Abstract
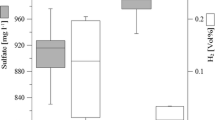
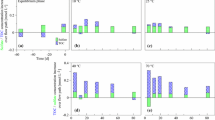
Abstract Enhanced process understanding of engineered geothermal systems is a prerequisite to optimize plant reliability and economy. We investigated microbial, geochemical and mineralogical aspects of a geothermal groundwater system located in the Molasse Basin by fluid analysis. Fluids are characterized by temperatures ranging from 61°C to 103°C, salinities from 600 to 900 mg/l and a dissolved organic carbon content (DOC) between 6.4 to 19.3 mg C/l. The microbial population of fluid samples was analyzed by genetic fingerprinting techniques based on PCR-amplified 16S rRNA- and dissimilatory sulfite reductase genes. Despite of the high temperatures, microbes were detected in all investigated fluids. Fingerprinting and DNA sequencing enabled a correlation to metabolic classes and biogeochemical processes. The analysis revealed a broad diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Overall, the detection of microbes known to be involved in biocorrosion and mineral precipitation indicates that microorganisms could play an important role for the understanding of processes in engineered geothermal systems.
Zusammenfassung
Die Verbesserung des Prozessverständnisses ist eine grundlegende Voraussetzung für eine Optimierung der Betriebssicherheit und der Ökonomie geothermischer Anlagen in Bezug auf die Partikelbildung und Korrosion. Daher wurden Prozessfluide einer Anlage im Molassebecken unter mikrobiologischen, geochemischen und mineralogischen Gesichtspunkten untersucht. Die Fluidtemperatur der vor und nach dem Wärmetauscher entnommenen Fluide betrug zwischen 103 °C und 61 °C. Die Salinität variierte zwischen 600 und 900 mg/l und der gelöste organische Kohlenstoff (DOC) lag zwischen 6,4 und 19,3 mg C/l. Die mikrobielle Lebensgemeinschaft in der Anlage wurde mithilfe einer genetischen Fingerprinting-Methode charakterisiert. Hierzu wurde das 16S rRNA Gen sowie die für sulfatreduzierende Bakterien (SRB) spezifische dissimilatorische Sulfitreduktase untersucht. In allen Fluidproben konnten Mikroorganismen nachgewiesen werden. Die Zuordnung der Organismen zu stoffwechselphysiologischen Gruppen lieferte Hinweise auf verschiedene biogeochemische Prozesse. Die Untersuchungen zeigen eine beachtliche Diversität von SRB auf. Diese sind für ihre Rolle bei biologisch induzierten Korrosions- und Fällungsprozessen bekannt.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W., Lipman, D.J.J.: Basic local alignment search tool. Mol. Biol. 215(3), 403–410 (1990)
Amann, R.I., Ludwig, W., Schleifer, K.-H.: Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol. Rev. 59, 143–169 (1995)
Baker, G.C., Cowan, D.A.: 16S rDNA primers and the unbiased assessment of thermophile diversity. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 32, 218–221 (2004)
Barton, L.L., Tomei, F.A.: Characteristics and activities of sulfate-reducing bacteria. In: Barton, L.L. (ed.) Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. Biotechnology Handbooks, vol. 8. Plenum Press, New York (1995)
Basso, O., Caumette, P., Magot, M.: Desulfovibrio putealis sp. nov., a novel sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from a deep subsurface aquifer. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55(1), 101–104 (2005)
Beech, I.B., Sunner, J.: Biocorrosion: towards understanding interactions between biofilms and metals. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 15, 181–186 (2004)
Bryant, M.P., Campbell, L.L., Reddy, C.A., Crabill, M.R.: Growth on desulfovibrio in lactate or ethanol media low in sulfate in association with H2-utilizing methanogenic bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 33, 1162 (1977)
Chivian, D., Brodie, E.L., Alm, E.J., Culley, D.E., Dehal, P.S., DeSantis, T.Z., Gihring, T.M., Lapidus, A., Lin, L.-H., Lowry, S.R., Moser, D.P., Richardson, P.M., Southam, G., Wanger, G., Pratt, L.M., Andersen, G.L., Hazen, T.C., Brockman, F.J., Arkin, A.P., Onstott, T.C.: Environmental genomics reveals a single-species ecosystem deep within earth. Science 322(5899), 275–278 (2008)
Coetser, S.E., Cloete, T.E.: Biofouling and biocorrosion in industrial water systems. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 31(4), 213–232 (2005)
