Abstract
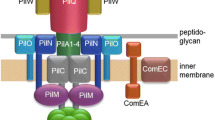
Thermus thermophilus is a model strain to unravel the molecular basis of horizontal gene transfer in hot environments. Previous genetic studies led to the identification of a macromolecular transport machinery mediating DNA uptake in an energy-dependent manner. Here, we have addressed how the transporter is energized. Inspection of the genome sequence revealed four putative transport (AAA) ATPases but only the deletion of one, PilF, led to a transformation defect. PilF is similar to transport ATPases of type IV and type II secretions systems but has a unique N-terminal sequence that carries a triplicated GSPII domain. To characterize PilF biochemically it was produced in Escherichia coli and purified. The recombinant protein displayed NTPase activity with a preference for ATP. Gel filtration analyses combined with dynamic light scattering demonstrated that PilF is monodispersed in solution and forms a complex of 590 ± 30 kDa, indicating a homooligomer of six subunits. It contains a tetracysteine motif, previously shown to bind Zn2+ in related NTPases. Using atomic absorption spectroscopy, indeed Zn2+ was detected in the enzyme, but in contrast to all known zinc-binding traffic NTPases only one zinc atom was bound to the hexamer. Deletion of the four cysteine residues led to a loss of Zn2+. Nevertheless, the mutant protein retained ATPase activity and hexameric complex formation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abendroth J, Murphy P, Sandkvist M, Bagdasarian M, Hol WG (2005) The X-ray structure of the type II secretion system complex formed by the N-terminal domain of EpsE and the cytoplasmic domain of EpsL of Vibrio cholerae. J Mol Biol 348:845–855
Aravind L, Tatusov RL, Wolf YI, Walker DR, Koonin EV (1998) Evidence for massive gene exchange between archaeal and bacterial hyperthermophiles. Trends Genet 14:442–444
Averhoff B (2004) DNA transport and natural transformation in mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria. J Bioenerg Biomembr 36:25–33
Averhoff B (2009) Shuffling genes around in hot environments: the unique DNA transporter of Thermus thermophilus. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:611–626
Banecki B, Wawrzynow A, Puzewicz J, Georgopoulos C, Zylicz M (2001) Structure-function analysis of the zinc-binding region of the ClpX molecular chaperone. J Biol Chem 276:18843–18848
Böhm G, Muhr R, Jaenicke R (1992) Quantitative analysis of protein far UV circular dichroism spectra by neural networks. Protein Eng 5:191–195
Camberg JL, Sandkvist M (2005) Molecular analysis of the Vibrio cholerae type II secretion ATPase EpsE. J Bacteriol 187:249–256
Camberg JL, Johnson TL, Patrick M, Abendroth J, Hol WG, Sandkvist M (2007) Synergistic stimulation of EpsE ATP hydrolysis by EpsL and acidic phospholipids. EMBO J 26:19–27
Chen I, Dubnau D (2003) DNA transport during transformation. Front Biosci 8:544–556
Chen I, Dubnau D (2004) DNA uptake during bacterial transformation. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:241–249
Chen I, Christie PJ, Dubnau D (2005a) The ins and outs of DNA transfer in bacteria. Science 310:1456–1460
Chen Y, Shiue SJ, Huang CW, Chang JL, Chien YL, Hu NT, Chan NL (2005b) Structure and function of the XpsE N-terminal domain, an essential component of the Xanthomonas campestris type II secretion system. J Biol Chem 280:42356–42363
Chen I, Provvedi R, Dubnau D (2006) A macromolecular complex formed by a pilin-like protein in competent Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 281:21720–21727
Chiang P, Sampaleanu LM, Ayers M, Pahuta M, Howell PL, Burrows LL (2008) Functional role of conserved residues in the characteristic secretion NTPase motifs of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type IV pilus motor proteins PilB, PilT and PilU. Microbiology 154:114–126
Clausen M, Jakovljevic V, Sogaard-Andersen L, Maier B (2009) High-force generation is a conserved property of type IV pilus systems. J Bacteriol 191:4633–4638
Collins RF, Frye SA, Balasingham S, Ford RC, Tonjum T, Derrick JP (2005) Interaction with type IV pili induces structural changes in the bacterial outer membrane secretin PilQ. J Biol Chem 280:18923–18930
Crowther LJ, Yamagata A, Craig L, Tainer JA, Donnenberg MS (2005) The ATPase activity of BfpD is greatly enhanced by zinc and allosteric interactions with other Bfp proteins. J Biol Chem 280:24839–24848
