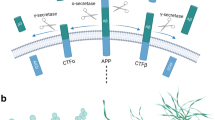
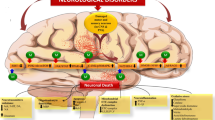
Abstract
In the present era, investigators seek to find therapeutic interventions that are multifaceted in their mode of action. Such targets provide the most advantageous routes for addressing the multiplicity of pathophysiological avenues that lead to neuronal dysfunction and death observed in neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. Taurine, an endogenous amino acid, exhibits a plethora of physiological functions in the central nervous system. In this review, we describe the mode of action of taurine and its clinical application in the neurological diseases: Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albin RL, Greenamyre JT (1992) Alternative excitotoxic hypotheses. Neurology 42:733–738
Albin RL, Young AB, Penney JB (1989) The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci 12:366–375
Albrecht J, Schousboe A (2005) Taurine interaction with neurotransmitter receptors in the CNS: an update. Neurochem Res 30:1615–1621
Alexander GE, Crutcher ME (1990) Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci 13:266–271
Alom J, Mahy JN, Brandi N, Tolosa E (1991) Cerebrospinal fluid taurine in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 30:735
Alzheimer’s disease Education and Referral Center Web site. Alzheimer’s disease-unraveling the mystery. http://www.nia.nih.gov/alzheimers/publication/alzheimers-disease-unraveling-mystery/preface
Alzheimer A (1907) A characteristic disease of the cerebral cortex. In: Bick K, Amaducci L, Pepeu G (eds) The early story of Alzheimer’s disease. Liviana Press, Padova, pp 1–3
Andrew SE, Goldberg YP, Kremer B, Telenius H, Theilmann J, Adam S, Starr E, Squitieri F, Lin B, Kalchman MA (1993) The relationship between trinucleotide (CAG) repeat length and clinical features of Huntington’s disease. Nat Genet 4:398–403
Arai H, Kobayashi K, Ichimiya Y, Kosaka K, Iizuka R (1984) A preliminary study of free amino acids in the postmortem temporal cortex from Alzheimer-type dementia patients. Neurobiol Aging 5:319–321
Auld DS, Kornecook TJ, Bastianetto S, Quirion R (2002) Alzheimer’s disease and the basal forebrain cholinergic system: relations to beta-amyloid peptides, cognition, and treatment strategies. Prog Neurobiol 68:209–245
Banerjee R, Vitvitsky V, Garg SK (2008) The undertow of sulfur metabolism on glutamatergic neurotransmission. Trends Biochem Sci 33:413–419
Beal MF, Hyman BT, Koroshetz W (1993) Do defects in mitochondrial energy metabolism underlie the pathology of neurodegenerative diseases? Trends Neurosci 16:125–131
Bear M, Abraham WC (1996) Long-term depression in hippocampus. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:437–462
Bence NF, Sampat RM, Kopito RR (2001) Impairment of the ubiquitin–proteasome system by protein aggregation. Science 292:1552–1555
Benchoua A, Trioulier Y, Zala D, Gaillard MC, Lefort N, Dufour N, Saudou F, Elalouf JM, Hirsch E, Hantraye P, Déglon N, Brouillet E (2006) Involvement of mitochondrial complex II defects in neuronal death produced by N-terminus fragment of mutated huntingtin. Mol Biol Cell 17:1652–1663
Bennett EJ, Shaler TA, Woodman B, Ryu KY, Zaitseva TS, Becker CH, Bates GP, Schulman H, Kopito RR (2007) Global changes to the ubiquitin system in Huntington’s disease. Nature 448:704–708
Berman SB, Hastings TG (1999) Dopamine oxidation alters mitochondrial respiration and induces permeability transition in brain mitochondria: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 73:1127–1137
Bianchi L, Bolam JP, Galeffi F, Frosini M, Palmi M, Della Corte L (1996) In vivo release of taurine from rat neostriatum and substantia nigra. Adv Exp Med Biol 403:427–433
Bianchi L, Colivicchi MA, Bolam JP, Della Corte L (1998) The release of amino acids from rat neostriatum and substantia nigra in vivo: a dual microdialysis probe analysis. Neuroscience 87:171–180
Birdsall TC (1998) Therapeutic applications of taurine. Altern Med Rev 3:128–136
