Abstract
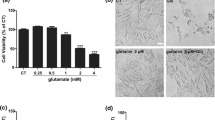
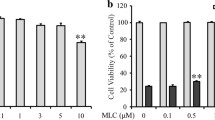
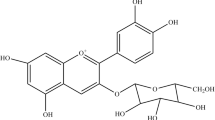
Neuronal cell death caused by oxidative stress is common in a variety of neural diseases and can be investigated in detail in cultured HT22 neuronal cells, where the amino acid glutamate at high concentrations causes glutathione depletion by inhibition of the glutamate/cystine antiporter system, intracellular accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and eventually oxidative stress-induced neuronal cell death. Using this paradigm, we have previously reported that resveratrol (3,5,4′-trans-trihydroxystilbene) protects HT22 neuronal cells from glutamate-induced oxidative stress by inducing heme oxygenase (HO)-1 expression. Piceatannol (3,5,4′,3′-trans-trihydroxystilbene), which is a hydroxylated resveratrol analog and one of the resveratrol metabolites, is estimated to exert neuroprotective effect similar to that of resveratrol. The aim of this study, thus, is to determine whether piceatannol, similarly to resveratrol, would protect HT22 neuronal cells from glutamate-induced oxidative stress. Glutamate at high concentrations induced neuronal cell death and ROS formation. Piceatannol reduced glutamate-induced cell death and ROS formation. The observed cytoprotective effect was much higher when HT22 neuronal cells were pretreated with piceatannol for 6 or 12 h prior to glutamate treatment than when pretreated for 0.5 h. Piceatannol also increased HO-1 expression and HO activity via its activation of nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). Interestingly, neuroprotective effect of piceatannol was partly (but not completely) abolished by either down-regulation of HO-1 expression or blockage of HO-1 activity. Taken together, our results suggest that piceatannol, similar to resveratrol, is capable of protecting HT22 neuronal cells against glutamate-induced cell death, at least in part, by inducing Nrf2-dependent HO-1 expression.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant responsive element
- DCF-DA:
-
2′,7′-Dichlorofluorescein diacetate
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- Glu:
-
Glutamate
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear transcription factor-E2-related factor 2
- OD:
-
Optical density
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- Pic:
-
Piceatannol
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- SnPP:
-
Tin protoporphyrin IX (SnPP)
- RuCO:
-
Tricarbonyldichlororuthenium-(II)-dimer
References
Albani D, Polito L, Batelli S, De Mauro S, Fracasso C, Martelli G, Colombo L, Manzoni C, Salmona M, Caccia S, Negro A, Forloni G (2009) The SIRT1 activator resveratrol protects SK-N-BE cells from oxidative stress and against toxicity caused by alpha-synuclein or amyloid-beta (1–42) peptide. J Neurochem 110:1445–1456
Albani D, Polito L, Signorini A, Forloni G (2010) Neuroprotective properties of resveratrol in different neurodegenerative disorders. BioFactors 36:370–376
Amri A, Chaumeil JC, Sfar S, Charrueau C (2012) Administration of resveratrol: what formulation solutions to bioavailability limitations? J Control Release 158:182–193
Bastianetto S, Dumont Y, Han Y, Quirion R (2009) Comparative neuroprotective properties of stilbene and catechin analogs: action via a plasma membrane receptor site? CNS Neurosci Ther 15:76–83
Billack B, Radkar V, Adiabouah C (2008) In vitro evaluation of the cytotoxic and anti-proliferative properties of resveratrol and several of its analogs. Cell Mol Biol Lett 13:553–569
Chowdhury SA, Kishino K, Satoh R, Hashimoto K, Kikuchi H, Nishikawa H, Shirataki Y, Sakagami H (2005) Tumor-specificity and apoptosis-inducing activity of stilbenes and flavonoids. Anticancer Res 25:2055–2063
Eghwrudjakpor PO, Allison AB (2010) Oxidative stress following traumatic brain injury: enhancement of endogenous antioxidant defense systems and the promise of improved outcome. Niger J Med 19:14–21
Esposito E, Cuzzocrea S (2010) New therapeutic strategy for Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Med Chem 17:2764–2774
Frombaum M, Therond P, Djelidi R, Beaudeux JL, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Borderie D (2011) Piceatannol is more effective than resveratrol in restoring endothelial cell dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase expression and activity after high-glucose oxidative stress. Free Radic Res 45:293–302
Fukui M, Choi HJ, Zhu BT (2010) Mechanism for the protective effect of resveratrol against oxidative stress-induced neuronal death. Free Radic Biol Med 49:800–813