Deleage G, Geourjon C (1993) An interactive graphic program for calculating the secondary structure content of proteins from circular dichroism spectrum. Comput Appl Biosci 9:197–199
Donaldson LW, Wojtyra U, Houry WA (2003) Solution structure of the dimeric zinc binding domain of the chaperone ClpX. J Biol Chem 278:48991–48996
Draskovic I, Dubnau D (2005) Biogenesis of a putative channel protein, ComEC, required for DNA uptake: membrane topology, oligomerization and formation of disulphide bonds. Mol Microbiol 55:881–896
Facius D, Meyer TF (1993) A novel determinant (comA) essential for natural transformation competence in Neisseria gonorrhoeae and the effect of a comA defect on pilin variation. Mol Microbiol 10:699–712
Fekkes P, de Wit JG, Boorsma A, Friesen RH, Driessen AJ (1999) Zinc stabilizes the SecB binding site of SecA. Biochemistry 38:5111–5116
Forest KT, Satyshur KA, Worzalla GA, Hansen JK, Herdendorf TJ (2004) The pilus-retraction protein PilT: ultrastructure of the biological assembly. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60:978–982
Freitag NE, Seifert HS, Koomey M (1995) Characterization of the pilF-pilD pilus-assembly locus of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol Microbiol 16:575–586
Friedrich A, Hartsch T, Averhoff B (2001) Natural transformation in mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria: identification and characterization of novel, closely related competence genes in Acinetobacter sp. strain BD413 and Thermus thermophilus HB27. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3140–3148
Friedrich A, Prust C, Hartsch T, Henne A, Averhoff B (2002) Molecular analyses of the natural transformation machinery and identification of pilus structures in the extremely thermophilic bacterium Thermus thermophilus strain HB27. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:745–755
Friedrich A, Rumszauer J, Henne A, Averhoff B (2003) Pilin-like proteins in the extremely thermophilic bacterium Thermus thermophilus HB27: implication in competence for natural transformation and links to type IV pilus biogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3695–3700
Fussenegger M, Rudel T, Barten R, Ryll R, Meyer TF (1997) Transformation competence and type-IV pilus biogenesis in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Gene 192:125–134
Heinonen JK, Lahti RJ (1981) A new and convenient colorimetric determination of inorganic orthophosphate and its application to the assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase. Anal Biochem 113:313–317
Herdendorf TJ, McCaslin DR, Forest KT (2002) Aquifex aeolicus PilT, homologue of a surface motility protein, is a thermostable oligomeric NTPase. J Bacteriol 184:6465–6471
Hobbs M, Mattick JS (1993) Common components in the assembly of type 4 fimbriae, DNA transfer systems, filamentous phage and protein-secretion apparatus: a general system for the formation of surface-associated protein complexes. Mol Microbiol 10:233–243
Hoshino T, Kageyama M (1980) Purification and properties of a binding protein for branched-chain amino acids in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 141:1055–1063
Jakovljevic V, Leonardy S, Hoppert M, Sogaard-Andersen L (2008) PilB and PilT are ATPases acting antagonistically in type IV pilus function in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol 190:2411–2421
Krause S, Barcena M, Pansegrau W, Lurz R, Carazo JM, Lanka E (2000a) Sequence-related protein export NTPases encoded by the conjugative transfer region of RP4 and by the cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori share similar hexameric ring structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3067–3072
Krause S, Pansegrau W, Lurz R, de la Cruz F, Lanka E (2000b) Enzymology of type IV macromolecule secretion systems: the conjugative transfer regions of plasmids RP4 and R388 and the cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori encode structurally and functionally related nucleoside triphosphate hydrolases. J Bacteriol 182:2761–2770
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Maier B, Potter L, So M, Long CD, Seifert HS, Sheetz MP (2002) Single pilus motor forces exceed 100 pN. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16012–16017
