Abstract
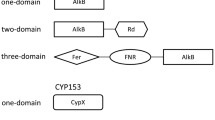
Two clones 9E7 and 21G8 in a metagenomic library of the east Pacific deep-sea sediment were found to contain alkane hydroxylase genes (alkB). The whole insert sequences of the two cosmid clones were determined. The insert sequences of 9E7 and 21G8 are 40 and 35 kb, respectively. Besides alkB, several alcohol/aldehyde dehydrogenase genes were also determined. A homolog of rubredoxin 2 of Pseudomonas putida was identified on 9E7 immediately downstream the alkB gene, but was lacking on 21G8. Unlike previous reports, the alkB genes on 9E7 and 21G8 have opposite transcription directions to those of linked alcohol/aldehyde dehydrogenase genes. Phylogenetic analysis put these two deep-sea AlkBs into a unique branch of integral membrane hydroxylases. The two alkB genes (9E7–alkB and 21G8-alkB) were cloned into pCom8 and introduced into two alkB expression host systems P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1 and P. putida GPo12 (pGEc47ΔB). The transformed strains can grow on the n-alkanes from C5 to C16, indicating that both 9E7-AlkB and 21G8-AlkB have a wide substrate range. The data further indicate that the deep sea would be a rich resource for exploring novel alkane-degrading strains and genes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bühler M, Schindler J (1984) Aliphatic hydrocarbons. In: Kieslich K (ed) Biotransformations, vol 6a. Verlag Chemie Weinheim, Weinheim pp 329–385
Ditta G, Stanfield S, Corbin D, Helinski DR (1980) Broad host range DNA cloning system for Gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:7347–7351
Fernando R (2005) Specificity at the end of the tunnel: understanding substrate length discrimination by the AlkB alkane hydroxylase. J Bacteriol 187:19–22
Guo C, Sun W, Harsh JB, Ogram A (1997) Hybridisation analysis of microbial DNA from fuel oil-contaminated and noncontaminated soil. Microb Ecol 34:178–187
Henne A, Schmitz RA, Bömeke M, Gottschalk G, Daniel R (2000) Screening of environmental DNA libraries for the presence of genes conferring lipolytic activity on Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3113–3116
HӨjberg O, Schnider U, Winteler HV, Sørensen J, Haas D (1999) Oxygen-sensing reporter strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens for monitoring the distribution of low-oxygen habitats in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4085–4093
Knaebel DB, Crawford RL (1995) Extraction and purification of microbial DNA from petroleum-contaminated soils and detection of low numbers of toluene, octane and pesticide degraders by multiplex polymerase chain reaction and Southern analysis. Mol Ecol 4:579–591
Knietsch A, Bowien S, Whited G, Gottschalk G, Daniel R (2003) Identification and characterization of coenzyme B-12-dependent glycerol dehydratase- and diol dehydratase-encoding genes from metagenomic DNA ibraries derived from enrichment cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3048–3060
Labinger JA., Bercaw JE (2002) Understanding and exploiting C–H bond activation. Nature 417:507–514
Li Z, Feiten HJ, Chang D, Duetz WA, van Beilen JB, Witholt B (2001) Preparation of (R)- and (S)-N-protected 3-hydroxypyrrolidines by hydroxylation with Sphingomonas sp. HXN-200, a highly active, regio- and stereoselective, and easy-to-handle biocatalyst. J Org Chem 66:8424–8430
Liu C, Shao Z (2005) Alcanivorax dieselolei sp. nov., a novel alkane-degrading bacterium isolated from sea water and deep-sea sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1181–1186
Rondon MR, August PR, Bettermann AD, Brady SF, Grossman TH, Liles MR, von Voget S, Leggewie C, Uesbeck A, Raasch C, Jaeger KE (2003) Prospecting for novel biocatalysts in a soil metagenome. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6235–6242
Rosenberg E, Ron EZ (1996) Bioremediation of petroleum contamination. In: Crawford RL, Crawford DL (eds) Bioremediation: principles and applications, vol 6. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 100–124
