for technical assistance and support. This research was funded by the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) Discovery Grants (DG) to Elena Bennett and the Economics for the Anthropocene (E4A) program. We thank two anonymous reviewers for their invaluable feedback.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusmer, A.S., Goyette, JO., MacDonald, G.K. et al. Watershed Buffering of Legacy Phosphorus Pressure at a Regional Scale: A Comparison Across Space and Time. Ecosystems 22, 91–109 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-018-0255-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-018-0255-z