Biron KE, Dickstein DL, Gopaul R, Jefferies WA (2011) Amyloid triggers extensive cerebral angiogenesis causing blood brain barrier permeability and hypervascularity in Alzheime’s disease. PLoS ONE 6:e23789
Bitan G, Fradinger EA, Spring SM, Teplow DB (2005) Neurotoxic protein oligomers—what you see is not always what you get. Amyloid 12:88–95
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P (2003) Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset Parkinsonism. Science 299:256–259
Braak H, Braak E (1998) Evolution of neuronal changes in the course of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 53:127–140
Brouillet E, Hantraye P, Ferrante RJ, Dolan R, Leroy-Willi A, Kowall NW, Beal MF (1995) Chronic mitochondrial energy impairment produces selective striatal degeneration and abnormal choreiform movements in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7105–7109
Burdick D, Soreghan B, Kwon M, Kosmoski J, Knauer M, Henschen A, Yates J, Cotman C, Glabe C (1992) Assembly and aggregation properties of synthetic Alzheimer’s A4/beta amyloid peptide analogs. J Biol Chem 267:546–554
Chan P, DeLanney LE, Irwin I, Langston JW, Di Monte D (1991) Rapid ATP loss caused by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in mouse brain. J Neurochem 57:348–351
Chen WQ (2000) Mode of action of taurine. Ph.D Dissertation, University of Kansas
Chen QS, Kagan BL, Hirakura Y, Xie CW (2000) Impairment of hippocampal long-term potentiation by Alzheimer amyloid b-peptides. J Neurosci Res 60:65–72
Chen WQ, Jin H, Nguyen M, Carr J, Lee YJ, Hsu CC, Faiman MD, Schloss JV, Wu JY (2001) Role of taurine in regulation of intracellular calcium level and neuroprotective function in cultured neurons. J Neurosci Res 66:612–619
Chen QS, Wei WZ, Shimahara T, Xie CW (2002) Alzheimer amyloid b-peptide inhibits the late phase of long-term potentiation through calcineurin-dependent mechanisms in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Neurobiol Learn Mem 77:354–371
Chen K, Zhang Q, Wang J, Liu F, Mi M, Xu H, Chen F, Zeng K (2009) Taurine protects transformed rat retinal ganglion cells from hypoxia-induced apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction. Brain Res 1279:131–138
Chipuk JE, Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, Droin NM, Newmeyer DD, Schuler M, Green DR (2004) Direct activation of Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Science 30:1010–1014
Choo YS, Johnson GV, MacDonald M, Detloff PJ, Lesort M (2004) Mutant huntingtin directly increases susceptibility of mitochondria to the calcium-induced permeability transition and cytochrome c release. Hum Mol Genet 13:1407–1420
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sil PC (2011) Taurine suppresses doxorubicin-triggered oxidative stress and cardiac apoptosis in rat via up-regulation of PI3-K/Akt and inhibition of p53, p38-JNK. Biochem Pharm 81:891–909
Dauer W, Kholodilov N, Vila M, Trillat AC, Goodchild R, Larsen KE, Staal R, Tieu K, Schmitz Y, Yuan CA, Rocha M, Jackson-Lewis V, Hersch S, Sulzer D, Przedborski S, Burke R, Hen R (2002) Resistance of alpha-synuclein null mice to the parkinsonian neurotoxin MPTP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14524–14529
Davison AN, Kaczmarek LK (1971) Taurine—a possible neurotransmitter. Nature Lond 234:107–108
Dawson R Jr, Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Gollub M, Liu S (1999) An age-related decline in striatal taurine is correlated with a loss of dopaminergic markers. Brain Res Bull 48:319–324
Dawson R Jr, Baker D, Eppler B, Tang E, Shih D, Hern H, Hu M (2000) Taurine inhibition of metal-stimulated catecholamine oxidation. Neurotox Res 2:1–15
Del Olmo N, Handlera A, Alvarezb L, Bustamantec J, Martín del Ríoa R, Solísa JM (2003) Taurine-induced synaptic potentiation and the late phase of long-term potentiation are related mechanistically. Neuropharmacology 44:26–39
Della Corte L, Bolam JP, Clarke DJ, Parry DM, Smith AD (1990) Sites of [3H] taurine uptake in the rat substantia nigra in relation to the release of taurine from the striatonigral pathway. Eur J Neurosci 2:50–61
