Abstract
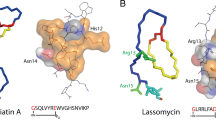
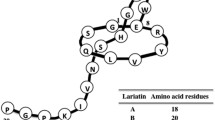
Lasso peptide belongs to a new class of natural product with highly compact and stable structure. It has varieties of biological activities, among which the most important one is its antibacterial efficacy. Novel lasso peptides have been constantly discovered and analyzed by advanced techniques, and the biosynthesis or even chemical synthesis of lasso peptide has been studied after learning its constituent amino acids and maturation process. Structural identification of lasso peptide provides information for elucidating the mechanisms of its antibacterial activity and basis for further modifications. Ring of lasso peptide is the key to both its highly compact and stable structure and its intrinsic antibacterial property. The loop has been considered as suitable modification region of lasso peptide, such as V11–S18 of MccJ25 being modifiable without disrupting the lasso structure in biosynthesis. The tail is the immunity protein that can export lasso peptide out of its produced strain and serve as a self-protection mechanism at the same time. Most of currently known lasso peptides are non-pathogenic, which implies that the modified lasso peptides are promising candidates for medical applications. Arginine, glycine, and aspartic acid as a ligands of cancer-specific receptor have been grafted to the loop of lasso peptide without losing its bioactivity, and many other targets are expected to be used for lasso peptide modification. Multi-molecular modification and large-scale production need to be studied and solved in future for designing and using multifunctional lasso peptide based on its extraordinary stable structure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnison PG, Bibb MJ, Bierbaum G, Bowers AA, Bugni TS, Bulaj G, Camarero JA, Campopiano DJ, Challis GL, Clardy J, Cotter PD, Craik DJ, Dawson M, Dittmann E, Donadio S, Dorrestein PC, Entian K-D, Fischbach MA, Garavelli JS, Göransson U, Gruber CW, Haft DH, Hemscheidt TK, Hertweck C, Hill C, Horswill AR, Jaspars M, Kelly WL, Klinman JP, Kuipers OP, Link AJ, Liu W, Marahiel MA, Mitchell DA, Moll GN, Moore BS, Müller R, Nair SK, Nes IF, Norris GE, Olivera BM, Onaka H, Patchett ML, Piel J, Reaney MJT, Rebuffat S, Ross RP, Sahl H-G, Schmidt EW, Selsted ME, Severinov K, Shen B, Sivonen K, Smith L, Stein T, Süssmuth RD, Tagg JR, Tang G-L, Truman AW, Vederas JC, Walsh CT, Walton JD, Wenzel SC, Willey JM, van der Donk WA (2013) Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural products: overview and recommendations for a universal nomenclature. Nat Prod Rep 30(1):108–160
Bagley MC, Dale JW, Merritt EA, Xiong X (2005) Thiopeptide antibiotics. Chem Rev 105(2):685–714
Bellomio A, Rintoul MaR, Morero RD (2003) Chemical modification of microcin J25 with diethylpyrocarbonate and carbodiimide: evidence for essential histidyl and carboxyl residues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303(2):458–462
Bierbaum G, Jansen A (2007) Tying the knot: making of lasso peptides. Chem Biol 14(7):734–735
Chalon MC, Bellomio A, Solbiati JO, Morero RD, Farias RN, Vincent PA (2009) Tyrosine 9 is the key amino acid in microcin J25 superoxide overproduction. FEMS Microbiol Lett 300(1):90–96
Chalón MC, Wilke N, Pedersen J, Rufini S, Morero RD, Cortez L, Chehín RN, Farias RN, Vincent PA (2011) Redox-active tyrosine residue in the microcin J25 molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 406(3):366–370
Cheung WL, Pan SJ, Link AJ (2010) Much of the microcin J25 leader peptide is dispensable. J Am Chem Soc 132(8):2514–2515
Choudhury HG, Tong Z, Mathavan I, Li Y, Iwata S, Zirah S, Rebuffat S, van Veen HW, Beis K (2014) Structure of an antibacterial peptide ATP-binding cassette transporter in a novel outward occluded state. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(25):9145–9150
