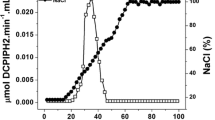
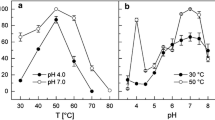
Abstract
Psychrophilic organisms have evolved a number of modifications of cellular structures to survive in the cold environment; among them it is worth noting an increased efficiency of enzymes at lower temperatures. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH; EC 1.1.1.49) was purified and characterised from the psychrophilic green alga Koliella antarctica (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) from the Ross Sea (Antarctica). It was possible to isolate a single G6PDH using biochemical strategies; its maximum activity was measured at 35 °C, and the enzyme showed an E a of 39.6 kJ mol−1. This protein reacted with antibodies raised against higher plants plastidic isoforms. KaG6PDH showed peculiar kinetic properties, with a K iNADPH value lower than \( K_{{{\text{mNADP}}^{ + } }} \). Notably, catalytic activity was inactivated in vitro by DTT and chloroplastic thioredoxin f. These biochemical properties of G6PDH are discussed with respect to higher plant G6PDHs and the adaptation of K. antarctica to polar low-temperature environment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- G6P:
-
Glucose-6-phosphate
- G6PDH:
-
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- Ka :
-
Koliella antarctica
- NaTT:
-
Sodium tetrathionate
- OPPP:
-
Oxidative pentose phosphate pathway
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- Tris:
-
Tris-(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane
References
Andreoli C, Lokhorst GM, Mani AM, Scarabel L, Moro I, La Rocca N, Tognetto L (1998) Koliella antartica sp. nov. (Klebsormidiales) a new marine green microalga form the Ross Sea (Antarctica). Arc Hydrobiol/Algol Stud 90:1–8
Baldisserotto C, Ferroni L, Andreoli C, Fasulo MP, Bonora A, Pancaldi S (2005) Dark acclimation of the chloroplast in Koliella antarctica exposed to a simulated Austral night condition. Arct Antarct Alp Res 37:146–156
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein dye-binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cavicchioli R, Charlton T, Ertan H, Omar SM, Siddiqui KS, Williams TJ (2011) Biotechnological uses of enzymes from psychrophiles. Microb Biotechnol 4:449–460. doi:10.1111/j.1751-7915.2011.00258.x
Chen Z, He C, Hu H (2012) Temperature responses of growth, photosynthesis, fatty acid and nitrate reductase in Antarctic and temperate Stichococcus. Extremophiles 16:127–133. doi:10.1007/s00792-011-0412-1
Di Martino Rigano V, Vona V, Lobosco O, Carillo P, Lunn JE, Carfagna S, Caiazzo M, Esposito S, Rigano C (2006) Temperature dependence of nitrate reductase in the psychrophilic unicellular alga Koliella antarctica and the mesophilic alga Chlorella sorokiniana. Plant Cell Environ 29:1400–1409
Esposito S, Carfagna S, Massaro G, Vona V, Di Martino Rigano V (2001) Glucose-6P dehydrogenase in barley roots: kinetic properties and localisation of the isoforms. Planta 212:627–634
Esposito S, Massaro G, Vona V, Di Martino Rigano V, Carfagna S (2003) Glutamate synthesis in barley roots: the role of the plastidic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Planta 216:639–647
Esposito S, Guerriero G, Vona V, Di Martino Rigano V, Carfagna S, Rigano C (2005) Glutamate synthase activities and protein changes in relation to nitrogen nutrition in barley: the dependence on different plastidic glucose-6P dehydrogenase isoforms. J Exp Bot 56:55–64
Esposito S, Guerriero G, Vona V, Di Martino Rigano V, Carfagna S, Rigano C (2006) Glucose-6P dehydrogenase in Chlorella sorokiniana (211/8k): an enzyme with unusual characteristics. Planta 223:796–804
Feller G, Gerday C (1997) Psychrophilic enzymes; molecular basis of cold adaption. Cell Mol Life Sci 53:830–841
Feller G, Gerday C (2003) Psychrophilic enzymes: hot topics in cold adaption. Nat Rev Microbiol 1:200–208
Forti G, Furia A, Bombelli P, Finazzi G (2003) In vivo changes of the oxidation–reduction state of NADP+ and of the ATP/ADP cellular ratio linked to the photosynthetic activity in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol 132:1464–1474
Foyer CH, Lelandis M, Kunert KJ (1994) Photooxidative stress in plants. Physiol Plant 92:696–717
Hauschild R, von Schaewen A (2003) Differential regulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase isoenzyme activities in potato. Plant Physiol 133:47–62
Honjoh K, Mimura A, Kuroiwa E, Hagisako T, Suga K, Shimizu H, Dubey RS, Miyamoto T, Hatano S, Lio M (2003) Purification and characterization of two isoforms of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) from Chlorella vulgaris C-27. Biosci Biotech Biochem 67:1888–1896
Honjoh K, Machida T, Hagisako T, Suga Y, Yonekura M, Shimizu H, Ohashi N, Miyamot T, Hatano S, Lio M (2007) Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA for low-temperature-inducible cytosolic glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene from Chlorella vulgaris and expression of the gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant Sci 172:649–658
