Abstract
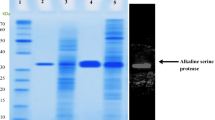
A gene encoding an extracellular protease, sptA, was cloned from the halophilic archaeon Natrinema sp. J7. It encoded a polypeptide of 565 amino acids containing a putative 49-amino acid signal peptide, a 103-amino acid propeptide, as well as a mature region and C-terminal extension, with a high proportion of acidic amino acid residues. The sptA gene was expressed in Haloferax volcanii WFD11, and the recombinant enzyme could be secreted into the medium as an active mature form. The N-terminal amino acid sequencing and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analysis of the purified SptA protease indicated that the 152-amino acid prepropeptide was cleaved and the C-terminal extension was not processed after secretion. The SptA protease was optimally active at 50°C in 2.5 M NaCl at pH 8.0. The NaCl removed enzyme retained 20% of its activity, and 60% of the activity could be restored by reintroducing 2.5 M NaCl into the NaCl removed enzyme. When the twin-arginine motif in the signal peptide of SptA protease was replaced with a twin-lysine motif, the enzyme was not exported from Hfx. volcanii WFD11, suggesting that the SptA protease was a Tat-dependent substrate.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berks BC (1996) A common export pathway for proteins binding complex redox cofactors? Mol Microbiol 22:393–404
Bolhuis A (2002) Protein transport in the halophilic archaeon Halobacterium sp. NRC-1: a major role for the twin-arginine translocation pathway? Microbiology 148:3335–3346
Cline SW, Lam WL, Charlebois RL, Schalkwyk LC, Doolittle WF (1989) Transformation methods for halophilic archaebacteria. Can J Microbiol 35:148–152
Connaris H, Chaudhuri JB, Danson MJ, Hough DW (1999) Expression, reactivation, and purification of enzymes from Haloferax volcanii in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 64:38–45
De Castro RE, Maupin-Furlow JA, Giménez MI, Herrera Seitz MK, Sánchez JJ (2006) Haloarchaeal proteases and proteolytic systems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30:17–35
Diaz S, Perez-Pomares F, Pire C, Ferrer J, Bonete MJ (2006) Gene cloning, heterologous overexpression and optimized refolding of the NAD-glutamate dehydrogenase from Haloferax mediterranei. Extremophiles 10:105–115
Elsztein C, Herrera Seitz MK, Sanchez JJ, De Castro RE (2001) Autoproteolytic activation of the haloalkaliphilic archaeon Natronococcus occultus extracellular serine protease. J Basic Microbiol 41:319–327
Gibbons NE (1957) The effect of salt concentrations on the biochemical reactions of some halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol 3:349–255
Giménez MI, Studdert CA, Sanchez JJ, De Castro RE (2000) Extracellular protease of Natrialba magadii: purification and biochemical characterization. Extremophiles 4:181–188
Hutcheon GW, Vasisht N, Bolhuis A (2005) Characterisation of a highly stable α-amylase from the halophilic archaeon Haloarcula hispanica. Extremophiles 9:487–495
Izotova LS, Strongin AY, Chekulaeva LN, Sterkin VE, Ostoslavskaya VI, Lyublinskaya EA, Timokhina EA, Stepanov VM (1983) Purification and properties of serine protease from Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol 155:826–830
Kamekura M, Seno Y (1990) A halophilic extracellular protease from a halophilic archaebacterium strain 172 P1. Biochem Cell Biol 68:352–359
Kamekura M, Seno Y, Holmes ML, Dyall-Smith ML (1992) Molecular cloning and sequencing of the gene for a halophilic alkaline serine protease (halolysin) from an unidentified halophilic archaea strain (172P1) and expression of the gene in Haloferax volcanii. J Bacteriol 174:736–742
Kamekura M, Seno Y, Dyall-Smith ML (1996) Halolysin R4, a serine proteinase from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei; gene cloning, expression and structural studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1294:159–167
Kim J, Dordick JS (1997) Unusual salt and solvent dependence of a protease from an extreme halophile. Biotech Bioeng 55:471–479
King J, Laemmli UK (1971) Polypeptides of the fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol 62:465–477
Lanyi JK (1974) Salt-dependent properties of proteins from extremely halophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 8:272–290
Liu YG, Whittier RF (1995) Thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR: automatable amplification and sequencing of insert end fragments from P1 and YAC clones for chromosome walking. Genomics 35:674–681
Madern D, Ebel C, Zaccai G (2000) Halophilic adaptation of enzymes. Extremophiles 4:91–98
Martin VJ, Mohn WW (1999) An alternative inverse PCR (IPCR) method to amplify DNA sequences flanking Tn5 transposon insertions. J Microbiol Methods 35:163–166
