Abstract
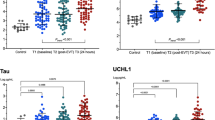
We developed a hollow fiber centrifugal ultrafiltration (HFCF-UF) method to study the change of plasma levels of free glycine (Gly) in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Twenty-four patients with AIS confirmed by diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) were enrolled. During the study period, the patients did not receive any supplemental amino acids therapy that could affect the obtained results. Our results showed that although AIS patients adopted different methods of treatment (thrombolytic and non-thrombolytic), the clinical NIHSS score of AIS showed a downward trend whereas Gly concentration showed increased trend. Moreover, plasma free Gly concentration was positively correlated with ASPECTS score. The correlation between Gly levels and infarct volume showed a statistical significance. That is to say, higher Gly level predicted smaller infarct size. Thus, the change of free Gly level in plasma could be considered as a potential biomarker of AIS.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Bhattacharyya S, Ghosh J, Sil PC (2012) Iron induces hepatocytes death via MAPK activation and mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway: Beneficial role of glycine. Free Radic Res 46(10):1296–1307. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2012.712690
Chen L, Zhang JQ, Li CH, Wang ZW, Li JJ, Zhao D et al (2018) Glycine Transporter-1 and glycine receptor mediate the antioxidant effect of glycine in diabetic rat islets and INS-1 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 123:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.05.007
Domingues DS, Crevelin EJ, Moraes LD, Hallak JEC, Crippa JAD, Queiroz MEC (2015) Simultaneous determination of amino acids and neurotransmitters in plasma samples from schizophrenic patients by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 38(5):780–787. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201400943
Dong WC, Guo JL, Wu XK, Zhao MQ, Li HR, Zhang ZQ et al (2021a) Relationship between the free and total methotrexate plasma concentration in children and application to predict the toxicity of HD-MTX. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.636975
Dong WC, Guo JL, Zhao MQ, Wu XK, Cui YX, Feng JY et al (2021b) A simple and accurate HFCF-UF method for the analysis of homocysteine, cysteine, cysteinyl-glycine, and glutathione in human blood. Anal Bioanal Chem 413(25):6225–6237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03578-z
Gao JL, Wang XY, An J, Du CH, Li MJ, Ma HY et al (2017) The significance of a new parameter-plasma protein binding in therapeutic drug monitoring and its application to carbamazepine in epileptic patients. RSC Adv 7(45):28048–28055. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra02991h
Han ML, Xie MY, Han J, Yuan DY, Yang T, Xie Y (2018) Development and validation of a rapid, selective, and sensitive LC–MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of d - and l -amino acids in human serum: application to the study of hepatocellular carcinoma. Anal Bioanal Chem 410(10):2517–2531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-0883-3
Hogeveen M, Blom HJ, Van AM, Boogmans B, Van BIM, Van DBM (2002) Hyperhomocysteinemia as risk factor for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in newborn infants. J Pediatr 141(3):429–431. https://doi.org/10.1067/mpd.2002.126598
Huang KJ, Yu S, Li J, Wu ZW, Wei CY (2012) Extraction of neurotransmitters from rat brain using graphene as a solid-phase sorbent, and their fluorescent detection by HPLC. Microchim Acta 176(3–4):327–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0719-8
Huang D, Jiang QS, Yang JQ, Yang JQ, Cui T, Wang NR et al (2018) Simultaneous determination of nine analytes related to the pathogenesis of diabetic encephalopathy in diabetic rat cortex and hippocampus by HPLC-FLD. Biomed Chromatogr. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.4338
Icme F, Erel O, Avci A, Satar S, Gulen M, Acehan S (2015) The relation between oxidative stress parameters, ischemic stroke, and hemorrhagic stroke. Turk J Med Sci 45(4):947–953. https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1402-96
Joyce R, Kuziene V, Zou X, Wang XT, Pullen F, Loo RL (2016) Development and validation of an ultra-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry method for rapid quantification of free amino acids in human urine. Amino Acids 48(1):219–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2076-0