Clarke DJ, Campopiano DJ (2007) Maturation of McjA precursor peptide into active microcin MccJ25. Org Biomol Chem 5(16):2564–2566
Constantine KL, Friedrichs MS, Detlefsen D, Nishio M, Tsunakawa M, Furumai T, Ohkuma H, Oki T, Hill S, Bruccoleri RE (1995) High-resolution solution structure of siamycin II: novel amphipathic character of a 21-residue peptide that inhibits HIV fusion. J Biomol NMR 5(3):271–286
Cook N, Brais R, Qian W, Hak CCW, Corrie PG (2015) Endothelin-1 and endothelin B receptor expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Pathol 68(4):309–313
Destoumieux-Garzón D, Peduzzi J, Rebuffat S (2002) Focus on modified microcins: structural features and mechanisms of action. Biochimie 84(5–6):511–519
Destoumieux-Garzón D, Duquesne S, Peduzzi J, Goulard C, Desmadril M, Letellier L, Rebuffat S, Boulanger P (2005) The iron-siderophore transporter FhuA is the receptor for the antimicrobial peptide microcin J25: role of the microcin Val11–Pro16 β-hairpin region in the recognition mechanism. Biochem J 389(3):869–876
Douglas GP, Annika W, Keishi I, Christian H, Elke D (2014) Functional analysis of environmental DNA-derived microviridins provides new insights into the diversity of the tricyclic peptide family. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(4):1380–1387
Ducasse R, Yan K-P, Goulard C, Blond A, Li Y, Lescop E, Guittet E, Rebuffat S, Zirah S (2012) Sequence determinants governing the topology and biological activity of a lasso peptide, microcin J25. ChemBioChem 13(3):371–380
Duquesne S, Destoumieux-Garzón D, Zirah S, Goulard C, Peduzzi J, Rebuffat S (2007a) Two enzymes catalyze the maturation of a lasso peptide in Escherichia coli. Chem Biol 14(7):793–803
Duquesne S, Destoumieux-Garzon D, Peduzzi J, Rebuffat S (2007b) Microcins, gene-encoded antibacterial peptides from enterobacteria. Nat Prod Rep 24(4):708–734
Elsayed SS, Trusch F, Deng H, Raab A, Prokes I, Busarakam K, Asenjo JA, Andrews BA, van West P, Bull AT, Goodfellow M, Yi Y, Ebel R, Jaspars M, Rateb ME (2015) Chaxapeptin, a lasso peptide from extremotolerant Streptomyces leeuwenhoekii strain C58 from the hyperarid atacama desert. J Org Chem 80(20):10252–10260
Foubert P, Varner J (2012) Integrins in tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. In: Shimaoka M (ed) Integrin and cell adhesion molecules. Methods in molecular biology, vol 757. Humana Press, New York, pp 471–486
Frechet D, Guitton JD, Herman F, Faucher D, Helynck G, Monegier du Sorbier B, Ridoux JP, James-Surcouf E, Vuilhorgne M (1994) Solution structure of RP 71955, a new 21 amino acid tricyclic peptide active against HIV-1 virus. Biochemistry 33(1):42–50
Gu R-X, Corradi V, Singh G, Beis K, Tieleman P (2015) Conformational changes of the ABC transporter McjD revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. Biophysical Journal 108(2, Supplement 1):89a
Hammami R, Bédard F, Gomaa A, Subirade M, Biron E, Fliss I (2015) Lasso-inspired peptides with distinct antibacterial mechanisms. Amino Acids 47(2):417–428
Hegemann JD, Zimmermann M, Xie X, Marahiel MA (2013) Caulosegnins I–III: a highly diverse group of lasso peptides derived from a single biosynthetic gene cluster. J Am Chem Soc 135(1):210–222
Hegemann JD, De Simone M, Zimmermann M, Knappe TA, Xie X, Di Leva FS, Marinelli L, Novellino E, Zahler S, Kessler H, Marahiel MA (2014a) Rational improvement of the affinity and selectivity of integrin binding of grafted lasso peptides. J Med Chem 57(13):5829–5834
Hegemann JD, Zimmermann M, Zhu S, Steuber H, Harms K, Xie X, Marahiel MA (2014b) Xanthomonins I–III: a new class of lasso peptides with a seven-residue macrolactam ring. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53(8):2230–2234
Hinz A, Tampé R (2012) ABC transporters and immunity: mechanism of self-defense. Biochemistry 51(25):4981–4989
