Abstract
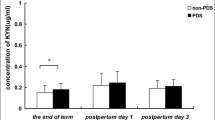
The rate-limiting enzyme of serotonin biosynthesis, tryptophan hydroxylase 2 (TPH2), is one of the most promising candidate genes for psychiatric disorders. Although evidence strongly suggests that the TPH2 is significant in the etiology of major depression and anxiety disorder, whether it also contributes to the etiology of peripartum major depression and anxiety disorder, a specific subtype influenced considerably by other environmental factors like hormones, is unclear. This study investigated the role of TPH2 in the etiology of peripartum major depression and anxiety disorder in a Han Chinese population in Taiwan. Six single nucleotide polymorphisms were selected from previously profiled genetic information of TPH2 in Han Chinese. A cohort of postpartum Chinese women that included 117 patients with major depression, anxiety disorder, or both and 83 healthy controls were genotyped with selected TPH2 markers. The TPH2 2755A allele was found only in women with peripartum major depression and anxiety disorder (p = 0.043) and exhibited a dominant gene action (p = 0.038) with an estimated disease risk of 1.73. Although the sample size is small, results from this study suggest that the TPH2 C2755A polymorphism may represent a population-specific risk factor for peripartum major depression and anxiety disorder, perhaps by interacting with hormones.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis GR, Cookson WO (2000) GOLD—graphical overview of linkage disequilibrium. Bioinformatics 16(2):182–183
Altshuler LL et al (1998) Course of mood and anxiety disorders during pregnancy and the postpartum period. J Clin Psychiatry 59(Suppl):229–233
Andrade L et al (2003) The epidemiology of major depressive episodes: results from the International Consortium of Psychiatric Epidemiology (ICPE) Surveys. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 12(1):3–21
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington
Bach-Mizrachi H et al (2006) Neuronal tryptophan hydroxylase mRNA expression in the human dorsal and median raphe nuclei: major depression and suicide. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(4):814–824
Bach-Mizrachi H et al (2008) Elevated expression of tryptophan hydroxylase-2 mRNA at the neuronal level in the dorsal and median raphe nuclei of depressed suicides. Mol Psychiatry 13(5):507–513
Bell C et al (2001) Tryptophan depletion and its implications for psychiatry. Br J Psychiatry 178:399–405
Blehar MC (1995) Gender differences in risk factors for mood and anxiety disorders: implications for clinical treatment research. Psychopharmacol Bull 31(4):687–691
Bloch M et al (2000) Effects of gonadal steroids in women with a history of postpartum depression. Am J Psychiatry 157(6):924–930
Bodmer W, Bonilla C (2008) Common and rare variants in multifactorial susceptibility to common diseases. Nat Genet 40(6):695–701
Breidenthal SE et al (2004) Identification of genetic variants in the neuronal form of tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH2). Psychiatr Genet 14(2):69–72
Chen GL et al (2008) Functional characterization of the human TPH2 5′ regulatory region: untranslated region and polymorphisms modulate gene expression in vitro. Hum Genet 122(6):645–657
Cichon S et al (2008) Brain-specific tryptophan hydroxylase 2 (TPH2): a functional Pro206Ser substitution and variation in the 5′-region are associated with bipolar affective disorder. Hum Mol Genet 17(1):87–97
Cohen JC et al (2006) Multiple rare variants in NPC1L1 associated with reduced sterol absorption and plasma low-density lipoprotein levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(6):1810–1815
Coon H et al (2005) Possible association between autism and variants in the brain-expressed tryptophan hydroxylase gene (TPH2). Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 135(1):42–46
De Luca V et al (2005) Tryptophan hydroxylase 2 gene expression and promoter polymorphisms in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:378–382
Eley TC, Stevenson J (1999) Exploring the covariation between anxiety and depression symptoms: a genetic analysis of the effects of age and sex. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 40(8):1273–1282
Endicott J, Spitzer RL (1978) A diagnostic interview: the schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 35(7):837–844
Feder JN et al (1996) A novel MHC class I-like gene is mutated in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis. Nat Genet 13(4):399–408
Fink G et al (1996) Estrogen control of central neurotransmission: effect on mood, mental state, and memory. Cell Mol Neurobiol 16(3):325–344
Frayling IM et al (1998) The APC variants I1307K and E1317Q are associated with colorectal tumors, but not always with a family history. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(18):10722–10727
Gavin NI et al (2005) Perinatal depression: a systematic review of prevalence and incidence. Obstet Gynecol 106(5 Pt 1):1071–1083
Gutknecht L et al (2007) Tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene variation influences personality traits and disorders related to emotional dysregulation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10(3):309–320
Hiroi R et al (2006) Estrogen selectively increases tryptophan hydroxylase-2 mRNA expression in distinct subregions of rat midbrain raphe nucleus: association between gene expression and anxiety behavior in the open field. Biol Psychiatry 60(3):288–295
Invernizzi RW (2007) Role of TPH-2 in brain function: news from behavioral and pharmacologic studies. J Neurosci Res 85(14):3030–3035
Kammerer M et al (2006) The HPA axis and perinatal depression: a hypothesis. Arch Womens Ment Health 9(4):187–196
Kaplan HI, Sadock BJ (1998) Kaplan & Sadock's synopsis of psychiatry. Behavioral sciences/clinical psychiatry, 8th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Kendler KS et al (1992) A population-based twin study of major depression in women. The impact of varying definitions of illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49(4):257–266
Kendler KS et al (1993) The lifetime history of major depression in women. Reliability of diagnosis and heritability. Arch Gen Psychiatry 50(11):863–870
Kessler RC, Walters EE (1998) Epidemiology of DSM-III-R major depression and minor depression among adolescents and young adults in the National Comorbidity Survey. Depress Anxiety 7(1):3–14