Kazan RM, Seddik HA, Marstani ZM, Elsutohy MM, Yasri NG (2019) Determination of amino acids content in tea species using liquid chromatography via pre-column fluorescence derivatization. Microchem J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104103
Kumar P, Liu C, Suliburk JW, Minard CG, Muthupillai R, Chacko S et al (2020) Supplementing glycine and N-acetylcysteine (GlyNAC) in aging HIV patients improves oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, insulin resistance, genotoxicity, strength, and cognition: results of an open-label clinical trial. Biomedicines. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100390
Kumar P, Liu CW, Hsu JW, Chacko S, Minard C, Jahoor F et al (2021) Glycine and N-acetylcysteine (GlyNAC) supplementation in older adults improves glutathione deficiency, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, insulin resistance, endothelial dysfunction, genotoxicity, muscle strength, and cognition: Results of a pilot clinical trial. Clin Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.372
Li JM, Li C, Jiang Y, Ren SM (2010) Pretreatment of plasma samples by a novel hollow fiber centrifugal ultrafiltrate device for the determination of cefaclor concentrations in human plasma. J Chromatogr A 1217(44):6824–6828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.08.059
Li QZ, Huang QX, Li SC, Yang MZ, Rao B (2012) Simultaneous determination of glutamate, glycine, and alanine in human plasma using precolumn derivatization with 6-aminoquinolyl-n-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate and high-performance liquid chromatography. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 16(5):355–360. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.5.355
Li JM, Shi QW, Jiang Y, Liu Y (2015) Pretreatment of plasma samples by a novel hollow fiber centrifugal ultrafiltration technique for the determination of plasma protein binding of three coumarins using acetone as protein binding releasing agent. J Chromatogr B 1001:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.07.048
Lima JEBF, Moreira NCS, Sakamoto-Hojo ET (2022) Mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes: From risk factors to oxidative stress, metabolic dysfunction, and hyperglycemia. Mutat Res Genetic Toxicol Environ Mutagenesis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2021.503437
Liu LS (2019) 2018 Chinese guidelines for prevention and treatment of hypertension-a report of the revision committee of Chinese guidelines for prevention and treatment of hypertension. J Geriatr Cardiol 16(3):182. https://doi.org/10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2019.03.014
Liu R, Liao XY, Pan MX, Tang JC, Chen SF, Zhang Y et al (2019) Glycine exhibits neuroprotective effects in ischemic stroke in rats through the inhibition of M1 microglial polarization via the NF-κB p65/Hif-1α signaling pathway. J Immunol 202:1704–1714. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1801166
Lorenzano S, Rost NS, Khan M, Li H, Batista LM, Chutinet A et al (2019) Early molecular oxidative stress biomarkers of ischemic penumbra in acute stroke. Neurology 93(13):E1288–E1298. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000008158
Lorenzo MP, Villasenor A, Ramamoorthy A, Garcia A (2013) Optimization and validation of a capillary electrophoresis laser-induced fluorescence method for amino acids determination in human plasma: application to bipolar disorder study. Electrophoresis 34(11):1701–1709. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201200632
Lu Y, Zhang J, Ma BQ, Li KX, Li XY, Bai H et al (2012) Glycine attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis in mice. Neurochem Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.07.005
Lu YR, Fu XY, Shi LG, Jiang Y, Wu JL, Weng XJ et al (2014) Decreased plasma neuroactive amino acids and increased nitric oxide levels in melancholic major depressive disorder. BMC Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-244X-14-123
Mauriz JL, Matilla B, Culebras JM, Gonzalez P, Gonzalez-Gallego J (2001) Dietary glycine inhibits activation of nuclear factor kappa B and prevents liver injury in hemorrhagic shock in the rat. Free Radic Biol Med 31(10):1236–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00716-X
McTaggart RA, Jovin TG, Lansberg MG, Mlynash M, Jayaraman MV, Choudhri OA et al (2015) Alberta stroke program early computed tomographic scoring performance in a series of patients undergoing computed tomography and MRI: reader agreement, modality agreement, and outcome prediction. Stroke 46:407–412. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.006564