Inokoshi J, Matsuhama M, Miyake M, Ikeda H, Tomoda H (2012) Molecular cloning of the gene cluster for lariatin biosynthesis of Rhodococcus jostii K01–B0171. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(2):451–460
Iwatsuki M, Tomoda H, Uchida R, Gouda H, Hirono S, Ōmura S (2006) Lariatins, antimycobacterial peptides produced by Rhodococcus sp. K01–B0171, have a lasso structure. J Am Chem Soc 128(23):7486–7491
Iwatsuki M, Uchida R, Takakusagi Y, Matsumoto A, Cheng-Lin J, Takahashi Y, Arai M, Kobayashi S, Matsumoto M, Inokoshi J, Tomoda H, Omura S (2007) Lariatins, novel anti-mycobacterial peptides with a lasso structure, produced by Rhodococcus jostii K01–B0171. J Antibiot 60(6):357–363
Iwatsuki M, Koizumi Y, Gouda H, Hirono S, Tomoda H, Ōmura S (2009) Lys17 in the ‘lasso’ peptide lariatin A is responsible for anti-mycobacterial activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19(10):2888–2890
Katahira R, Shibata K, Yamasaki M, Matsuda Y, Yoshida M (1995) Solution structure of endothelin B receptor selective antagonist RES-701-1 determined by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Bioorg Med Chem 3(9):1273–1280
Katahira R, Yamasaki M, Matsuda Y, Yoshida M (1996) MS-271, a novel inhibitor of calmodulin-activated myosin light chain kinase from Streptomyces sp. II. Solution structure of MS-271: characteristic features of the “lasso’ structure. Bioorg Med Chem 4(1):121–129
Kersten RD, Yang YL, Xu Y, Cimermancic P, Nam SJ, Fenical W, Fischbach MA, Moore BS, Dorrestein PC (2011) A mass spectrometry-guided genome mining approach for natural product peptidogenomics. Nat Chem Biol 7(11):794–802
Kimura K-I, Yamazaki M, Sasaki N, Yamashita T, Negishi S, Nakamura T, Koshino H (2007) Novel propeptin analog, propeptin-2, missing two amino acid residues from the propeptin C terminus loses antibiotic potency. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 60(8):519–523
Kimura K, Kanou F, Takahashi H, Esumi Y, Uramoto M, Yoshihama M (1997) Propeptin, a new inhibitor of prolyl endopeptidase produced by Microbispora. I. Fermentation, isolation and biological properties. J Antibiot 50(5):373–378
Knappe TA, Linne U, Zirah S, Rebuffat S, Xie X, Marahiel MA (2008) Isolation and structural characterization of capistruin, a lasso peptide predicted from the genome sequence of Burkholderia thailandensis E264. J Am Chem Soc 130(34):11446–11454
Knappe TA, Linne U, Robbel L, Marahiel MA (2009) Insights into the biosynthesis and stability of the lasso peptide capistruin. Chem Biol 16(12):1290–1298
Knappe TA, Linne U, Xie X, Marahiel MA (2010) The glucagon receptor antagonist BI-32169 constitutes a new class of lasso peptides. FEBS Lett 584(4):785–789
Knappe TA, Manzenrieder F, Mas-Moruno C, Linne U, Sasse F, Kessler H, Xie X, Marahiel MA (2011) Introducing lasso peptides as molecular scaffolds for drug design: engineering of an integrin antagonist. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(37):8714–8717
Li Y, Ducasse R, Zirah S, Blond A, Goulard C, Lescop E, Giraud C, Hartke A, Guittet E, Pernodet J-L, Rebuffat S (2015a) Characterization of Sviceucin from Streptomyces provides insight into enzyme exchangeability and disulfide bond formation in lasso peptides. ACS Chem Biol 10(11):2641–2649
Li Y, Zirah S, Rebuffat S (2015b) Lasso peptides. Springerbriefs in microbiology
Liu Z, Yu L, Wang X, Zhang X, Liu M, Zeng W (2016) Integrin (αvβ3) targeted RGD peptide based probe for cancer optical imaging. Curr Protein Pept Sci
Makarova KS, Aravind L, Koonin EV (1999) A superfamily of archaeal, bacterial, and eukaryotic proteins homologous to animal transglutaminases. Protein Sci Publ Protein Soc 8(8):1714–1719
Maksimov MO, Link AJ (2013) Discovery and characterization of an isopeptidase that linearizes lasso peptides. J Am Chem Soc 135(32):12038–12047
Maksimov MO, Link AJ (2014) Prospecting genomes for lasso peptides. J Ind Microbiol 41(2):333–344
