Abstract
Objectives
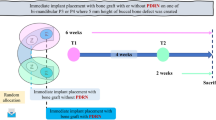
Simultaneous lateral augmentation and implant placement is considered as standard procedure in deficient edentulous ridges in oral implantology. Histological studies monitoring osteogenesis after application of alloplastic bone substitutes in humans are scarce. Bone formation upon simultaneous augmentation with biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) and implantation was histologically investigated after 6 months in situ. The results of this secondary analysis are reported tempting to ascribe specific observations to uneventful submerged healing or compromised healing of soft tissues including occurrence of dehiscences and premature graft exposure.
Materials and methods
Histology of biopsies from lateral, crestal bone augmentations using alloplastic BCP comprising seven sites with compromised, prematurely exposed healing and six sites with uneventful submerged healing was investigated for expression of osteogenic, osteoclastogenic, and angiogenic differentiation markers.
Results
Histology revealed alkaline phosphatase (ALP)-positive osteoblasts and immunoreactivity for osteogenic markers osteocalcin and collagen type I in biopsies with submerged healing, while inflammatory infiltrates and accumulations of multinucleated giant cells around BCP granules were observed in compromised sites. All specimens presented adequate vessel density. Multinucleated giant cells showed inconsistent staining for the osteoclast marker tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP).
Conclusions
The histological findings of this study indicate an osteoconductive nature of the BCP applied. Premature exposure of the bone substitute reduced new bone formation and may bear a risk for inflammatory and foreign body reactions.
Clinical relevance
A predictable appositional bone formation in simultaneously augmented sites using BCP is linked to an uneventful healing process.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen SS, Terheyden H (2009) Bone augmentation procedures in localized defects in the alveolar ridge: clinical results with different bone grafts and bone-substitute materials. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 24(Suppl):218–236
Donos N, Mardas N, Chadha V (2008) Clinical outcomes of implants following lateral bone augmentation: systematic assessment of available options (barrier membranes, bone grafts, split osteotomy). J Clin Periodontol 35:173–202
Retzepi M, Donos N (2010) Guided bone regeneration: biological principle and therapeutic applications. Clin Oral Implants Res 21:567–576
Kolk A, Handschel J, Drescher W, Rothamel D, Kloss F, Blessmann M, Heiland M, Wolff KD, Smeets R (2012) Current trends and future perspectives of bone substitute materials—from space holders to innovative biomaterials. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 40:706–718
Tal H, Artzi Z, Kolerman R, Beitlitum I, Goshen G (2012) Augmentation and preservation of the alveolar process and alveolar ridge of bone. Bone Regeneration, InTech Rijeka, pp 139–184
Cordaro L, Bosshardt DD, Palattella P, Rao W, Serino G, Chiapasco M (2008) Maxillary sinus grafting with Bio-Oss or Straumann Bone Ceramic: histomorphometric results from a randomized controlled multicenter clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 19:796–803
Artzi Z, Kozlovsky A, Nemcovsky CE, Weinreb M (2005) The amount of newly formed bone in sinus grafting procedures depends on tissue depth as well as the type and residual amount of the grafted material. J Clin Periodontol 32:193–199
Schmitt CM, Doering H, Schmidt T, Lutz R, Neukam FW, Schlegel KA (2013) Histological results after maxillary sinus augmentation with Straumann®, BoneCeramic, Bio-Oss®, Puros®, and autologous bone. A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 24:576–585
Becker J, Al-Nawas B, Klein MO, Schliephake H, Terheyden H, Schwarz F (2009) Use of a new cross-linked collagen membrane for the treatment of dehiscence-type defects at titanium implants: a prospective, randomized-controlled double-blinded clinical multicenter study. Clin Oral Implants Res 20:742–749
Moses O, Pitaru S, Artzi Z, Nemcovsky CE (2005) Healing of dehiscence-type defects in implants placed together with different barrier membranes: a comparative clinical study. Clin Oral Implants Res 16:210–219
Schwarz F, Hegewald A, Sahm N, Becker J (2013) Long-term follow-up of simultaneous guided bone regeneration using native and cross-linked collagen membranes over 6 years. Clin Oral Implants Res. doi:10.1111/clr.12220
Friedmann A, Gissel K, Soudan M, Kleber BM, Pitaru S, Dietrich T (2011) Randomized controlled trial on lateral augmentation using two collagen membranes: morphometric results on mineralized tissue compound. J Clin Periodontol 38:677–685