Ko HC (1996) Causes and consequence of postpartum depression. National Science Council, Taiwan
Lambert JJ et al (2003) Neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptors. Prog Neurobiol 71(1):67–80
Lewinsohn PM et al (1998) Major depressive disorder in older adolescents: prevalence, risk factors, and clinical implications. Clin Psychol Rev 18(7):765–794
Lewontin RC (1988) On measures of gametic disequilibrium. Genetics 120(3):849–852
Lin YM et al (2007) Association of functional polymorphisms of the human tryptophan hydroxylase 2 gene with risk for bipolar disorder in Han Chinese. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64(9):1015–1024
Mani SK et al (1997) Progesterone receptor function from a behavioral perspective. Horm Behav 31(3):244–255
McGuffin P et al (1996) A hospital-based twin register of the heritability of DSM-IV unipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53(2):129–136
McKinney J et al (2008) A loss-of-function mutation in tryptophan hydroxylase 2 segregating with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry 13(4):365–367
McQueen JK et al (1997) Estradiol-17 beta increases serotonin transporter (SERT) mRNA levels and the density of SERT-binding sites in female rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 45(1):13–23
Mitchell EA et al (2008) Neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptors: molecular determinants and significance in health and disease. Neurochem Int 52(4–5):588–595
Mossner R et al (2006) Transmission disequilibrium of polymorphic variants in the tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene in children and adolescents with obsessive–compulsive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 9(4):437–442
Nielsen DM et al (1998) Detecting marker-disease association by testing for Hardy–Weinberg disequilibrium at a marker locus. Am J Hum Genet 63(5):1531–1540
Nielsen DA et al (2008) TPH2 and TPH1: association of variants and interactions with heroin addiction. Behav Genet 38(2):133–150
Ostlund H et al (2003) Estrogen receptor gene expression in relation to neuropsychiatric disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci 100:754–763
Reimold M et al (2008) Reduced serotonin transporter availability in patients with unipolar major depression reflect the level of anxiety. Mol Psychiatry 13(6):557
Rice JP et al (1992) Stability of psychiatric diagnoses. An application to the affective disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49(10):824–830
Risch NJ (2000) Searching for genetic determinants in the new millennium. Nature 405(6788):847–856
Ross LE, McLean LM (2006) Anxiety disorders during pregnancy and the postpartum period: a systematic review. J Clin Psychiatry 67(8):1285–1298
Rouillon F (1999) Anxiety with depression: a treatment need. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 9(Suppl. 3):S87–S92
Schmidt PJ et al (1998) Differential behavioral effects of gonadal steroids in women with and in those without premenstrual syndrome. N Engl J Med 338(4):209–216
Shear MK, Mammen O (1995) Anxiety disorders in pregnant and postpartum women. Psychopharmacol Bull 31(4):693–703
Sheehan K et al (2005) Tryptophan hydroxylase 2 (TPH2) gene variants associated with ADHD. Mol Psychiatry 10(10):944–949
Steiner M et al (2003) Hormones and mood: from menarche to menopause and beyond. J Affect Disord 74(1):67–83
Sumner BE et al (2007) Raloxifene blocks estradiol induction of the serotonin transporter and 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptor in female rat brain. Neurosci Lett 417(1):95–99
Sun HS et al (2004) Association of tryptophan hydroxylase gene polymorphism with depression, anxiety and comorbid depression and anxiety in a population-based sample of postpartum Taiwanese women. Genes Brain Behav 3(6):328–336
Thompson TL et al (2000) Estrogen priming modulates autoreceptor-mediated potentiation of dopamine uptake. Eur J Pharmacol 401(3):357–363
Torgersen S (1986) Genetic factors in moderately severe and mild affective disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 43(3):222–226
Van Praag HM (1994) 5-HT-related, anxiety- and/or aggression-driven depression. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 9(Suppl):15–16
Veenstra-VanderWeele J, Cook EH Jr (2003) Knockout mouse points to second form of tryptophan hydroxylase. Mol Interv 3(2):72–75, 50
Walitza S et al (2005) Transmission disequilibrium of polymorphic variants in the tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry 10:1126–1132
Walther DJ, Bader M (2003) A unique central tryptophan hydroxylase isoform. Biochem Pharmacol 66(9):1673–1680
Wittchen HU et al (2000) Why do people with anxiety disorders become depressed? A prospective-longitudinal community study. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl (406):14–23
Xu J et al (2002) Positive results in association studies are associated with departure from Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium: hint for genotyping error? Hum Genet 111(6):573–574
Zhang X et al (2005) Loss-of-function mutation in tryptophan hydroxylase-2 identified in unipolar major depression. Neuron 45(1):11–16
Zhou Z et al (2005) Haplotype-based linkage of tryptophan hydroxylase 2 to suicide attempt, major depression, and cerebrospinal fluid 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in 4 populations. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62(10):1109–1118
Zill P et al (2004) SNP and haplotype analysis of a novel tryptophan hydroxylase isoform (TPH2) gene provide evidence for association with major depression. Mol Psychiatry 9(11):1030–1036
Zonana J, Gorman JM (2005) The neurobiology of postpartum depression. CNS Spectr 10(10):792–799, 805
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grant NSC97-3112-B-006-003 from the National Science Council, Taiwan. The authors would like to thank Miss Kai-Hsin Cheng for her excellent technical assistance in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YM.J., Ko, HC., Chang, FM. et al. Population-specific functional variant of the TPH2 gene 2755C>A polymorphism contributes risk association to major depression and anxiety in Chinese peripartum women. Arch Womens Ment Health 12, 401–408 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00737-009-0088-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00737-009-0088-z