Maksimov MO, Pan SJ, James Link A (2012a) Lasso peptides: structure, function, biosynthesis, and engineering. Nat Prod Rep 29(9):996–1006
Maksimov MO, Pelczer I, Link AJ (2012b) Precursor-centric genome-mining approach for lasso peptide discovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(38):15223–15228
Rintoul MaR, de Arcuri BF, Salomón RA, Farı́as RN, Morero RD (2001) The antibacterial action of microcin J25: evidence for disruption of cytoplasmic membrane energization in Salmonella newport. FEMS Microbiol Lett 204(2):265–270
Mathavan I, Zirah S, Mehmood S, Choudhury HG, Goulard C, Li Y, Robinson CV, Rebuffat S, Beis K (2014) Structural basis for hijacking siderophore receptors by antimicrobial lasso peptides. Nat Chem Biol 10(5):340–342
Metelev M, Tietz JI, Melby JO, Blair PM, Zhu L, Livnat I, Severinov K, Mitchell DA (2015) Structure, bioactivity, and resistance mechanism of streptomonomicin, an unusual lasso peptide from an understudied halophilic actinomycete. Chem Biol 22(2):241–250
Meyer A, Auernheimer J, Modlinger A, Kessler H (2006) Targeting RGD recognizing integrins: drug development, biomaterial research, tumor imaging and targeting. Curr Pharm Des 12(22):2723–2747
Pan SJ, Link AJ (2011) Sequence diversity in the lasso peptide framework: discovery of functional microcin J25 variants with multiple amino acid substitutions. J Am Chem Soc 133(13):5016–5023
Pan SJ, Cheung WL, Link AJ (2010) Engineered gene clusters for the production of the antimicrobial peptide microcin J25. Protein Expr Purif 71(2):200–206
Pan SJ, Rajniak J, Cheung WL, Link AJ (2012a) Construction of a single polypeptide that matures and exports the lasso peptide microcin J25. ChemBioChem 13(3):367–370
Pan SJ, Rajniak J, Maksimov MO, Link AJ (2012b) The role of a conserved threonine residue in the leader peptide of lasso peptide precursors. Chem Commun 48(13):1880–1882
Pavlova O, Mukhopadhyay J, Sineva E, Ebright RH, Severinov K (2008) Systematic structure–activity analysis of microcin J25. J Biol Chem 283(37):25589–25595
Potterat O, Stephan H, Metzger JW, Gnau V, Zähner H, Jung G (1994) Aborycin—a tricyclic 21-peptide antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces griseoflavus. Eur J Org Chem 7:741–743
Salomón RA, Farías RN (1992) Microcin 25, a novel antimicrobial peptide produced by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 174(22):7428–7435
Shibata K, Suzawa T, Ohno T, Yamada K, Tanaka T, Tsukuda E, Matsuda Y, Yamasaki M (1998) Hybrid peptides constructed from RES-701-1, an endothelin B receptor antagonist, and endothelin; binding selectivity for endothelin receptors and their pharmacological activity. Bioorg Med Chem 6(12):2459–2467
Shibata K, Suzawa T, Soga S, Mizukami T, Yamada K, Hanai N, Yamasaki M (2003) Improvement of biological activity and proteolytic stability of peptides by coupling with a cyclic peptide. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13(15):2583–2586
Soohyun U, Young-Joo K, Hyuknam K, He W, Seong-Hwan K, Hak Cheol K, Sunghyouk P, Jongheon S, Dong-Chan O (2013) Sungsanpin, a Lasso Peptide from a Deep-Sea Streptomycete. J Nat Prod 76(5):873–879
Soudy R, Wang L, Kaur K (2012) Synthetic peptides derived from the sequence of a lasso peptide microcin J25 show antibacterial activity. Bioorg Med Chem 20(5):1794–1800
Tarling EJ, Vallim TQdA, Edwards PA (2013) Role of ABC transporters in lipid transport and human disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab 24(7):342–350
Valiante V, Monteiro MC, Martín J, Altwasser R, El Aouad N, González I, Kniemeyer O, Mellado E, Palomo S, de Pedro N, Pérez-Victoria I, Tormo JR, Vicente F, Reyes F, Genilloud O, Brakhage AA (2015) Hitting the caspofungin salvage pathway of human-pathogenic fungi with the novel lasso peptide humidimycin (MDN-0010). Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59(9):5145–5153