Mudiam MKR, Ratnasekhar C, Jain R, Saxena PN, Chauhan A, Murthy RC (2012) Rapid and simultaneous determination of twenty amino acids in complex biological and food samples by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry with the aid of experimental design after ethyl chloroformate derivatization. J Chromatogr B 907:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.08.035
Nassiri M, Hashemi S, Chabari A (2021) Modified vortex-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography for determination of amino acids in human plasma and seawater specimens. J Iran Chem Soc 18(11):3007–3016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-021-02246-4
Pal PB, Pal S, Das J, Sil PC (2012) Modulation of mercury-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis by glycine in hepatocytes. Amino Acids 42(5):1669–1683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0869-3
Pexman JH, Barber PA, Hill MD, Sevick RJ, Demchuk AM, Hudon ME et al (2001) Use of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) for assessing CT scans in patients with acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1534–1542
Poddar R (2021) Hyperhomocysteinemia is an emerging comorbidity in ischemic stroke. Exp Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113541
Puetz V, Khomenko A, Hill MD, Dzialowski I, Michel P, Weimar C et al (2008) Extent of hypoattenuation on CT angiography source images predicts functional outcome in patients with basilar artery occlusion. Stroke 39(9):2485–2490. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.511162
Razak MA, Begum PS, Viswanath B, Rajagopal S (2017) Multifarious beneficial effect of nonessential amino acid, glycine: a review. Oxid Med Cell Longev 5:5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1716701
Ren JX, Li C, Yan XL, Qu Y, Yang Y, Guo ZN (2021) Crosstalk between oxidative stress and ferroptosis/oxytosis in ischemic stroke: possible targets and molecular mechanisms. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6643382
Richard YD, Macdonald PE (2020) Impaired “Glycine”-mia in type 2 diabetes and potential mechanisms contributing to glucose homeostasis. Endocrinology 158(5):1064–1073. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2017-00148
Saylan M, Er EO, Tekin Z, Bakirdere S (2020) An accurate and sensitive analytical method for the simultaneous determination of glycine, methionine and homocysteine in biological matrices by matrix matching strategy and LC–quadrupole-time-of-flight-MS/MS. Spectrochim Acta Part A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118394
Sekhar RV, McKay SV, Patel SG, Guthikonda AP, Reddy VT, Balasubramanyam A et al (2011) Glutathione synthesis is diminished in patients with uncontrolled diabetes and restored by dietary supplementation with cysteine and glycine. Diabetes Care 34(1):162–167. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-1006
Sun N, Wu YJ, Zhao LB, He H, Mei D, Zhang SY et al (2019) A rapid and sensitive HPLC-MS/MS method for determination of endogenous creatine biosynthesis precursors in plasma of children with viral myocarditis. J Chromatogr B 1118:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.04.014
Szpetnar M, Hordyjewska A, Malinowska I, Golab P, Kurzepa J (2016) The fluctuation of free amino acids in serum during acute ischemic stroke. Curr Issues Pharm Med Sci 29(4):151–154. https://doi.org/10.1515/cipms-2016-0031
Tamashima E, Hayama T, Yoshida H, Imakyure O, Yamaguchi M, Nohta H (2015) Direct tandem mass spectrometric analysis of amino acids in plasma using fluorous derivatization and monolithic solid-phase purification. J Pharm Biomed Anal 115:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2015.07.008
Tekin Z, Er EO, Bakirdere S (2019) Determination of glycine in body fluids at trace levels using the combination of quadrupole isotope dilution strategy and Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Time of Flight-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Measurement 146:606–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.07.006
Tessari P, Cecchet D, Cosma A, Puricelli L, Millioni R, Vedovato M et al (2011) Insulin resistance of amino acid and protein metabolism in type 2 diabetes. Clin Nutr 30(3):267–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2011.02.009
Topcuoglu MA, Demirkaya S (2000) Low plasma antioxidant activity is associated with high lesion volume and neurological impairment in stroke. Stroke 31(1):33–39. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.31.1.33