Dahle, H., Birkeland, N.-K.: Thermovirga lienii gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel moderately thermophilic, anaerobic, amino-acid-degrading bacterium isolated from a North Sea oil well. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 1539–1545 (2006)
Flemming, H.C.: Biofouling in water systems—cases causes and countermeasures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 59, 629–640 (2002)
Galouchko, A.S., Rozanova, E.P.: Sulfidogenic oxidation of acetate by a syntrophic association of anaerobic mesophilic bacteria. Microbiology 65(2), 134–139 (1996)
Geets, J., Borremans, B., Diels, L., Springael, D., Vangronsveld, J., van der Lelie, D., Vanbroekhoven, K.: DsrB gene-based DGGE for community and diversity surveys of sulfate-reducing bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 66(2), 194–205 (2006)
Honegger, J.L., Czernichowski-Lauriol, I., Criaud, A., Menjoz, A., Sainson, S., Guezennec, J.: Detailed study of sulfide scaling at la Courneuue Nord a geothermal exploitation of the Paris Basin, France. Geothermics 18(1–2), 137–144 (1989)
Huber, S.A., Frimmel, F.H.: Size-exclusion chromatography with organic carbon detection (LC-OCD): a fast and reliable method for the characterization of hydrophilic organic matter in natural waters. Vom Wasser 86, 277–290 (1996)
Imachi, H., Sekiguchi, Y., Kamagata, Y., Loy, A., Qiu, Y.L., Hugenholtz, P., Kimura, N., Wagner, M., Ohashi, A., Harada, H.: Non-sulfate-reducing, syntrophic bacteria affiliated with desulfotomaculum cluster i are widely distributed in methanogenic environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 2080–2091 (2006)
Inagaki, F., Motomura, Y., Ogata, S.: Microbial silica deposition in geothermal hot waters. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 60, 605–611 (2003)
Javerhadashti, R.: Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion. An Engineering Insight. Springer, London (2008)
Jørgensen, B.B., Isaksen, M.F., Jannasch, H.: Bacterial sulfate-reduction above 100 °C in the deep-sea hydrothermal vent sediments. Science (1756–1757) (1992)
Kato, C., Li, L., Nogi, Y., Nakamura, Y., Tamaoka, J., Horikoshi, K.: Extremely barophilic bacteria isolated from the Mariana trench challenger deep, at a depth of 11,000 meters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64(4), 1510–1513 (1998)
Kashefi, K., Lovley, D.R.: Extending the upper temperature limit for life. Science 301, 934 (2003)
Kimura, H., Nashimoto, H., Shimizu, M., Hattori, S., Yamada, K., Koba, K., Yoshida, N., Kato, K.: Microbial methane production in deep aquifer associated with the accretionary prism in Southwest Japan. ISME J. 4, 531–541 (2010)
Lerm, S., Alawi, M., Miethling-Graff, R., Seibt, A., Wolfgramm, M., Rauppach, K., Würdemann, H.: Mikrobiologisches Monitoring in zwei geothermisch genutzten Aquiferen Norddeutschlands. Z. Geol. Wissensch. (2011)
Little, B.J., Lee, J.S.: Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion. Wiley, Hoboken (2007)
Machel, H.G.: Bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction in diagenetic settings—old and new insights. Sediment. Geol. 140(1–2), 143–175 (2001)
Muyzer, G., Brinkhoff, T., Nübel, U., Santegoeds, C., Schäfer, H., Wawer, C.: Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) in microbial ecology. In: Akkermans, A.D.L., van Elsas, J.D., de Bruijn, F.J. (eds.) Molecular Microbial Ecology Manual, vol. 3.4.4, pp. 1–27. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht (1997)
Nivens, D.E., Nichols, P.D., Henson, J.M., Geesey, G.G., White, D.C.: Reversible acceleration of the corrosion of AISI304 stainless steel exposed to seawater induced by growth of the marine bacterium Vibrio natriegens. Corrosion 42, 204–210 (1986)
Nilsen, R.K., Torsvik, T., Lien, T.: Desulfotomaculum thermocisternum sp. nov., a sulfate reducer isolated from a hot North Sea oil reservoir. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 46, 397–402 (1996)
Pakchung, A.A.H., Simpson, P.J.L., Codd, R.: Life on earth. Extremophiles continue to move the goal posts. Environ. Chem. 3, 77–93 (2006)
Robinson, J.A., Tiedje, J.M.: Competition between sulfate-reducing and methanogenic bacteria for H2 under resting and growing conditions. Arch. Microbiol. 137(1), 26–32 (1984)