Nelson KE, Clayton RA, Gill SR, Gwinn ML, Dodson RJ, Haft DH, Hickey EK, Peterson JD, Nelson WC, Ketchum KA, McDonald L, Utterback TR, Malek JA, Linher KD, Garrett MM, Stewart AM, Cotton MD, Pratt MS, Phillips CA, Richardson D, Heidelberg J, Sutton GG, Fleischmann RD, Eisen JA, White O, Salzberg SL, Smith HO, Venter JC, Fraser CM (1999) Evidence for lateral gene transfer between archaea and bacteria from genome sequence of Thermotoga maritima. Nature 399:323–329
Pantazaki AA, Pritsa AA, Kyriakidis DA (2002) Biotechnologically relevant enzymes from Thermus thermophilus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:1–12
Planet PJ, Kachlany SC, DeSalle R, Figurski DH (2001) Phylogeny of genes for secretion NTPases: identification of the widespread tadA subfamily and development of a diagnostic key for gene classification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2503–2508
Possot O, d’Enfert C, Reyss I, Pugsley AP (1992) Pullulanase secretion in Escherichia coli K-12 requires a cytoplasmic protein and a putative polytopic cytoplasmic membrane protein. Mol Microbiol 6:95–105
Rivas S, Bolland S, Cabezon E, Goni FM, de la Cruz F (1997) TrwD, a protein encoded by the IncW plasmid R388, displays an ATP hydrolase activity essential for bacterial conjugation. J Biol Chem 272:25583–25590
Robien MA, Krumm BE, Sandkvist M, Hol WG (2003) Crystal structure of the extracellular protein secretion NTPase EpsE of Vibrio cholerae. J Mol Biol 333:657–674
Rumszauer J, Schwarzenlander C, Averhoff B (2006) Identification, subcellular localization, and functional interactions of PilMNOWQ and PilA4 involved in transformation competency and pilus biogenesis in the thermophilic bacterium Thermus thermophilus HB27. FEBS J 273:3261–3272
Savvides SN, Yeo HJ, Beck MR, Blaesing F, Lurz R, Lanka E, Buhrdorf R, Fischer W, Haas R, Waksman G (2003) VirB11 ATPases are dynamic hexameric assemblies: new insights into bacterial type IV secretion. EMBO J 22:1969–1980
Schwarzenlander C, Averhoff B (2006) Characterization of DNA transport in the thermophilic bacterium Thermus thermophilus HB27. FEBS J 273:4210–4218
Schwarzenlander C, Haase W, Averhoff B (2009) The role of single subunits of the DNA transport machinery of Thermus thermophilus HB27 in DNA binding and transport. Environ Microbiol 11:801–808
Sexton JA, Pinkner JS, Roth R, Heuser JE, Hultgren SJ, Vogel JP (2004) The Legionella pneumophila PilT homologue DotB exhibits ATPase activity that is critical for intracellular growth. J Bacteriol 186:1658–1666
Tonjum T, Koomey M (1997) The pilus colonization factor of pathogenic neisserial species: organelle biogenesis and structure/function relationships. Gene 192:155–163
Turner LR, Lara JC, Nunn DN, Lory S (1993) Mutations in the consensus ATP-binding sites of XcpR and PilB eliminate extracellular protein secretion and pilus biogenesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 175:4962–4969
Whitchurch CB, Mattick JS (1994) Characterization of a gene, pilU, required for twitching motility but not phage sensitivity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 13:1079–1091
Wolfgang M, Lauer P, Park HS, Brossay L, Hebert J, Koomey M (1998) PilT mutations lead to simultaneous defects in competence for natural transformation and twitching motility in piliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol Microbiol 29:321–330
Acknowledgments
Work from the Averhoff laboratory was supported by grants Av9/4-4, Av9/4-5 and Av9/5-1 from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie, the BMBF and the Center for Membrane Proteomics, Goethe University, Frankfurt. We are especially grateful to Katharina Baatz and Alexandra Friedrich for generating Thermus TTC1844 and TTC1621 mutants and Jose Berenguer (Madrid) for providing S-layer antibodies. Research performed by the laboratory of G. Grüber was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Singapore (ARC 6/06) and the School of Biological Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by A. Driessen.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rose, I., Biuković, G., Aderhold, P. et al. Identification and characterization of a unique, zinc-containing transport ATPase essential for natural transformation in Thermus thermophilus HB27. Extremophiles 15, 191–202 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-010-0343-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-010-0343-2