Wang WW, Wu ZL, Lin G, Hu SD, Wang B, Dai ZL et al (2014) Glycine stimulates protein synthesis and inhibits oxidative stress in pig small intestinal epithelial cells. J Nutr 144(10):1540–1548. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.114.194001
Wang XY, Li C, Du CH, Gao JL, Zhao KX, Shi R et al (2017) Plasma protein binding monitoring of therapeutic drugs in patients using single set of hollow fiber centrifugal ultrafiltration. Bioanalysis 9(7):579–592. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio-2016-0257
Wang CY, Yu JJ, Zhang RH, Wang WT, Shi ZY, Liu Y et al (2020a) Small intestine proteomics coupled with serum metabolomics reveal disruption of amino acid metabolism in Chinese hamsters with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Proteom. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2020.103823
Wang JG, Chia YC, Chen CH, Park S, Hoshide S, Tomitani N et al (2020b) What is new in the 2018 Chinese hypertension guideline and the implication for the management of hypertension in Asia? J Clin Hypertens 22(3):363–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.13803
Wang SY, Li M, Lin H, Wang GX, Xu Y, Zhao XJ et al (2022) Amino acids, microbiota-related metabolites, and the risk of incident diabetes among normoglycemic Chinese adults: Findings from the 4C study. Cell reports. Medicine 3(9):1027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100727
Wen YQ, Yuan XM, Qin F, Zhao LS, Xiong ZL (2019) Development and validation of a hydrophilic interaction ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for rapid simultaneous determination of 19 free amino acids in rat plasma and urine. Biomed Chromatogr. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.4387
Xie Y, Li ZN (2015) Determination of 18 types of amino acids in the serum of ischemic stroke patients by high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector derivatized with 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate. Cell Biochem Biophys 73(1):111–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0648-y
Xu WH, Zhong CC, Zou CP, Wang B, Zhang N (2020) Analytical methods for amino acid determination in organisms. Amino Acids 52(8):1071–1088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-020-02884-7
Zare F, Ghaedi M, Jannesar R, Tayebi L (2018) Switchable polarity solvents for preconcentration and simultaneous determination of amino acids in human plasma samples. New J Chem 42(12):10007–10015. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj04576j
Zhang L, Zhang ZQ, Dong WC, Jing SJ, Zhang JF, Jiang Y (2013) Accuracy assessment on the analysis of unbound drug in plasma by comparing traditional centrifugal ultrafiltration with hollow fiber centrifugal ultrafiltration and application in pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr A 1318:265–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.09.078
Zhang JF, Yang XL, Zhang ZQ, Dong WC, Jiang Y (2014) Accuracy of the analysis of free vancomycin concentration by ultrafiltration in various disease states. RSC Adv 4(76):40214–40222. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra06575a
Zhao XJ, Wang N, Zhang MJ, Liu SS, Yu H, Tang MH et al (2020) Simultaneous determination of five amino acid neurotransmitters in rat and porcine blood and brain by two-dimensional liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122507
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province [grant numbers H2021206299].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study conception and design, acquisition of data, and first draft of the manuscript were performed by HW. The authors XN and WD helped in the acquisition of data, material preparation, respectively. WQ and LX helped in the collection of clinical plasma sample. YJ and LX are responsible for the guidance of the method part and the clinical part, respectively. All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflict of interest among any of the authors related to this manuscript.
Ethical statement
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, in accordance with the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki. Written consent was obtained from all the patients. Research Ethics Committee Ethical Approval number: 2022-R318.
Additional information
Handling editor: T. Bohn.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Ni, X., Dong, W. et al. Accurately quantified plasma free glycine concentration as a biomarker in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Amino Acids 55, 385–402 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03236-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03236-x