Friedmann A, Dard M, Kleber BM, Bernimoulin JP, Bosshardt DD (2009) Ridge augmentation and maxillary sinus grafting with a biphasic calcium phosphate: histologic and histomorphometric observations. Clin Oral Implants Res 20:708–714
Jung RE, Windisch SI, Eggenschwiler AM, Thoma DS, Weber FE, Hammerle CH (2009) A randomized-controlled clinical trial evaluating clinical and radiological outcomes after 3 and 5 years of dental implants placed in bone regenerated by means of GBR techniques with or without the addition of BMP-2. Clin Oral Implants Res 20:660–666
Götz W, Gerber T, Michel B, Lossdörfer S, Henkel KO, Heinemann F (2008) Immunohistochemical characterization of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite silica gel (NanoBone(r)) osteogenesis: a study on biopsies from human jaws. Clin Oral Implants Res 19:1016–1026
Frenken JW, Bouwman WF, Bravenboer N, Zijderveld SA, Schulten EA, ten Bruggenkate CM (2010) The use of Straumann Bone Ceramic in a maxillary sinus floor elevation procedure: a clinical, radiological, histological and histomorphometric evaluation with a 6-month healing period. Clin Oral Implants Res 21:201–208
Chan RC, Marino V, Bartold PM (2012) The effect of Emdogain and platelet-derived growth factor on the osteoinductive potential of hydroxyapatite tricalcium phosphate. Clin Oral Investig 16:1217–1227
Mrozik KM, Gronthos S, Menicanin D, Marino V, Bartold PM (2012) Effect of coating Straumann Bone Ceramic with Emdogain on mesenchymal stromal cell hard tissue formation. Clin Oral Investig 16:867–878
Mardas N, Chadha V, Donos N (2010) Alveolar ridge preservation with guided bone regeneration and a synthetic bone substitute or a bovine-derived xenograft: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 21:688–698
Iezzi G, Degidi M, Piattelli A, Mangano C, Scarano A, Shibli JA, Perrotti V (2012) Comparative histological results of different biomaterials used in sinus augmentation procedures: a human study at 6 months. Clin Oral Implants Res 23:1369–1376
Boyan BD, Bonewald LF, Paschalis EP, Lohmann CH, Rosser J, Cochran DL, Dean DD, Schwartz Z, Boskey AL (2002) Osteoblast-mediated mineral deposition in culture is dependent on surface microtopography. Calcif Tissue Int 71:519–529
Knabe C, Koch C, Rack A, Stiller M (2008) Effect of beta-tricalcium phosphate particles with varying porosity on osteogenesis after sinus floor augmentation in humans. Biomaterials 29:2249–2258
de Lange GL, Overman JR, Farré-Guasch E, Korstjens CM, Hartman B, Langenbach GE, Van Duin MA, Klein-Nulend J (2014) A histomorphometric and micro-computed tomography study of bone regeneration in the maxillary sinus comparing biphasic calcium phosphate and deproteinized cancellous bovine bone in a human split-mouth model. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 117:8–22
Koerdt S, Siebers J, Bloch W, Ristow O, Kuebler AC, Reuther T (2013) Immunohistochemial study on the expression of von Willebrand factor (vWF) after onlay autogenous iliac grafts for lateral alveolar ridge augmentation. Head Face Med 9:40
Götz W, Reichert C, Canullo L, Jäger A, Heinemann F (2012) Coupling of osteogenesis and angiogenesis in bone substitute healing—a brief overview. Ann Anat 194:171–173
Hammerle CH, Lang NP (2001) Single stage surgery combining transmucosal implant placement with guided bone regeneration and bioresorbable materials. Clin Oral Implants Res 12:9–18
Anderson JM, Rodriguez A, Chang DT (2008) Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin Immunol 20:86–100
Chappard D, Guillaume B, Mallet R, Pascaretti-Grizon F, Baslé MF, Libouban H (2010) Sinus lift augmentation and ß-TCP: a microCT and histological analysis on human bone biopsies. Micron 41:321–326
Kucera T, Sponer P, Urban K, Kohout A (2013) Histological assessment of tissue from large human bone defects repaired with ß-tricalcium phosphate. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol In press.
Ghanaati S, Barbeck M, Ort C, Willershausen I, Thimm BW, Hoffmann C, Rasic A, Sader RA, Unger RE, Peters F, Kirckpatrick CJ (2010) Influence of ß-tricalcium phosphate granule size and morphology on tissue reaction in vivo. Acta Biomater 6:4476–4487
Acknowledgments
We thank Mrs. Inka Müller-Bay for technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Anton Friedmann and Kirsten Gissel contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friedmann, A., Gissel, K., Konermann, A. et al. Tissue reactions after simultaneous alveolar ridge augmentation with biphasic calcium phosphate and implant insertion—histological and immunohistochemical evaluation in humans. Clin Oral Invest 19, 1595–1603 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-014-1385-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-014-1385-0