Abstract
Introduction
Estrogen receptor α (ERα) plays important roles in the etiology of osteoarthritis (OA), in which cartilage degradation and cellular inflammation are involved. MiR-203 is reported to direct target ERα, but its roles in chondrocytes remain uncovered.
Methods
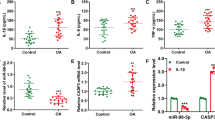
In this study, ELISA showed that the level of estrogen hormone in the serum of postmenopausal OA patients was significantly lower than the one in patients without OA. RT-PCR revealed that the expression level of miR-203 was significantly up-regulated in the OA patients. Furthermore, western blotting demonstrated the lower expression levels of aggrecan, Col2A1, and ERα in the isolated articular cartilage tissues of OA patients. To decipher the association between ERα and miR-203 in the pathogenesis of OA, IL-1β stimulated cultured chondrocyte cell model was established to measure the cell viability, cellular inflammation, cell injury, as well as cartilage degradation with miR-203 inhibitor and ERα.
Results
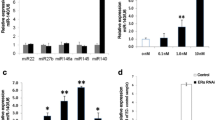
The results showed that IL-1β stimulation induced the expression of miR-203, which promoted cellular inflammation and cell injury, and caused down-regulation of aggrecan and Col2A1. Luciferase assay indicated the direct binding between miR-203 and ERα, and ERα-specific SiRNA inversed the protective role of miR-203 inhibitor in the progression of OA in the cell system.
Conclusions
MiR-203 is critical in the onset and progression of OA, at least in part, caused by estrogen deficiency and ERα instability in OA patients, providing a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of OA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arden N, Blanco F, Cooper C, Guermazi A, Hayashi D, Hunter D, Javaid MK, Rannou F, Roemer F, Reginster J-Y (2014) Atlas of osteoarthritis. Springer, New York
Oliveria SA, Felson DT, Reed JI, Cirillo PA, Walker AM (1995) Incidence of symptomatic hand, hip, and knee osteoarthritis among patients in a health maintenance organization. Arthritis Rheum 38:1134–1141
Linn S, Murtaugh B, Casey E (2012) Role of sex hormones in the development of osteoarthritis. PM & R 4:S169–S173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2012.01.013
Felson DT, Lawrence RC, Dieppe PA, Hirsch R, Helmick CG et al (2000) Osteoarthritis: new insights Part 1: the disease and its risk factors. Ann Intern Med 133:635–646
Arden N, Nevitt MC (2006) Osteoarthritis: epidemiology. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 20:3–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2005.09.007
Conde J, Scotece M, Gomez R, Lopez V, Gomez-Reino JJ, Gualillo O (2011) Adipokines and osteoarthritis: novel molecules involved in the pathogenesis and progression of disease. Arthritis 2011:203901. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/203901
Rukavina I, Mortier G, Van Laer L, Frkovic M, Dapic T, Jelusic M (2014) Mutation in the type II collagen gene (COL2AI) as a cause of primary osteoarthritis associated with mild spondyloepiphyseal involvement. Semin Arthritis Rheum 44:101–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.03.003
Lankisch P, Honscheid A, Schaper J, Borkhardt A, Laws HJ (2014) COL2A1 mutation as a cause of premature osteoarthritis in a 13-year-old child. Joint Bone Spine 81:83–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2013.06.007
Loughlin J (2001) Genetic epidemiology of primary osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 13:111–116
Richette P, Corvol M, Bardin T (2003) Estrogens, cartilage, and osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine 70:257–262
Khalid AB, Krum SA (2016) Estrogen receptors alpha and beta in bone. Bone 87:130–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2016.03.016
Cheung E, Schwabish MA, Kraus WL (2003) Chromatin exposes intrinsic differences in the transcriptional activities of estrogen receptors alpha and beta. EMBO J 22:600–611. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg037
Daheshia M, Yao JQ (2008) The interleukin 1beta pathway in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 35:2306–2312
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Lin J, Wang L, Gao J, Zhu S (2017) MiR-203 inhibits estrogen-induced viability, migration and invasion of estrogen receptor alpha-positive breast cancer cells. Exp Ther Med 14:2702–2708. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4828
Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, Bole G, Borenstein D, Brandt K, Christy W, Cooke TD, Greenwald R, Hochberg M et al (1986) Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum 29:1039–1049
Hoffman BE, Newman-Tarr TM, Gibbard A, Wang S, Hanning C, Pratta MA, Boyle RJ, Kumar S, Majumdar MK (2010) Development and characterization of a human articular cartilage-derived chondrocyte cell line that retains chondrocyte phenotype. J Cell Physiol 222:695–702. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.21994
Zheng X, Zhao FC, Pang Y, Li DY, Yao SC, Sun SS, Guo KJ (2017) Downregulation of miR-221-3p contributes to IL-1beta-induced cartilage degradation by directly targeting the SDF1/CXCR1 signaling pathway. J Mol Med (Berl) 95:615–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1516-6
Chen D, Pan X, Xiao P, Farwell MA, Zhang B (2011) Evaluation and identification of reliable reference genes for pharmacogenomics, toxicogenomics, and small RNA expression analysis. J Cell Physiol 226:2469–2477. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22725
