Abstract
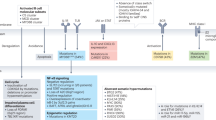
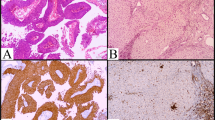
In recent years, the features of lymphomas associated with chronic inflammation, referred to as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) associated with chronic inflammation (DLBCL-CI), have been elucidated. DLBCL-CI is an aggressive lymphoma occurring in the context of long-standing chronic inflammation and showing an association with Epstein–Barr virus. Fibrin-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (F-DLBCL) was suggested as a new and unusual form of DLBCL-CI in the most recent version of the World Health Organization classification. From the perspective of genetics, DLBCL-CI was associated with frequent TP53 mutation, MYC amplification and complex karyotypes, but cases of F-DLBCL behaved indolently and showed a relatively lower genetic complexity. In the central nervous system (CNS), several examples of DLBCL-CI and F-DLBCL have been reported. As with DLBCL-CI outside the CNS, DLBCL-CI in the CNS is an aggressive lymphoma. However, the clinical outcome of F-DLBCL in the CNS is good. Immunohistochemistry for p53 and c-Myc in DLBCL-CI and F-DLBCL in the CNS showed similar findings of those outside the CNS. However, one aggressive case showed transitional genetics and morphology between F-DLBCL and DLBCL-CI. These findings suggest that some cases of F-DLBCL in the CNS might have the potential to progress to DLBCL-CI.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boroumand N, Ly TL, Sonestein J, Medeiros LJ (2012) Microscopic diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) occurring in pseudocysts. Do these tumors belong to the category of DLBL associated with chronic inflammation? Am J Surg Pathol 36(7):1074–1080
Boyer DF, McKelvie PA, de Leval L et al (2017) Fibrin-associated EBV-positive large B-cell lymphoma an indolent neoplasm with features distinct from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation. Am J Surg Pathol 41(3):299–312
Chan JKC, Aozasa K, Gaulard P (2017) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, et al. (eds) WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissue. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, pp 309–311
Cherian A, Baheti NN, Easwar HV, Nair DS, Iype T (2012) Recurrent meningitis due to epidermoid. J Pediatr Neurosci 7(1):47–48
Dobre MC, Smoker WR, Moritani T, Kirby P (2012) Spontaneously ruptured intraspinal epidermoid cyst causing chemical meningitis. J Clin Neurosci 19(4):587–589
Fujimoto M, Haga H, Okamoto M et al (2008) EBV-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arising in the chest wall with surgical mesh implant. Pathol Int 58(10):668–671
Green TM, Nielsen O, de Stricker K et al (2012) High levels of nuclear MYC protein predict the presence of MYC rearrangement in diffuse large cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol 36(4):612–619
Gruver AM, Huba MA, Dogan A, His ED (2012) Fibrin-associated large B-cell lymphoma. Part of the spectrum of cardiac lymphomas. Am J Surg Pathol 36(10):1527–1537
Iuchi K, Ichimiya A, Akashi A et al (1987) Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the pleural cavity developing from long-standing pyothorax. Cancer 60(8):1771–1775
Imaizumi S, Onuma T, Kameyama M, Naganuma H (2001) Organized chronic subdural hematoma requiring craniotomy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 41(1):19–24
Kameda K, Shono T, Takagishi S et al (2015) Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with–organized chronic subdural hematoma: a case report and review of the literature. Pathol Int 65(3):138–143
Kirschenbaum D, Prömmel P, Vasella F et al (2017) Fibrin-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in a hemorrhagic cranial arachnoid cyst. Acta Neuropathol Commun 5(1):60
Loong F, Chan AC, Ho BC et al (2010) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation as an incidental finding and new clinical scenarios. Mod Pathol 23(4):493–501
Masuoka J, Sakata S, Maeda K, Sugita Y (2008) Adjacent epidermoid cyst and primary central nervous system: case report. Surg Neurol 69(5):530–534
Miller DV, Firchau DJ, McClure RF, Kurtin PJ, Feldman AL (2010) Epstein-Barr virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arising on cardiac prosthesis. Am J Surg Pathol 34(3):377–384
Nakatsuka S, Yao M, Hoshida Y, Yamamoto S, Iuchi K, Aozasa K (2002) Pyothorax–associated lymphoma: a review of 106 cases. J Clin Oncol 20(20):4255–4260
Nanko N, Tanikawa M, Mase M et al (2009) Involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor in the mechanism of development of chronic subdural hematoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 49(9):379–385
Nishiu M, Tomita Y, Nakatsuka S et al (2004) Distinct pattern of gene expression in pyothorax-associated lymphoma, a lymphoma developing in long-standing inflammation. Cancer Sci 95(10):828–834
Sanchez-Gonzalez B, Garcia M, Montserrat F et al (2013) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation in metallic implant. J Clin Oncol 31(10):e148–151
Sugita Y, Ohta M, Ohshima K et al (2012) Epstein-Barr virus–positive lymphoproliferative disorder with organized chronic subdural hematoma. Pathol Int 62(6):412–417
Suzuki M, Endo S, Inada K et al (1998) Inflammatory cytokines locally elevated in Chronic subdural hematoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140(1):51–55
Valli R, Froio E, de Celis M, Mandato VD, Piana S (2014) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma occurring in an ovarian cystic teratoma: expanding the spectrum of large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation. Hum Pathol 45(12):2507–2511
Xu-Monette ZY, Wu L, Visco C et al (2012) Mutational profile and prognostic significance of TP53 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP: report from an International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Blood 120(19):3986–3996
Yan J, Luo D, Zhang F et al (2017) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation arising within atrial myxoma: aggressive histological features but indolent clinical behavior. Histopathology 71(6):951–959
Yorita K, Tanaka Y, Hirano K et al (2019) Fibrin-associated large B-cell lymphoma arising in a mature cystic teratoma: a case report. Pathol Int 69(5):312–314
Zanelli M, Zizzo M, Montanaro M et al (2019) Fibrin-associated large B-cell lymphoma: first case report within a cerebral artery aneurysm and literature review. BMC Cancer 19(1):916
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Drs. Shinji Kohno (Harasanshin Hospital) and Daisuke Mori (Saga Prefectural Hospital Koseikan) who gave us valuable materials. The authors also wish to thank Ms. Fumiko Arakawa (Kurume University School of Medicine) for her valuable technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugita, Y., Masuoka, J., Kameda, K. et al. Primary central nervous system lymphomas associated with chronic inflammation: diagnostic pitfalls of central nervous system lymphomas. Brain Tumor Pathol 37, 127–135 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-020-00373-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-020-00373-z