Schwartz RD, McCoy CJ (1973) Pseudomonas oleovorans hydroxylation–epoxidation system: additional strain improvements. Appl Microbiol 26:217–218
Siciliano SD, Fortin N, Mihoc A, Wisse G, Labelle S, Beaumier D, Ouellette D, Roy R, Whyte LG, Banks MK, Schwab P, Lee K, Greer CW (2001) Selection of specific endophytic bacterial genotypes by plants in response to soil contamination. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2469–2475
Smits THM, Seeger MA, Witholt B, van Beilen JB (2001) New alkane-responsive expression vectors for E. coli and Pseudomonas. Plasmid 46:16–24
Smits THM, Balada SB, Witholt B, van Beilen JB (2002) Functional analysis of alkane hydroxylases from gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 184:1733–1742
Sotsky JB, Greer CW, Atlas RM (1994) Frequency of genes in aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbon biodegradation pathways within bacterial populations from Alaskan sediments. Can J Microbiol 40:981–985
Stapleton RD, Sayler GS (1998) Assessment of the microbiological potential for the natural attenuation of petroleum hydrocarbons in a shallow aquifer system. Microb Ecol 36:349–361
van Beilen JB, Li Z, Duetz WA, Smits THM, Witholt B (2003) Diversity of alkane hydroxylase systems in the environment. Oil Gas Sci Technol 58:427–440
van Beilen JB, Smits THM, Roos FF, Brunner T, Balada SB, RÖthlisberger M, Witholt B (2005) Identification of an amino acid position that determines the substrate range of integral membrane alkane hydroxylases. J Bacteriol 187:85–91
van Beilen JB, Panke S, Lucchini S, Franchini AG, Röthlisberger M, Witholt B (2001) Analysis of Pseudomonas putida alkane degradation gene clusters and flanking insertion sequences: evolution and regulation of the alk-genes. Microbiology 147:1621–1630
van Beilen JB, Funhoff EG (2005) Expanding the alkane oxygenase toolbox: new enzymes and applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:308–314
Witholt B, de Smet MJ, Kingma J, van Beilen JB, Kok M, Lageveen RG, Eggink G (1990) Bioconversions of aliphatic compounds by Pseudomonas oleovorans in multiphase biorectors: background and economic potential. Trends Biotechnol 8:46–52
Whyte LG, Greer CW, Inniss WE (1996) Assessment of the biodegradation potential of psychrotrophic microorganisms. Can J Microbiol 42:99–106
Whyte LG, Schultz A, van Beilen JB, Luz AP, Pellizari D, Labbé D, Greer CW (2002a) Prevalence of alkane monooxygenase genes in Arctic and Antarctic hydrocarbon-contaminated and pristine soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 41:141–150
Whyte LG, Smits THM, Labbe D, Witholt B, Greer W, van Beilen JB (2002b) Gene cloning and characterization of multiple alkane hydroxylase systems in Rhodococcus strains Q15 and NRRL B-16531. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5933–5942
Xu MX, Wang FP, Men J, Xiao X (2007) Construction and preliminary analysis of a metagenomic library from a deep-sea sediment of east Pacific nodule province. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62:233–241
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Jan B van Beilen for generously providing us the alkB gene expressed system including strains and vector of P. putida GPo1, P. putida GPo12 (pGEc47ΔB), P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1, E. coli RK600 and pCom8. We are indebted to Dr. Zongze Shao for his kind recommendations and helpful discussions. Our thanks are due to the crew on the R/V Dayang Yihao for help in collecting the samples. This work was supported by the NSF China Award (40476054), COMRA fund (DY7000M-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Horikoshi.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Xiao, X. & Wang, F. Isolation and characterization of alkane hydroxylases from a metagenomic library of Pacific deep-sea sediment. Extremophiles 12, 255–262 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-007-0122-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-007-0122-x