Abstract
Objectives
This study focused on the clinical investigation of the internal and marginal fit of CAD/CAM-fabricated zirconia single crowns produced via conventional and digital impression techniques.
Materials and methods
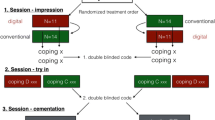
In a private practice, 20 molar teeth, one from each of 20 patients, were prepared with a circumferential 1.0-mm deep chamfer and an occlusal reduction of 1.5 mm. Conventional impression (CI) taking with a polyvinylsiloxane material (Aquasil Monophase + Aquasil XLV; Dentsply, Konstanz, Germany) and intraoral scanning (IS) (Cara TRIOS; Heraeus, Hanau, Germany) of each of the preparations was performed, and then two respective zirconia copings per tooth were produced (20 crowns per group). The marginal and internal fit of the restorations was evaluated employing a replica technique. For statistical analysis, a pairwise comparison (Wilcoxon rank test) was performed.
Results
Zirconia single crowns produced with the IS technique revealed a statistically significant better precision of internal fit only in specific areas (chamfer area/occlusal area). The evaluation of marginal fit showed no significant differences between the two groups. All restorations of both groups offered internal and marginal gaps within the postulated clinical tolerance ranges.
Conclusions
CAD/CAM-fabricated zirconia single crowns produced with CI and IS techniques offer adequate marginal and internal precision. However, the IS technique provides lower internal gaps in some specific areas.
Clinical relevance
The clinical precision of fit of restorations produced with a CI and an IS technique appeared to be equivalent. Therefore, the IS technique can be rated as a suitable alternative for the manufacturing of single crowns.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gjelvold B, Chrcanovic BR, Korduner EK, Collin-Bagewitz I, Kisch J (2015) Intraoral digital impression technique compared to conventional impression technique. A randomized clinical trial. J Prosthodont. doi:10.1111/jopr.12410 [Epub ahead of print]
Reich S, Vollborn T, Mehl A, Zimmermann M (2013) Intraoral optical impression system: an overview. Int J Comput Dent 16:143–162
Ting-Shu S, Jian S (2015) Intraoral digital impression technique: a review. J Prosthodont 24:313–321
Zimmermann M, Mehl A, Mörmann WH, Reich S (2015) Intraoral scanning systems—a current overview. Int J Comput Dent 18:101–129
Lee SJ, Macarthur RX 4th, Gallucci GO (2013) An evaluation of student and clinician perception of digital and conventional implant impressions. J Prosthet Dent 110(5):420–423
Yuzbasioglu E, Kurt H, Turunc R, Bilir H (2014) Comparison of digital and conventional impression techniques: evaluation of patients’ perception, treatment comfort, effectiveness and clinical outcomes. BMC Oral Health 14:10–17
Hunter AJ, Hunter AR (1990) Gingival margins for crowns: a review and discussion. Part II: discrepancies and configurations. J Prosthet Dent 64:636–642
Karlsson S (1993) The fit of Procera titanium crowns. An in vitro and clinical study. Acta Odontol Scand 51:129–134
Contrepois M, Soenen A, Bartala M, Laviole O (2013) Marginal adaptation of ceramic crowns: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent 110:447–454
Boitelle P, Mawussi B, Tapie L, Fromentin O (2014) A systematic review of CAD/CAM fit restoration evaluations. J Oral Rehabil 41:853–874
Wettstein F, Sailer I, Roos M, Hämmerle CH (2008) Clinical study of the internal gaps of zirconia and metal frameworks for fixed partial dentures. Eur J Oral Sci 116(3):272–279
Seelbach P, Brueckel C, Wostmann B (2013) Accuracy of digital and conventional impression techniques and workflow. Clin Oral Investig 17:1759–1764
Almeida e Silva JS, Erdelt K, Edelhoff D, Araújo É, Stimmelmayr M, Vieira LC, Guth J (2014) Marginal and internal fit of four-unit zirconia fixed dental prostheses based on digital and conventional impression techniques. Clin Oral Investig 18:515–523
Keul C, Stawarczyk B, Erdelt KJ, Beuer F, Edelhoff D, Güth JF (2014) Fit of 4-unit FDPs made of zirconia and CoCr-alloy after chairside and labside digitalization—a laboratory study. Dent Mater 30(4):400–407
Tidehag P, Ottosson K, Sjögren G (2014) Accuracy of ceramic restorations made using an in-office optical scanning technique: an in vitro study. Oper Dent 39(3):308–316
