Abstract
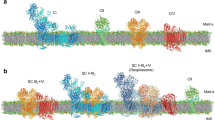
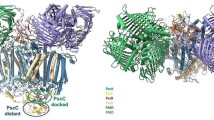
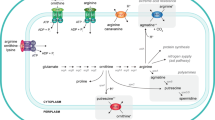
Mrp antiporters are the sole antiporters in the Cation/Proton Antiporter 3 family of transporter databases because of their unusual structural complexity, 6–7 hydrophobic proteins that function as a hetero-oligomeric complex. The two largest and homologous subunits, MrpA and MrpD, are essential for antiport activity and have direct roles in ion transport. They also show striking homology with proton-conducting, membrane-embedded Nuo subunits of respiratory chain complex I of bacteria, e.g., Escherichia coli. MrpA has the closest homology to the complex I NuoL subunit and MrpD has the closest homology to the complex I NuoM and N subunits. Here, introduction of mutations in MrpD, in residues that are also present in MrpA, led to defects in antiport function and/or complex formation. No significant phenotypes were detected in strains with mutations in corresponding residues of MrpA, but site-directed changes in the C-terminal region of MrpA had profound effects, showing that the MrpA C-terminal region has indispensable roles in antiport function. The results are consistent with a divergence in adaptations that support the roles of MrpA and MrpD in secondary antiport, as compared to later adaptations supporting homologs in primary proton pumping by the respiratory chain complex I.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amarneh B, Vik SB (2010) Transmembrane topology of subunit N of complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) from Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg Biomembr 42:511–516. doi:10.1007/s10863-010-9318-3
Baradaran R, Berrisford JM, Minhas GS, Sazanov LA (2013) Crystal structure of the entire respiratory complex I. Nature 494:443–448. doi:10.1038/nature11871
Batista AP, Marreiros BC, Pereira MM (2012) The role of proton and sodium ions in energy transduction by respiratory complex I. IUBMB Life 64:492–498. doi:10.1002/iub.1050
Brett CL, Donowitz M, Rao R (2005) Evolutionary origins of eukaryotic sodium/proton exchangers. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C223–C239. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00360.2004
Efremov RG, Sazanov LA (2011) Structure of the membrane domain of respiratory complex I. Nature 476:414–420. doi:10.1038/nature10330
Hamamoto T, Hashimoto M, Hino M, Kitada M, Seto Y, Kudo T, Horikoshi K (1994) Characterization of a gene responsible for the Na+/H+ antiporter system of alkalophilic Bacillus species strain C-125. Mol Microbiol 14:939–946
Ito M, Guffanti AA, Wang W, Krulwich TA (2000) Effects of nonpolar mutations in each of the seven Bacillus subtilis mrp genes suggest complex interactions among the gene products in support of Na+ and alkali but not cholate resistance. J Bacteriol 182:5663–5670
Kaila VR, Wikstrom M, Hummer G (2014) Electrostatics, hydration, and proton transfer dynamics in the membrane domain of respiratory complex I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:6988–6993. doi:10.1073/pnas.1319156111
Kajiyama Y, Otagiri M, Sekiguchi J, Kudo T, Kosono S (2009) The MrpA, MrpB and MrpD subunits of the Mrp antiporter complex in Bacillus subtilis contain membrane-embedded and essential acidic residues. Microbiology 155:2137–2147. doi:10.1099/mic.0.025205-0
Kosono S, Haga K, Tomizawa R, Kajiyama Y, Hatano K, Takeda S, Wakai Y, Hino M, Kudo T (2005) Characterization of a multigene-encoded sodium/hydrogen antiporter (sha) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: its involvement in pathogenesis. J Bacteriol 187:5242–5248. doi:10.1128/JB.187.15.5242-5248.2005
Krulwich TA, Ito M (2013) Prokaryotic alkaliphiles. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Thompson F, Lory S, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes, 4th edn. Springer, New York
Krulwich TA, Sachs G, Padan E (2011) Molecular aspects of bacterial pH sensing and homeostasis. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:330–343. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2549
Lee BL, Sykes BD, Fliegel L (2013) Structural and functional insights into the cardiac Na+/H+ exchanger. J Mol Cell Cardiol 61:60–67. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.11.019
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mathiesen C, Hägerhäll C (2003) The ‘antiporter module’ of respiratory chain complex I includes the MrpC/NuoK subunit—a revision of the modular evolution scheme. FEBS Lett 549:7–13
Moparthi VK, Hägerhäll C (2011a) The evolution of respiratory chain complex I from a smaller last common ancestor consisting of 11 protein subunits. J Mol Evol 72:484–497. doi:10.1007/s00239-011-9447-2
Moparthi VK, Hägerhäll C (2011b) Recruitment of the antiporter module—a key event in complex I evolution. In: Sazanov LA (ed) A structural perspective on complex I. Springer, Berlin, pp 123–143
Moparthi VK, Kumar B, Mathiesen C, Hägerhäll C (2011) Homologous protein subunits from Escherichia coli NADH:quinone oxidoreductase can functionally replace MrpA and MrpD in Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1807:427–436. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.01.005
Moparthi VK, Kumar B, AI-Eyani Y, Sperling E, Gorecki E, Drakenberg T, Hägerhäll C (2014) Functional role of the MrpA- and MrpD-homologous protein subunits in enzyme complexes evolutionary related to respiratory chain complex I. Biochim Biophys Acta 1837:178–185. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.09.012
Morino M, Ito M (2012) Functional expression of the multi-subunit type calcium/proton antiporter from Thermomicrobium roseum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 335:26–30. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02634.x