McGenity TJ, Gemmell RT, Grant WD (1998) Proposal of a new halobacterial genus Natrinema gen. nov., with two species Natrinema pellirubrum nom. nov. and Natrinema pallidum nom. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:1187–1196
Norberg P, Von Hofsten B (1969) Proteolytic enzymes from extremely halophilic bacteria. J Gen Microbiol 55:251–256
Oren A (2002) Halophilic microorganisms and their environments. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Pire C, Esclapez J, Ferrer J, Bonete MJ (2001) Heterologous overexpression of glucose dehydrogenase from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei, an enzyme of the medium chain dehydrogenase/reductase family. FEMS Microbiol Lett 200:221–227
Pohlschröder M, Dilks K, Hand NJ, Rose RW (2004) Translocation of proteins across archaeal cytoplasmic membranes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:3–24
Ring G, Eichler J (2004) Extreme secretion: protein translocation across the archaeal plasma membrane. J Bioenerg Biomembr 36:35–45
Rose TM, Schultz ER, Henikoff JG, Pietrokovski S, McCallum CM, Henikoff S (1998) Consensus-degenerate hybrid oligonucleotide primers for amplification of distantly related sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 26:1637–1644
Rose RW, Bruser T, Kissinger JC, Pohlschröder M. (2002) Adaptation of protein secretion to extremely high-salt conditions by extensive use of the twin-arginine translocation pathway. Mol Microbiol 45:943–950
Ryu K, Kim J, Dordick JS (1994) Catalytic properties and potential of an extracellular protease from an extreme halophile. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 16:266–275
Sellek GA, Chaudhuri JB (1999) Biocatalysis in organic media using enzymes from extremophiles. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 25:471–482
Siezen RJ, Leunissen JA (1997) Subtilases: the superfamily of subtilisin-like serine proteases. Protein Sci 6:501–523
Stan-lotter H, Doppler E, Jarosch M, Radax C, Gruber C, Inatomi K (1999) Isolation of a chymotrypsinogen B–like enzyme from the archaeon Natronomonas pharaonis and other halobacteria. Extremophiles 3:153–161
Stepanov VM, Rudenskaya GN (1983) Proteinase affinity chromatography on bacitracin-Sepharose. J Appl Biochem 5:420–428
Stepanov VM, Rudenskaya GN, Revina LP, Gryaznova YB, Lysogorskaya EN, Filippova IY, Ivanova II (1992) A serine proteinase of an archaebacterium, Halobacterium mediterranei a homologue of eubacterial subtilisins. Biochem J 285:281–286
Studdert CA, De Castro RE, Seitz KH, Sanchez JJ (1997) Detection and preliminary characterization of extracellular proteolytic activities of the haloalkaliphilic archaeon Natronococcus occultus. Arch Microbiol 168:532–535
Studdert CA, Herrera Seitz MK, Plasencia Gil MI, Sanchez JJ, De Castro RE (2001) Purification and biochemical characterization of the haloalkaliphilic archaeon Natronococcus occultus extracellular serine protease. J Basic Microbiol 41:375–383
Teplyakov AV, Kuranova IP, Harutyunyan EH, Frommel C, Hohne WE (1989) Crystal structure of thermitase from Thermoactinomyces vulgaris at 2.2 Å resolution. FEBS Lett 244:208–212
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improvement the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position–specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Wilson HL, Aldrich HC, Maupin-Furlow J (1999) Halophilic 20S proteasomes of the archaeon Haloferax volcanii: purification, characterization, and gene sequence analysis. J Bacteriol 181:5814–5824
Wu J, Bian Y, Tang B, Chen X, Shen P, Peng Z (2004) Cloning and analysis of WF146 protease, a novel thermophilic subtilisin–like protease with four inserted surface loops. FEMS Microbiol Lett 230:251–258
Yang Y, Huang YP, Shen P (2003) The 492-bp RM07 DNA fragment from the halophilic archaea confers promoter activity in all three domains of life. Curr Microbiol 47:388–394
Ye X, Ou J, Ni L, Shi W, Shen P (2003) Characterization of a novel plasmid from extremely halophilic Archaea: nucleotide sequence and function analysis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 221:53–57
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Grand Fundamental Research Program (973) of China (No.2004CB719600) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.301700189, 30470033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Horikoshi
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, W., Tang, XF., Huang, Y. et al. An extracellular halophilic protease SptA from a halophilic archaeon Natrinema sp. J7: gene cloning, expression and characterization. Extremophiles 10, 599–606 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-006-0003-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-006-0003-8