Abdel-Azim T, Rogers K, Elathamna E, Zandinejad A, Metz M, Morton D (2015) Comparison of the marginal fit of lithium disilicate crowns fabricated with CAD/CAM technology by using conventional impressions and two intraoral digital scanners. J Prosthet Dent 114(4):554–559
Ueda K, Beuer F, Stimmelmayr M, Erdelt K, Keul C, Güth F (2015) Fit of 4-unit FDPs from CoCr and zirconia after conventional and digital impressions. Clin Oral Investig. doi:10.1007/s00784-015-1513-5 [Epub ahead of print]
Syrek A, Reich G, Ranftl D, Klein C, Cerny B, Brodesser J (2010) Clinical evaluation of all-ceramic crowns fabricated from intraoral digital impressions based on the principle of active wavefront sampling. J Dent 38:553–559
Brawek PK, Wolfart S, Endres L, Kirsten A, Reich S (2013) The clinical accuracy of single crowns exclusively fabricated by digital workflow--the comparison of two systems. Clin Oral Investig 17(9):2119–2125
Tamim H, Skjerven H, Ekfeldt A, Rønold HJ (2014) Clinical evaluation of CAD/CAM metal-ceramic posterior crowns fabricated from intraoral digital impressions. Int J Prosthodont 27(4):331–337
Selz CF, Bogler J, Vach K, Strub JR, Guess PC (2015) Veneered anatomically designed zirconia FDPs resulting from digital intraoral scans: preliminary results of a prospective clinical study. J Dent 43(12):1428–1435
Holmes JR, Bayne SC, Holland GA, Sulik WD (1989) Considerations in measurement of marginal fit. J Prosthet Dent 62:405–408
Abduo J, Lyons K, Swain M (2010) Fit of zirconia fixed partial denture: a systematic review. J Oral Rehabil 37:866–876
Laurent M, Scheer P, Dejou J, Laborde G (2008) Clinical evaluation of the marginal fit of cast crowns—validation of the silicone replica method. J Oral Rehabil 35:116–122
McLean JW, von Fraunhofer JA (1971) The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br Dent J 131:107–111
Fransson B, Oilo G, Gjeitanger R (1985) The fit of metal-ceramic crowns, a clinical study. Dent Mater 1:197–199
Reich S, Uhlen S, Gozdowski S, Lohbauer U (2011) Measurement of cement thickness under lithium disilicate crowns using an impression material technique. Clin Oral Investig 15:521–526
Ahrberg D, Lauer CL, Ahrberg M, Weigl P (2015) Evaluation of fit and efficiency of CAD/CAM fabricated all-ceramic restorations based on direct and indirect digitalization: a double-blinded, randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig. doi:10.1007/s00784-015-1504-6 [Epub ahead of print]
Boeddinghaus M, Breloer ES, Rehmann P, Wöstmann B (2015) Accuracy of single-tooth restorations based on intraoral digital and conventional impressions in patients. Clin Oral Investig 19:2027–2034
Pradíes G, Zarauz C, Valverde A, Ferreiroa A, Martínez-Rus F (2015) Clinical evaluation comparing the fit of all-ceramic crowns obtained from silicone and digital intraoral impressions based on wavefront sampling technology. J Dent 43(2):201–208
Zarauz C, Valverde A, Martinez-Rus F, Hassan B, Pradies G (2015) Clinical evaluation comparing the fit of all-ceramic crowns obtained from silicone and digital intraoral impressions. Clin Oral Investig. doi:10.1007/s00784-015-1590-5 [Epub ahead of print]
Ender A, Mehl A (2013) Influence of the scanning strategies on the accuracy of digital intraoral scanning systems. Int J Comput Dent 16:11–21
Rinke S, Fornefett D, Gersdorff N, Lange K, Roediger M (2012) Multifactorial analysis of the impact of different manufacturing processes on the marginal fit of zirconia copings. Dent Mater J 31(4):601–609
Pak HS, Han JS, Lee JB, Kim SH, Yang JH (2010) Influence of porcelain veneering on the marginal fit of Digident and Lava CAD/CAM zirconia ceramic crowns. J Adv Prosthodont 2:33–38
Su TS, Sun J (2015) Comparison of repeatability between intraoral digital scanner and extraoral digital scanner: an in vitro study. J Prosthodont Res 59:236–242
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Heraeus Kulzer GmbH, Hanau, Germany.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the Georg-August-University, Goettingen, Germany (application no. 5/11/11).
Informed consent
All patients included in this study gave written informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rödiger, M., Heinitz, A., Bürgers, R. et al. Fitting accuracy of zirconia single crowns produced via digital and conventional impressions—a clinical comparative study. Clin Oral Invest 21, 579–587 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-016-1924-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-016-1924-y