Rosnes, J.T., Torsvik, T., Lien, T.: Spore-forming thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria isolated from North Sea oil field waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57(8), 2302–2307 (1991)
Rothschild, L.J., Mancinelli, R.L.: Life in extreme environments. Nature 409, 1092–1101 (2001)
Sand, W.: Microbial life in geothermal waters. Geothermics 32, 655–667 (2003)
Schieber, J.: Sedimentary pyrite: a window into the microbial past. Geology 30(6), 531–534 (2002)
Schink, B., Stams, A.J.M.: Syntrophism among prokaryotes. In: The Procaryotes, pp. 2–57. Springer, New York (2002)
Schreurs, M.L.: The health and care of wells. JAWWA 62(7), 434–436 (1970)
Schröder, H., Hesshaus, A.: Abschlussbericht zum Forschungsvorhaben 0329937A. Langfristige Betriebssicherheit geothermischer Anlagen – Aspekte der langfristigen Betriebssicherheit und der zukünftigen Technologie geothermischer Anlagen in Deutschland. Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe (2009)
Sitte, J., Akob, D.M., Kaufmann, C., Finster, K., Banerjee, D., Burkhardt, E.-M., Kostka, J.E., Scheinost, A.C., Büchel, G., Küsel, K.: Microbial Links between sulfate reduction and metal retention in uranium- and heavy metal-contaminated soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76, 3143–3152 (2010)
Sharma, A., Scott, J.H., Cody, J.D., Fogel, M.L., Hazen, R.M., Hemley, R.J., Huntress, W.T.: Microbial activity at gigapascal pressures. Science 295(5559), 1514–1516 (2002)
Takai, K., Komatsu, T., Inagaki, F., Horikoshi, K.: Distribution of archaea in a black smoker chimney structure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 3618–3629 (2001)
Takai, K., Nakamura, K., Toki, T., Tsunogai, U., Miyazaki, M., Miyazaki, J., Hirayama, H., Nakagawa, S., Nunoura, T., Horikoshi, K.: Cell proliferation at 122 degrees C and isotopically heavy CH4 production by a hyperthermophilic methanogen under high-pressure cultivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105(31), 10949–10954 (2008)
Torsvik, V., Goksoyr, J., Daae, F.L.: High diversity of DNA of soil bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56, 782–787 (1990)
Valdez, B., Schorr, M., Quintero, M., Carrillo, M., Zlatev, R., Stoytcheva, M., de Dios Ocampo, J.: Corrosion and scaling at Cerro Prieto geothermal field. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 56(1), 28–34 (2009)
van Beek, C.G.E.M., Kooper, W.F.: The clogging of shallow discharge wells in the Netherlands river region. Ground Water 18(6), 578–586 (1980)
Walker, C.B., He, Z., Yang, Z.K., Ringbauer, J.A.Jr., He, Q., Zhou, J., Voordouw, G., Wall, J.D., Arkin, A.P., Hazen, T.C., Stolyar, S., Stahl, D.A.: The electron transfer system of syntrophically grown Desulfovibrio vulgaris. J. Bacteriol. 191, 5793–5801 (2009)
Wimpenny, J., Manz, W., Szewzyk, U.: Heterogeneity in biofilms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 24, 661–671 (2000)
Würdemann, H., Möller, F., Kühn, M., Heidug, W., Christensen, N.P., Borm, G., Schilling, F.R., the CO2SINK group: CO2SINK-From site characterisation and risk assessment to monitoring and verification: one year of operational experience with the field laboratory for CO2 storage at Ketzin, Germany. Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control 4(6), 938–951 (2010)
Wolfgramm, M., Seibt, A.: Zusammensetzung von Tiefenwässern in Deutschland und ihre Relevanz für geothermische Anlagen. GTV-Tagung, Karlsruhe, pp. 503–516 (2008)
Zettlitzer, M., Moeller, F., Morozova, D., Lokay, P., Würdemann, H.: Re-establishment of the proper injectivity of the CO2-injection well Ktzi 201 in Ketzin, Germany. Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control 4(6), 952–959 (2010)
Acknowledgements
We thank Ben Cowie and Rona Miethling-Graff for proofreading the manuscript and helpful advices. This research was funded by the BMU project “AquiScreen” (Nr. 0327634): Betriebssicherheit der geothermischen Nutzung von Aquiferen unter besonderer Berücksichtigung mikrobiologischer Aktivität und Partikelumlagerungen—Screening an repräsentativen Standorten.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alawi, M., Lerm, S., Vetter, A. et al. Diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in a plant using deep geothermal energy. Grundwasser 16, 105–112 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00767-011-0164-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00767-011-0164-y