Taylor SC, Berkelman T, Yadav G, Hammond M (2013) A defined methodology for reliable quantification of Western blot data. Mol Biotechnol 55:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-013-9672-6
Cheng XY, Liu JD, Lu XY, Yan X, Huang C, Meng XM, Li J (2018) miR-203 inhibits alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis by targeting Lipin1. Front Pharmacol 9:275. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00275
Yin Q, Wang J, Fu Q, Gu S, Rui Y (2018) CircRUNX2 through has-miR-203 regulates RUNX2 to prevent osteoporosis. J Cell Mol Med 22:6112–6121. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13888
Tu C, Huang X, Xiao Y, Song M, Ma Y, Yan J, You H, Wu H (2019) Schisandrin A inhibits the IL-1beta-induced inflammation and cartilage degradation via suppression of MAPK and NF-kappaB signal pathways in rat chondrocytes. Front Pharmacol 10:41. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00041
Li Z, Chen B, Feng M, Ouyang H, Zheng M, Ye Q, Nie Q, Zhang X (2015) MicroRNA-23b promotes avian leukosis virus subgroup J (ALV-J) replication by targeting IRF1. Sci Rep 5:10294. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10294
Maldonado M, Nam J (2013) The role of changes in extracellular matrix of cartilage in the presence of inflammation on the pathology of osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int 2013:284873. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/284873
Ma H, Wu W, Yang X, Liu J, Gong Y (2015) Genetic effects of common polymorphisms in estrogen receptor alpha gene on osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:13446–13454
Ren Y, Tan B, Yan P, You Y, Wu Y, Wang Y (2015) Association between polymorphisms in the estrogen receptor alpha gene and osteoarthritis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 16:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-015-0506-5
David F, Farley J, Huang H, Lavoie JP, Laverty S (2007) Cytokine and chemokine gene expression of IL-1beta stimulated equine articular chondrocytes. Vet Surg 36:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-950X.2007.00253.x
Clutterbuck AL, Mobasheri A, Shakibaei M, Allaway D, Harris P (2009) Interleukin-1beta-induced extracellular matrix degradation and glycosaminoglycan release is inhibited by curcumin in an explant model of cartilage inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:428–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04687.x
Martel-Pelletier J (2004) Pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 12:31–33
Miagkov AV, Kovalenko DV, Brown CE, Didsbury JR, Cogswell JP, Stimpson SA, Baldwin AS, Makarov SS (1998) NF-kappaB activation provides the potential link between inflammation and hyperplasia in the arthritic joint. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13859–13864
Wang C, Zheng X, Shen C, Shi Y (2012) MicroRNA-203 suppresses cell proliferation and migration by targeting BIRC5 and LASP1 in human triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 31:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-31-58
Ding X, Park SI, McCauley LK, Wang CY (2013) Signaling between transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) and transcription factor SNAI2 represses expression of microRNA miR-203 to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis. J Biol Chem 288:10241–10253. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.443655
Zhang Z, Zhang B, Li W, Fu L, Zhu Z, Dong JT (2011) Epigenetic silencing of miR-203 upregulates SNAI2 and contributes to the invasiveness of malignant breast cancer cells. Genes Cancer 2:782–791. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601911429743
Muhammad N, Bhattacharya S, Steele R, Ray RB (2016) Anti-miR-203 suppresses ER-positive breast cancer growth and stemness by targeting SOCS3. Oncotarget 7:58595–58605. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11193
Zhao J, Imbrie GA, Baur WE, Iyer LK, Aronovitz MJ, Kershaw TB, Haselmann GM, Lu Q, Karas RH (2013) Estrogen receptor-mediated regulation of microRNA inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33:257–265. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300200
Zierau O, Helle J, Schadyew S, Morgenroth Y, Bentler M, Hennig A, Chittur S, Tenniswood M, Kretzschmar G (2018) Role of miR-203 in estrogen receptor-mediated signaling in the rat uterus and endometrial carcinoma. J Cell Biochem 119:5359–5372. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26675
Yang RC, Chen MH, Chen PY, Chen CY, Tsai SF, Cheng CK, Sun JS (2014) A mutation of the Col2a1 gene (G1170S) alters the transgenic murine phenotype and cartilage matrix homeostasis. J Formos Med Assoc 113:803–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2013.09.015
Huang K, Wu LD (2008) Aggrecanase and aggrecan degradation in osteoarthritis: a review. J Int Med Res 36:1149–1160. https://doi.org/10.1177/147323000803600601
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Health Department Research Foundation of Hebei Province (20181044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yusong Guo, Lijun Tian, Xiqiao Du, and Zhigang Deng declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Tian, L., Du, X. et al. MiR-203 regulates estrogen receptor α and cartilage degradation in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes. J Bone Miner Metab 38, 346–356 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-019-01062-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-019-01062-4