Jazwa A, Cuadrado A (2010) Targeting heme oxygenase-1 for neuroprotection and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Drug Targets 11:1517–1531
Jellinger KA (2009) Recent advances in our understanding of neurodegeneration. J Neural Transm 116:1111–1162
Jomova K, Vondrakova D, Lawson M, Valko M (2010) Metals, oxidative stress and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Cell Biochem 345:91–104
Kaplan S, Bisleri G, Morgan JA, Cheema FH, Oz MC (2005) Resveratrol, a natural red wine polyphenol, reduces ischemia–reperfusion-induced spinal cord injury. Ann Thorac Surg 80:2242–2249
Kelsey NA, Wilkins HM, Linseman DA (2010) Nutraceutical antioxidants as novel neuroprotective agents. Molecules 15:7792–7814
Kim HP, Pae HO, Back SH, Chung SW, Woo JM, Son Y, Chung HT (2011) Heme oxygenase-1 comes back to endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404:1–5
Kim DW, Kim YM, Kang SD, Han YM, Pae HO (2012) Effects of resveratrol and trans-3,5,4’-trimethoxystilbene on glutamate-induced cytotoxicity, heme oxygenase-1, and sirtuin 1 in HT22 neuronal cells. Biomol Ther 20:306–312
Lee HH, Park SA, Almazari I, Kim EH, Na HK, Surh YJ (2010) Piceatannol induces heme oxygenase-1 expression in human mammary epithelial cells through activation of ARE-driven Nrf2 signaling. Arch Biochem Biophys 501:142–150
Li F, Gong Q, Dong H, Shi J (2012) Resveratrol, a neuroprotective supplement for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 18:27–33
Marambaud P, Zhao H, Davies P (2005) Resveratrol promotes clearance of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta peptides. J Biol Chem 280:37377–37382
Morimoto BH, Koshland DE Jr (1990) Induction and expression of long- and short-term neurosecretory potentiation in a neural cell line. Neuron 5:875–880
Pae HO, Kim EC, Chung HT (2008) Integrative survival response evoked by heme oxygenase-1 and heme metabolites. J Clin Biochem Nutr 42:197–203
Pae HO, Son Y, Kim NH, Jeong HJ, Chang KC, Chung HT (2010) Role of heme oxygenase in preserving vascular bioactive NO. Nitric Oxide 23:251–257
Panickar KS, Anderson RA (2011) Effect of polyphenols on oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in neuronal death and brain edema in cerebral ischemia. Int J Mol Sci 12:8181–8207
Piotrowska H, Kucinska M, Murias M (2012) Biological activity of piceatannol: leaving the shadow of resveratrol. Mutat Res 750:60–82
Raval AP, Dave KR, Pérez-Pinzón MA (2006) Resveratrol mimics ischemic preconditioning in the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1141–1147
Richard T, Pawlus AD, Iglésias ML, Pedrot E, Waffo-Teguo P, Mérillon JM, Monti JP (2011) Neuroprotective properties of resveratrol and derivatives. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1215:103–108
Robb EL, Stuart JA (2010) Trans-resveratrol as a neuroprotectant. Molecules 15:1196–1212
Roupe KA, Yáñez JA, Teng XW, Davies NM (2006) Pharmacokinetics of selected stilbenes. Rhapontigenin, piceatannol, and pinosylvin in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 58:1443–1450
Sakata Y, Zhuang H, Kwansa H, Koehler RC, Doré S (2010) Resveratrol protects against experimental stroke: putative neuroprotective role of heme oxygenase 1. Exp Neurol 224:325–329
Sun AY, Wang Q, Simonyi A, Sun GY (2010) Resveratrol as a therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol 41:375–383
Tan JW, Tham CL, Israf DA, Lee SH, Kim MK (2013) Neuroprotective effects of biochanin a against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells via apoptosis inhibition. Neurochem Res 38:512–518
Wung BS, Hsu MC, Wu CC, Hsieh CW (2006) Piceatannol upregulates endothelial heme oxygenase-1 expression via novel protein kinase C and tyrosine kinase pathways. Pharmacol Res 53:113–122
Yang H, Sung SH, Kim J, Kim YC (2011) Neuroprotective diarylheptanoids from the leaves and twigs of Juglans sinensis against glutamate-induced toxicity in HT22 cells. Planta Med 77:841–845
Yu C, Shin YG, Chow A, Li Y, Kosmeder JW, Lee YS, Hirschelman WH, Pezzuto JM, Mehta RG, van Breemen RB (2002) Human, rat, and mouse metabolism of resveratrol. Pharm Res 19:1907–1914
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. 2011-0030717).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, Y., Byun, S.J. & Pae, HO. Involvement of heme oxygenase-1 expression in neuroprotection by piceatannol, a natural analog and a metabolite of resveratrol, against glutamate-mediated oxidative injury in HT22 neuronal cells. Amino Acids 45, 393–401 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1518-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1518-9