Abstract
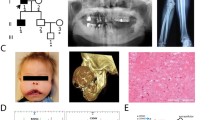
Autosomal dominant osteopetrosis type II (ADO-II) is a heritable bone disorder characterized by osteosclerosis, predominantly involving the spine (vertebral end-plate thickening, or rugger-jersey spine), the pelvis (“bone-within-bone” structures) and the skull base. Chloride channel 7 (CLCN7) has been reported to be the causative gene. In this study, we aimed to identify the pathogenic mutation in four Chinese families with ADO-II. All 25 exons of the CLCN7 gene, including the exon–intron boundaries, were amplified and sequenced directly in four probands from the Chinese families with ADO-II. The mutation site was then identified in other family members and 250 healthy controls. In family 1, a known missense mutation c.296A>G in exon 4 of CLCN7 was identified in the proband, resulting in a tyrosine (UAU) to cysteine (UGU) substitution at p.99 (Y99C); the mutation was also identified in his affected father. In family 2, a novel missense mutation c.865G>C in exon 10 was identified in the proband, resulting in a valine (GUC) to leucine (CUC) substitution at p.289 (V289L); the mutation was also identified in her healthy mother and sister. In family 3, a novel missense mutation c.1625C>T in exon 17 of CLCN7 was identified in the proband, resulting in an alanine (GCG) to valine (GUG) substitution at p.542 (A542V); the mutation was also identified in her father. In family 4, a hot spot, R767W (c.2299C>T, CGG>TGG), in exon 24 was found in the proband which once again proved the susceptibility of the site or the similar genetic background in different races. Moreover, two novel mutations, V289L and A542V, occurred at a highly conserved position, found by a comparison of the protein sequences from eight vertebrates, and were predicted to have a pathogenic effect by PolyPhen-2 software, which showed “probably damaging” with a score of approximately 1. These mutation sites were not identified in 250 healthy controls. Our present findings suggest that the novel missense mutations V289L and A542V in the CLCN7 gene were responsible for ADO-II in the two Chinese families.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnston CC Jr., Lavy N, Lord T, Vellios F, Merritt AD, Deiss WP Jr (1968) Osteopetrosis. A clinical, genetic, metabolic, and morphologic study of the dominantly inherited, benign form. Medicine 47:149–167
Cleiren E, Benichou O, Van Hul E, Gram J, Bollerslev J, Singer FR, Beaverson K, Aledo A, Whyte MP, Yoneyama T, deVernejoul MC, Van Hul W (2001) Albers-Schonberg disease (autosomal dominant osteopetrosis, type II) results from mutations in the ClCN7 chloride channel gene. Hum Mol Genet 10:2861–2867
Kornak U, Kasper D, Bosl MR, Kaiser E, Schweizer M, Schulz A, Friedrich W, Delling G, Jentsch TJ (2001) Loss of the ClC-7 chloride channel leads to osteopetrosis in mice and man. Cell 104:205–215
Frattini A, Pangrazio A, Susani L, Sobacchi C, Mirolo M et al (2003) Chloride channel ClCN7 mutations are responsible for severe recessive, dominant, and intermediate osteopetrosis. J Bone Miner Res 18:1740–1747
Campos-Xavier AB, Saraiva JM, Ribeiro LM, Munnich A, Cormier-Daire V (2003) Chloride channel 7 (CLCN7) gene mutations in intermediate autosomal recessive osteopetrosis. Hum Genet 112:186–189
Waguespack SG, Koller DL, White KE, Fishburn T, Carn G, Buckwalter KA, Johnson M, Kocisko M, Evans WE, Foroud T, Econs MJ (2003) Chloride channel 7 (ClCN7) gene mutations and autosomal dominant osteopetrosis, type II. J Bone Miner Res 18:1513–1518
Letizia C, Taranta A, Migliaccio S, Caliumi C, Diacinti D, Delfini E, D’Erasmo E, Iacobini M, Roggini M, Albagha OM, Ralston SH, Teti A (2004) Type II benign osteopetrosis (Albers-Schonberg disease) caused by a novel mutation in CLCN7 presenting with unusual clinical manifestations. Calcif Tissue Int 74:42–46
Zhang ZL, He JW, Zhang H, Hu WW, Fu WZ, Gu JM, Yu JB, Gao G, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ (2009) Identification of the CLCN7 gene mutations in two Chinese families with autosomal dominant osteopetrosis (type II). J Bone Miner Metab 27:444–451