DeLong MR (1990) Primate models of movement disorders of basal ganglia origin. Trends Neurosci 13:281–285
Dickinson DA, Forman HJ (2002) Cellular glutathione and thiols metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol 64:1019–1026
Dineley KT, Westerman M, Bui D, Bell K, Ashe KH, Sweatt JD (2001) Beta-amyloid activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade via hippocampal alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: in vitro and in vivo mechanisms related to Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 21:4125–4133
Dray A, Straughan DW (1976) Synaptic mechanisms in the substantia nigra. J Pharm Pharmacol 28:400–405
El Idrissi A (2008) Taurine increases mitochondrial buffering of calcium: role in neuroprotection. Amino Acids 34:321–328
El Idrissi A, Trenkner E (1999) Growth factors and taurine protect against excitotoxicity by stabilizing calcium homeostasis and energy metabolism. J Neurosci 19:9459–9468
El Idrissi A, Trenkner E (2003) Taurine regulates mitochondrial calcium homeostasis. Adv Exp Med Biol 526:527–536
El Idrissi A, Trenkner E (2004) Taurine as a modulator of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. Neurochem Res 29:189–197
Eliezer D, Kutluay E, Bussell R Jr, Browne G (2001) Conformational properties of alpha-synuclein in its free and lipid-associated states. J Mol Biol 307:1061–1073
Ferreira IL, Bajouco LM, Mota SI, Auberson YP, Oliveira CR, Rego AC (2012) Amyloid beta peptide 1–42 disturbs intracellular calcium homeostasis through activation of GluN2B-containing N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in cortical cultures. Cell Calcium 51:95–106
Foos TM, Wu JY (2002) The role of taurine in the central nervous system and the modulation of intracellular calcium homeostasis. Neurochem Res 27:21–26
Forno LS (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Pathol Exp Neurol 55:259–272
Frey U, Huang YY, Kandel ER (1993) Effects of cAMP stimulate a late stage of LTP in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Science 260:1661–1664
Frosini M, Sesti C, Saponara S, Ricci L, Valoti M, Palmi M, Machetti F, Sgaragli G (2003) A specific taurine recognition site in the rabbit brain is responsible for taurine effects on thermoregulation. Br J Pharmacol 139:487–494
George JM, Jin H, Woods WS, Clayton DF (1995) Characterization of a novel protein regulated during the critical period for song learning in the zebra finch. Neuron 15:361–372
Gerfen CF (1992) The neostriatal mosaic: multiple levels of compartmental organization. Trends Neurosci 15:133–139
Gervais FG, Xu D, Robertson GS, Vaillancourt JP, Zhu Y, Huang J, LeBlanc A, Smith D, Rigby M, Shearman MS, Clarke EE, Zheng H, Van Der Ploeg LH, Ruffolo SC, Thornberry NA, Xanthoudakis S, Zamboni RJ, Roy S, Nicholson DW (1999) Involvement of caspases in proteolytic cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta precursor protein and amyloidogenic A beta peptide formation. Cell 97:395–406
Geula C, Nagykery N, Nicholas A, Wu CK (2008) Cholinergic neuronal and axonal abnormalities are present early in aging and in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:309–318
Gleeson RA, Trapido-Rosenthal HG, Carr WE (1987) A taurine receptor model: taurine-sensitive olfactory cells in the lobster. Adv Exp Med Biol 217:253263
Goodman Y, Mattson MP (1994) Secreted forms of β-amyloid precursor protein protect hippocampal neurons against amyloid peptide-induced oxidative injury. Exp Neurol 128:1–12
Graham DG (1978) Oxidative pathways for catecholamines in the genesis of neuromelanin and cytotoxic quinones. Mol Pharmacol 14:633–643
Gu M, Gash MT, Mann VM, Javoy-Agid F, Cooper JM, Schapira AH (1996) Mitochondrial defect in Huntington’s disease caudate nucleus. Ann Neurol 39:385–389
Gu Z, Liu W, Yan Z (2009) Beta-amyloid impairs AMPA receptor trafficking and function by reducing Ca2+/calmodulindependent protein kinase II synaptic distribution. J Biol Chem 284:10639–10649
Haass C (2004) Take five-BACE and the γ-secretase quartet conduct Alzheimer’s amyloid β-peptide generation. EMBO J 23:483–488