Huppe HC, Turpin DH (1996) Appearance of a novel glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase isoforms in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii during growth on nitrate. Plant Physiol 110:1431–1433
Jin T, Huppe HC, Turpin DH (1998) In vitro reconstitution of electron transport from glucose-6-phosphate and NADPH to nitrite. Plant Physiol 117:303–309
Kroth PG, Chiovitti A, Gruber A, Martin-Jezequel V, Mock T, Schnitzler Parker M, Stanley MS, Kaplan A, Caron L, Weber T, Maheswari U, Armbrust EV, Bowler C (2008) A model for carbohydrate metabolism in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum deduced from comparative whole genome analysis. PLoS One 3:e1426
Kruger NJ, von Schaewen A (2003) The pentose phosphate pathway: structure and organisation. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:236–246
Lejay L, Wirth J, Pervent M, Cross JM-F, Tillard P, Gojon A (2008) Oxidative pentose phosphate pathway-dependent sugar sensing as a mechanism for regulation of root ion transporters by photosynthesis. Plant Physiol 146:2036–2053
Marx JC, Collins T, D’Amico S, Feller G, Gerday C (2007) Cold-adapted enzymes from marine Antarctic microorganisms. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 9:293–304
Michels AK, Wedel N, Kroth PG (2005) Diatom plastids possess a phosphoribulokinase with an altered regulation and no oxidative pentose phosphate pathway. Plant Physiol 137:911–920
Morgan-Kiss RM, Ivanov AG, Modla S, Czymmek K, Huner NPA, Priscu JC, Lisle JT, Hanson TE (2008) Identity and physiology of a new psychrophilic eukaryotic green alga, Chlorella sp., strain BI, isolated from a transitory pond near Bratina Island, Antarctica. Extremophiles 12:701–711. doi:10.1007/s00792-008-0176-4
Nagashima H, Matsumoto GI, Ohtani S, Momose H (1995) Temperature acclimation and the fatty acid composition of an Antarctic green alga Chlorella. Proc NIPR Symp Polar Biol 8:194–199
Née G, Zaffagnini M, Trost P, Issakidis-Bourguet E (2009) Redox regulation of chloroplastic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: a new role for f-type thioredoxin. FEBS Lett 17:2827–2832
Scheibe R, Geissler A, Fickenscher K (1989) Chloroplast glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: Km shift upon light modulation and reduction. Arch Biochem Biophys 274:290–297
Struvay C, Feller G (2012) Optimization to low temperature activity in psychrophilic enzymes. Int J Mol Sci 13:11643–11665. doi:10.3390/ijms130911643
Thompson PA, Guo M, Harrisonp J, Whyte JNC (1992) Effects of variation in temperature. II. On the fatty acid composition of eight species of marine phytoplankton. J Phycol 28:488–497
Van Heerden PDR, De Villiers MF, Van Staden J, Kruger GHJ (2003) Dark chilling increases glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity in soybean leaves. Physiol Plant 119:221–230
Vona V, Di Martino Rigano V, Lobosco O, Carfagna S, Esposito S, Rigano C (2004) Temperature responses of growth, photosynthesis, respiration and NADH: nitrate reductase in cryophilic and mesophilic algae. New Phytol 163:325–331
Wakao S, Benning C (2005) Genome-wide analysis of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in Arabidopsis. Plant J 41:243–256
Wendt UK, Wenderoth I, Tegeler A, von Schaewen A (2000) Molecular characterization of a novel glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plant J 23:723–733
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Prof. Andreoli, University of Padova (Italy), for the gift of Koliella antarctica. Thanks to Dr. M. Caiazzo and Dr. O. Lobosco for the batch growth of K. antarctica at the Plant Biology Section of the Dept of Biological Sciences at the University of Naples. We thank very much Prof. A. von Schaewen (Munster, Germany) for the generous gift of G6PDH antibodies. Dr. K. Chibani (University of Lorraine, Nancy, France) for the purified recombinant spinach thioredoxin f. We are in debt with Dr. M. Chiurazzi (IGB-CNR “Buzzati Traverso”, Naples) for the help and assistance to obtain the partial sequence of the G6PDH active site of K. antarctica. Many thanks to J.-P. Jacquot (University of Lorraine, Nancy, France), for reading the manuscript, the helpful discussion, and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Atomi.
The authors wish to dedicate this paper to Prof. Carmelo Rigano for his over 40 years of teaching and researching in Plant Physiology at the University of Naples “Federico II”.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrara, M., Guerriero, G., Cardi, M. et al. Purification and biochemical characterisation of a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from the psychrophilic green alga Koliella antarctica . Extremophiles 17, 53–62 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-012-0492-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-012-0492-6