Wang C, Zhang H, He JW, Gu JM, Hu WW, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ, Fu WZ, Yue H, Ke YH, Zhang ZL (2012) The virulence gene and clinical phenotypes of osteopetrosis in the Chinese population: six novel mutations of the CLCN7 gene in twelve osteopetrosis families. J Bone Miner Metab 30:338–348
Zheng H, Zhang Z, He JW, Fu WZ, Wang C, Zhang ZL (2013) Identification of two novel CLCN7 gene mutations in three Chinese families with autosomal dominant osteopetrosis type II. Joint Bone Spine 81:188–189
Rashid BM, Rashid NG, Schulz A, Lahr G, Nore BF (2013) A novel missense mutation in the CLCN7 gene linked to benign autosomal dominant osteopetrosis: a case series. J Med Case Rep 7:7
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev SR (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 7:248–249
Adzhubei I, Jordan DM, Sunyaev SR (2013) Predicting Functional Effect of Human Missense Mutations Using PolyPhen-2. Curr Protoc Hum Genet 7:2
Sui W, Ou M, Liang J, Ding M, Chen J, Liu W, Xiao R, Meng X, Wang L, Pan X (2013) Rapid gene identification in a Chinese osteopetrosis family by whole exome sequencing. Gene 516:311–315
Del Fattore A, Peruzzi B, Rucci N, Recchia I, Cappariello A et al (2006) Clinical, genetic, and cellular analysis of 49 osteopetrotic patients: implications for diagnosis and treatment. J Med Genet 43:315–325
Wang C, Zhang H, He JW, Gu JM, Hu WW, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ, Fu WZ, Yue H, Ke YH, Zhang ZL (2012) The virulence gene and clinical phenotypes of osteopetrosis in the Chinese population: six novel mutations of the CLCN7 gene in twelve osteopetrosis families. J Bone Miner Metab 30:338–348
Zhang ZL, He JW, Zhang H, Hu WW, Fu WZ, Gu JM, Yu JB, Gao G, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ (2009) Identification of the CLCN7 gene mutations in two Chinese families with autosomal dominant osteopetrosis (type II). J Bone Miner Metab 27:444–451
Waguespack SG, Koller DL, White KE, Fishburn T, Carn G, Buckwalter KA, Johnson M, Kocisko M, Evans WE, Foroud T, Econs MJ (2003) Chloride channel 7 (ClCN7) gene mutations and autosomal dominant osteopetrosis, type II. J Bone Miner Res 18:1513–1518
Pangrazio A, Pusch M, Caldana E, Frattini A, Lanino E et al (2010) Molecular and clinical heterogeneity in CLCN7-dependent osteopetrosis: report of 20 novel mutations. Hum Mutat 31:E1071–E1080
Benichou O, Laredo J, De Vernejoul M (2000) Type II autosomal dominant osteopetrosis (Albers-Schönberg disease): clinical and radiological manifestations in 42 patients. Bone 26:87–93
Chu K, Koller DL, Snyder R, Fishburn T, Lai D, Waguespack SG, Foroud T, Econs MJ (2005) Analysis of variation in expression of autosomal dominant osteopetrosis type 2: searching for modifier genes. Bone 37:655–661
Campos-Xavier AB, Casanova JL, Doumaz Y, Feingold J, Munnich A, Cormier-Daire V (2005) Intrafamilial phenotypic variability of osteopetrosis due to chloride channel 7 (CLCN7) mutations. Am J Med Genet A 133A:216–218
Chu K, Snyder R, Econs MJ (2006) Disease status in autosomal dominant osteopetrosis type 2 is determined by osteoclastic properties. J Bone Miner Res 21:1089–1097
Sulewska A, Niklinska W, Kozlowski M, Minarowski L, Naumnik W, Niklinski J, Dabrowska K, Chyczewski L (2007) DNA methylation in states of cell physiology and pathology. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 45:149–158
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81370978, 81270964), National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2014CB942903), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai municipality (14JC1405000), Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (2014ZYJB0009), and Shanghai Leading Talent Plan (051).
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Zheng, C. Shao and Y. Zheng contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Shao, C., Zheng, Y. et al. Two novel mutations of CLCN7 gene in Chinese families with autosomal dominant osteopetrosis (type II). J Bone Miner Metab 34, 440–446 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-015-0682-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-015-0682-2