Haass C, Selkoe DJ (1993) Cellular processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein and the genesis of amyloid beta-peptide. Cell 175:1039–1042
Haass C, De Strooper B (1999) The presenilins in Alzheimer’s disease—proteolysis holds the key. Science 286:916–919
Haass C, Selkoe DJ (2007) Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:101–112
Hagar HH (2004) The protective effect of taurine against cyclosporine A-induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Lett 151:335–343
Harkany T, Abrahám I, Timmerman W, Laskay G, Tóth B, Sasvári M, Kónya C, Sebens JB, Korf J, Nyakas C, Zarándi M, Soós K, Penke B, Luiten PG (2000) Beta-amyloid neurotoxicity is mediated by a glutamate-triggered excitotoxic cascade in rat nucleus basalis. Eur J Neurosci 12:2735–2745
Hastings TG (1995) Enzymatic oxidation of dopamine: role of prostaglandin H synthase. J Neurochem 64:919–924
Hayes KC (1985) Taurine requirement in primates. Nutr Rev 43:65–70
Hayes KC, Carey RE, Schmidt SY (1975) Retinal degeneration associated with taurine deficiency in the cat. Science 188:949–951
Hensley K, Carney JM, Mattson MP, Aksenova M, Harris M, Wu JF, Floyd RA, Butterfield DA (1994) A model for beta-amyloid aggregation and neurotoxicity based on free radical generation by the peptide: relevance to Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3270–3274
Heo JY, Park JH, Kim SJ, Seo KS, Han JS, Lee SH, Kim JM, Park JI, Park SK, Lim K, Hwang BD, Shong M, Kweon GR (2012) DJ-1 null dopaminergic neuronal cells exhibit defects in mitochondrial function and structure: involvement of mitochondrial complex I assembly. PLoS ONE 7:e32629
Hepler RW, Grimm KM, Nahas DD, Breese R, Dodson EC, Acton P, Keller PM, Yeager M, Wang H, Shughrue P, Kinney G, Joyce JG (2006) Solution state characterization of amyloid beta-derived diffusible ligands. Biochemistry 45:15157–15167
Hernandez-Benitez R, Pasantes-Morales H, Saldana IT, Ramos-Mandujano G (2010) Taurine stimulates proliferation of mice embryonic cultured neural progenitor cells. J Neurosci Res 88:1673–1681
Hofer A, Gasser T (2004) New aspects of genetic contributions to Parkinson’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 24:417–424
Hoshi M, Takashima A, Murayama M, Yasutake K, Yoshida N, Ishiguro K, Hoshino T, Imahori K (1997) Nontoxic amyloid beta peptide 1–42 suppresses acetylcholine synthesis. Possible role in cholinergic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 272:2038–2041
Hs.DCR Group (1993) A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosome. Cell 72:971–983
Hsu LJ, Sagara Y, Arroyo A, Rockenstein E, Sisk A, Mallory M, Wong J, Takenouchi T, Hashimoto M, Masliah E (2000) α-Synuclein promotes mitochondrial deficit and oxidative stress. Am J Pathol 157:401–410
Huxtable RJ (1976) Metabolism and function of taurine in the heart. In: Huxtable R, Barbeau A (eds) Taurine. Raven press, New York, pp 99–119
Huxtable RJ (1989) Taurine in the central nervous system and the mammalian actions of taurine. Prog Neurobiol 32:471–533
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev 72:101–163
Jacobsen JG, Smith LH (1968) Biochemistry and physiology of taurine and taurine derivatives. Physiol Rev 48:424–511
Jellinger KA (1999) The role of iron in neurodegeneration: prospects for pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease. Drugs Aging 14:115–140
Jenkins BG, Koroshetz WJ, Beal MF, Rosen BR (1993) Evidence for impairment of energy metabolism in vivo in Huntington’s disease using localized 1H NMR spectroscopy. Neurology 43:2689–2695
Jensen PH, Islam K, Kenney J, Nielsen MS, Power J, Gai WP (2000) Microtubule-associated protein 1B is a component of cortical Lewy bodies and binds alpha-synuclein filaments. J Biol Chem 275:21500–21507
Jin M, Shepardson N, Yang T, Chen G, Walsh D, Selkoe DJ (2011) Soluble amyloid β-protein dimers isolated from Alzheimer cortex directly induce Tau hyperphosphorylation and neuritic degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:5819–5824