Vincent PA, Morero RD (2009) The structure and biological aspects of peptide antibiotic microcin J25. Curr Med Chem 16(5):538
Vincent PA, Bellomio A, de Arcuri BF, Farías RN, Morero RD (2005) MccJ25 C-terminal is involved in RNA-polymerase inhibition but not in respiration inhibition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331(2):549–551
Weber W, Fischli W, Hochuli E, Kupfer E, Weibel EK (1991) Anantin—a peptide antagonist of the atrial natriuretic factor(ANF). I. Producing organism, fermentation, isolation and biological activity: I. Producing organism, fermentation, isolation and biological activity. Jpn J Antibiot 44(2):164–171
Willey JM, van der Donk WA (2007) Lantibiotics: peptides of diverse structure and function. Annu Rev Microbiol 61(1):477–501
Wilson K-A, Kalkum M, Ottesen J, Yuzenkova J, Chait BT, Landick R, Muir T, Severinov K, Darst SA (2003) Structure of microcin J25, a peptide inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase, is a lassoed tail. J Am Chem Soc 125(41):12475–12483
Wyss DF, Lahm HW, Manneberg M, Labhardt AM (1991) Anantin--a peptide antagonist of the atrial natriuretic factor (ANF). II. Determination of the primary sequence by NMR on the basis of proton assignments. J Antibiot 44(2):172–180
Xavier T, Delphine DG, Jean P, Carlos A, Alain B, Nicolas B, Christophe G, Lionel D, Robert T, Jean-Claude T (2004) Siderophore peptide, a new type of post-translationally modified antibacterial peptide with potent activity. J Biol Chem 279(27):28233–28242
Yan K, Phen Li Y, Zirah S, Goulard C, Knappe TA, Marahiel MA, Rebuffat S (2012) Dissecting the maturation steps of the lasso peptide microcin J25 in vitro. ChemBioChem 13(7):1046–1052
Yano K, Toki S, Nakanishi S, Ochiai K, Ando K, Yoshida M, Matsuda Y, Yamasaki M (1996) MS-271, a novel inhibitor of calmodulin-activated myosin light chain kinase from Streptomyces sp.—I. isolation, structural determination and biological properties of MS-271. Bioorg Med Chem 4(1):115–120
Yasuaki E, Yoshikatsu S, Yumiko I, Masakazu U, Ken-Ichi K, Masaaki G, Makoto Y, Teruo I (2002) Propeptin, a new inhibitor of prolyl endopeptidase produced by microbispora II. Determination of chemical structure. J Antibiot 55(3):296–300
Yee VC, Pedersen LC, Le Trong I, Bishop PD, Stenkamp RE, Teller DC (1994) Three-dimensional structure of a transglutaminase: human blood coagulation factor XIII. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(15):7296–7300
Ziemert N, Ishida K, Liaimer A, Hertweck C, Dittmann E (2008) Ribosomal synthesis of tricyclic depsipeptides in bloom-forming cyanobacteria. Angew Chem Int Ed 47(40):7756–7759
Zimmermann M, Hegemann Julian D, Xie X, Marahiel Mohamed A (2013) The Astexin-1 lasso peptides: biosynthesis, stability, and structural studies. Chem Biol 20(4):558–569
Zimmermann M, Hegemann JD, Xie X, Marahiel MA (2014) Characterization of caulonodin lasso peptides revealed unprecedented N-terminal residues and a precursor motif essential for peptide maturation. Chem Sci 5(10):4032–4043
Zong C, Maksimov MO, Link AJ (2016) Construction of lasso peptide fusion proteins. Acs Chem Biol 11(1):61–68
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities of China (N142003001, N130520001), the Natural Science Foundation of China (81201141), and the Office of Science (BER), US Department of Energy (DE-SC0008397).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with animal and human subjects performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Not available since no human study was involved.
Additional information
Handling Editor: M. S. Palma.
N. Zhao and Y. Pan contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, N., Pan, Y., Cheng, Z. et al. Lasso peptide, a highly stable structure and designable multifunctional backbone. Amino Acids 48, 1347–1356 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2228-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2228-x