Morino M, Natsui S, Swartz TH, Krulwich TA, Ito M (2008) Single gene deletions of mrpA to mrpG and mrpE point mutations affect activity of the Mrp Na+/H+ antiporter of alkaliphilic Bacillus and formation of hetero-oligomeric Mrp complexes. J Bacteriol 190:4162–4172. doi:10.1128/JB.00294-08
Morino M, Natsui S, Ono T, Swartz TH, Krulwich TA, Ito M (2010) Single site mutations in the hetero-oligomeric Mrp antiporter from alkaliphilic Bacillus pseudofirmus OF4 that affect Na+/H+ antiport activity, sodium exclusion, individual Mrp protein levels, or Mrp complex formation. J Biol Chem 285:30942–30950. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.118661
Nakamaru-Ogiso E, Kao MC, Chen H, Sinha SC, Yagi T, Ohnishi T (2010) The membrane subunit NuoL(ND5) is involved in the indirect proton pumping mechanism of Escherichia coli complex I. J Biol Chem 285:39070–39078. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.157826
Nozaki K, Kuroda T, Mizushima T, Tsuchiya T (1998) A new Na+/H+ antiporter, NhaD, of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1369:213–220
Orlowski J, Grinstein S (2007) Emerging roles of alkali cation/proton exchangers in organellar homeostasis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:483–492. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2007.06.001
Padan E, Venturi M, Gerchman Y, Dover N (2001) Na+/H+ antiporters. Biochim Biophys Acta 1505:144–157
Padan E, Bibi E, Ito M, Krulwich TA (2005) Alkaline pH homeostasis in bacteria: new insights. Biochim Biophys Acta 1717:67–88. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2005.09.010
Ren Q, Chen K, Paulsen IT (2007) TransportDB: a comprehensive database resource for cytoplasmic membrane transport systems and outer membrane channels. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D274–D279. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl925
Rimon A, Tzubery T, Padan E (2007) Monomers of the NhaA Na+/H+ antiporter of Escherichia coli are fully functional yet dimers are beneficial under extreme stress conditions at alkaline pH in the presence of Na+ or Li+. J Biol Chem 282:26810–26821
Roberts PG, Hirst J (2012) The deactive form of respiratory complex I from mammalian mitochondria is a Na+/H+ antiporter. J Biol Chem 287:34743–34751. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.384560
Saier MH Jr, Yen MR, Noto K, Tamang DG, Elkan C (2009) The transporter classification database: recent advances. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D274–D278. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn862
Sato M, Sinha PK, Torres-Bacete J, Matsuno-Yagi A, Yagi T (2013) Energy transducing roles of antiporter-like subunits in Escherichia coli NDH-1 with main focus on subunit NuoN (ND2). J Biol Chem 288:24705–24716. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.482968
Schuldiner S (2014) Competition as a way of life for H+-coupled antiporters. J Mol Biol 426:2539–2546. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2014.05.020
Steffen W, Steuber J (2013) Cation transport by the respiratory NADH:quinone oxidoreductase (complex I): facts and hypotheses. Biochem Soc Trans 41:1280–1287. doi:10.1042/BST20130024
Steimle S, Willistein M, Hegger P, Janoschke M, Erhardt H, Friedrich T (2012) Asp563 of the horizontal helix of subunit NuoL is involved in proton translocation by the respiratory complex I. FEBS Lett 586:699–704. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.01.056
Sturr MG, Guffanti AA, Krulwich TA (1994) Growth and bioenergetics of alkaliphilic Bacillus firmus OF4 in continuous culture at high pH. J Bacteriol 176:3111–3116
Swartz TH, Ikewada S, Ishikawa O, Ito M, Krulwich TA (2005) The Mrp system: a giant among monovalent cation/proton antiporters? Extremophiles 9:345–354. doi:10.1007/s00792-005-0451-6
Swartz TH, Ito M, Ohira T, Natsui S, Hicks DB, Krulwich TA (2007) Catalytic properties of Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus members of the secondary cation/proton antiporter-3 (Mrp) family are revealed by an optimized assay in an Escherichia coli host. J Bacteriol 189:3081–3090. doi:10.1128/JB.00021-07
Torres-Bacete J, Nakamaru-Ogiso E, Matsuno-Yagi A, Yagi T (2007) Characterization of the NuoM (ND4) subunit in Escherichia coli NDH-1: conserved charged residues essential for energy-coupled activities. J Biol Chem 282:36914–36922. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707855200
Virzintiene E, Moparthi VK, Al-Eryani Y, Shumbe L, Gorecki K, Hägerhäll C (2013) Structure and function of the C-terminal domain of MrpA in the Bacillus subtilis Mrp-antiporter complex–the evolutionary progenitor of the long horizontal helix in complex I. FEBS Lett 587:3341–3347. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.08.027
Zickermann V, Wirth C, Nasiri H, Siegmund K, Schwalbe H, Hunte C, Brandt U (2015) Structural biology. Mechanistic insight from the crystal structure of mitochondrial complex I. Science 347:44–49. doi:10.1126/science.1259859
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by research grant GM28454 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (to T.A.K.), as well as a special research Grant (2010) from Toyo University and JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 15K07012 (to M.I.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Atomi.
This article is part of a special feature based on the 11th International Congress on Extremophiles held in Kyoto, Japan, September 12–16, 2016.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morino, M., Ogoda, S., Krulwich, T.A. et al. Differences in the phenotypic effects of mutations in homologous MrpA and MrpD subunits of the multi-subunit Mrp-type Na+/H+ antiporter. Extremophiles 21, 51–64 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-016-0877-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-016-0877-z