Abstract
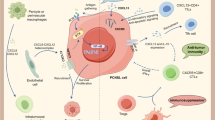
Chemokines are peptides that function as chemoattractant cytokines in cell activation, differentiation and trafficking. Endothelin B receptor (ETBR) is a receptor for endothelin, which is known to function as a vasoconstrictor. In the present study, to clarify the immune escape mechanism of primary central nervous system lymphomas (PCNSLs), the expression of ETBR and of subsets of chemokines (CXCL12, 13) in 24 PCNSLs was investigated. CXCL12 was expressed by lymphoma cells in different resident brain cell populations in 22/24 cases. CXCL13 expression was identified in tumor cells in 19/24 cases, but was only expressed by tumor cells and by proliferating vascular endothelial cells. In addition, tumor-infiltrated lymphocytes (TILs) accumulated in areas with expression of chemokines, particularly of CXCL13. ETBR expression was detected in 12/24 cases. Positive ETBR cases were associated with a paucity of TILs, particularly of cytotoxic T cells, whereas negative ETBR cases were associated with an abundance of TILs. The combined data indicate that CXCL12 and CXCL13 up-regulation may be differently linked to the development of PCNSLs and to the accumulation of TILs. In addition, ETBR expression by lymphoma and endothelial cells may mediate trafficking of TILs, which may explain the immune escape processes of PCNSLs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deckert M, Paulus W (2007) Malignant lymphomas. In: Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (eds) Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Nervous System. International Agency for Research on Cancer Press, Lyon, pp 188–192
Sugita Y, Tokunaga O, Nakashima A, Shigemori M (2004) SHP-1 expression in primary central nervous system B-cell lymphomas in immunocompetent patients reflects maturation stage of normal B cell counterparts. Pathol Int 54:659–666
Kucia M, Jankowski K, Reca R et al (2004) CXCR4-SDF1 signalling, locomotion, chemotaxis and adhesion. J Mol Histol 35:233–245
Teicher BA, Fricker SP (2007) CXCL12(SDF1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:2927–2931
Lazarini F, Tham TN, Casanova P et al (2003) Role of the alpha-chemokine stromal cell-derived factor (SDF1) in the developing and mature central nervous system. Glia 42:139–148
Barbieri F, Bajetto A, Florio T et al (2010) Network in the development and progression of ovarian cancer: a potential novel pharmacological target. J Oncol 61:4961–4965
Singh S, Singh UP, Grizzle WE et al (2004) CXCL12-CXCR4 interactions modulate prostate cancer cell migration, metalloproteinase expression and invasion. Lab Invest 84:1666–1676
Jiang Y, Wu X-H, Shi B et al (2006) Expression of chemokine CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 in human epithelial ovarian cancer: an independent prognostic factor for tumor progression. Gynecol Oncol 103:226–233
Yasumoto K, Koizumi K, Kawashima A et al (2006) Role of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in peritoneal carcinomatosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Res 66:2181–2187
Folkins C, Shaked Y, Man S et al (2009) Glioma tumor stem-like cells promote tumor angiogenesis and vasculogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor and stromal-derived factor 1. Cancer Res 69:7243–7251
Smith JR, Braziel RM, Paoletti S et al (2003) Expression of B-cell-attracting chemokine 1(CXCL13) by malignant lymphocytes and vascular endothelium in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Blood 101:815–821
Brunn A, Montesinos-Rongen M, Strack A et al (2007) Expression pattern and cellular sources of chemokines in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Neuropathathol 114:271–276
Smith JR, Falkenhagen KM, Coupland SE et al (2007) Malignant B cells from patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma express stromal cell-derived factor-1. Am J Clin Pathol 127:633–641
Jahnke K, Coupland SE, Na IK et al (2005) Expression of the chemokine receptors CXCR4, CXCR5, and CCR7 in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Blood 106:384–385
Fischer L, Korfel A, Pfeiffer S et al (2007) CXCL13 and CXCL12 in central nervous system lymphoma patients. Clin Cancer Res 15:5968–5973
Venetz D, Ponzoni M, Schiraldi M et al (2010) Perivascular expression of CXCL9 and CXCL12 in primary central nervous system lymphoma: T-cell infiltration and positioning of malignant B cells. Int J Cancer Res 127:2300–2312
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S et al (1988) A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature 332:411–415
Inoue A, Yanagisawa M, Kimura S et al (1989) The human endothelin family: three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc Natl Acad of Sci USA 86:2863–2867
Ahmed SI, Thompson J, Coulson JM, Woll PJ (2000) Studies on the expression of endothelin, its receptor subtypes, and converting enzymes in lung cancer and in human bronchial epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 22:422–431
Rosano L, Varmi M, Salani D, Di Castro V, Spinella F, Natali PG, Bagnato A (2001) Endothelin-1 induces tumor proteinase activation and invasiveness of ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 61:8340–8346
Kusuhara M, Yamaguchi K, Nagasaki K et al (1990) Production of endothelin in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 50:3257–3261
Nelson JB, Chan-Tack K, Hedican SP et al (1996) Endothelin-1 production and decreased endothelin B receptor expression in advanced prostate cancer. Cancer Res 56:663–668
Kandalaft LE, Facciabene A, Buckanovich RJ, Coukos G (2009) Endothelin B receptor, a new target in cancer immune therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15:4521–4528
Paolillo M, Barbieri A, Zanassi P, Schinelli S (2006) Expression of endothelins and their receptors in glioblastoma cell lines. J Neurooncol 79:1–7
Anguelova E, Beuvon F, Leonard N et al (2005) Functional endothelin ET B receptors are selectively expressed in human oligodendrogliomas. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 137:77–88
Buckanovich RJ, Facciabene A, Kim S et al (2008) Endothelin B receptor mediates the endothelial barrier to T cell homing to tumors and disables immune therapy. Nat Med 14:28–36
Sugita Y, Takase Y, Mori D, Tokunaga O, Nakashima A, Shigemori M (2007) Endoglin (CD 105) is expressed on endothelial cells in the primary central nervous system lymphomas and correlates with survival. J Neurooncol 82:249–256
Kiyasu J, Aoki R, Tanaka PY et al (2012) FOXP3+ regulatory and TIA-1+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in HIV-associated Hodgkin lymphoma. Pathol In 62:77–83
Komatani H, Sugita Y, Arakawa F et al. (2009) Expression of CXCL12 on pseudopalisading cells and proliferating microvessels in glioblastomas: an accelerated growth factor in glioblastomas. Int J Oncol 34:665–672
Ponzoni M, Berger F, Chassagne-Clement C et al (2007) Reactive perivascular T-cell infiltrate predicts survival in primary central nervous system B-cell lymphomas. Br J Haematol 138:316–323
Kandalaft LE, Facciabene A, Buckanovich RJ, Coukos G (2009) Endothelin B receptor, a new target in cancer immune therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15:4521–4528
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 24500427.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugita, Y., Terasaki, M., Nakashima, S. et al. The perivascular microenvironment in primary central nervous system lymphomas: the role of chemokines and the endothelin B receptor. Brain Tumor Pathol 32, 41–48 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-014-0206-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-014-0206-0