Jong CJ, Azuma J, Schaffer S (2012) Mechanism underlying the antioxidant activity of taurine: prevention of mitochondrial oxidant production. Amino Acids 42:2223–2232
Junyent F, Romero R, de Lemos L, Utrera J, Camins A, Pallàs M, Auladell C (2010) Taurine treatment inhibits CaMKII activity and modulates the presence of calbindin D28k, calretinin, and parvalbumin in the brain. J Neurosci Res 88:136–142
Kar S, Issa AM, Seto D, Auld DS, Collier B, Quirion R (1998) Amyloid beta-peptide inhibits high-affinity choline uptake and acetylcholine release in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurochem 70:2179–2187
Kawahara M, Kuroda Y (2000) Molecular mechanism of neurodegeneration induced by Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid protein: channel formation and disruption of calcium homeostasis. Brain Res Bull 53:389–397
Kazantsev A, Preisinger E, Dranovsky A, Goldgaber D, Housman D (1999) Insoluble detergent-resistant aggregates form between pathological and nonpathological lengths of polyglutamine in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:11404–11409
Kern SE, Kinzler KW, Bruskin A, Jarosz D, Friedman P, Prives C, Vogelstein B (1991) Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. Science 252:1708–1711
Kinoshita A, Fukumoto H, Shah T, Whelan CM, Irizarry MC, Hyman BT (2003) Demonstration by FRET of BACE interaction with the amyloid precursor protein at the cell surface and in early endosomes. J Cell Sci 116:3339–3346
Kirino Y, Yasukawa T, Ohta S, Akira S, Ishihara K, Watanabe K, Suzuki T (2004) Codon-specific translational defect caused by a wobble modification deficiency in mutant tRNA from a human mitochondrial disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15070–15075
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive Juvenile Parkinsonism. Nature 392:605–608
Koeppen AH (1995) The history of iron in the brain. J Neurol Sci 134:1–9
Kontro P, Oja SS (1987) Co-operativity in sodium-independent taurine binding to brain membranes in the mouse. Neuroscience 23:567–570
Kouroku Y, Fujita E, Jimbo A, Kikuchi T, Yamagata T, Momoi MY, Kominami E, Kuida K, Sakamaki K, Yonehara S, Momoi T (2002) Polyglutamine aggregates stimulate ER stress signals and caspase-12 activation. Hum Mol Genet 11:1505–1515
Kozlowski DJ, Chen Z, Zhuang L, Fei YJ, Navarre S, Ganapathy V (2008) Molecular characterization and expression pattern of taurine transporter in zebrafish during embryogenesis. Life Sci 82:1004–1011
Kudo Y, Akiyoshi E, Akagi H (1988) Identification of two taurine receptor subtypes on the primary afferent terminal of frog spinal cord. Br J Pharmacol 94:1051–1056
Kumar R (2009) Role of naturally occurring osmolytes in protein folding and stability. Arch Biochem Biophys 491:1–6
Kuperstein I, Broersen K, Benilova I, Rozenski J, Jonckheere W, Debulpaep M, Vandersteen A, Segers-Nolten I, Van Der Werf K, Subramaniam V, Braeken D, Callewaert G, Bartic C, D’Hooge R, Martins IC, Rousseau F, Schymkowitz J, De Strooper B (2010) Neurotoxicity of Alzheimer’s disease Abeta peptides is induced by small changes in the Abeta 42 to Abeta 40 ratio. EMBO J 29:3408–3420
Kuriyama K (1980) Taurine as a neuromodulator. Fed Proc 39:2680–2684
Kuwert T, Lange HW, Langer K-J, Herzog H, Aulich A, Feinendegen LE (1990) Cortical and subcortical glucose consumption measured by PET in patients with Huntington’s disease. Brain 113:1405–1423
LaFontaine MA, Geddes JW, Banks A, Butterfield DA (2000) 3-Nitropropionic acid induced in vivo protein oxidation in striatal and cortical synaptosomes: insights into Huntington’s disease. Brain Res 858:356–362
Landwehrmeyer GB, McNeil SM, Dure LS, Ge P, Aizawa H, Huang Q, Ambrose CM, Duyao MP, Bird ED, Bonilla E, de Young M, Avila-Gonzales AJ, Wexler NS, DiFiglia M, Gusella JF, MacDonald ME, Penney JB, Young AB, Vonsattel J-P (1995) Huntington’s disease gene: regional and cellular expression in brain of normal and affected individuals. Ann Neurol 37:218–230
Langston JW, Ballard P, Irwin I (1983) Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219:979–980
Lanska DJ (2000) George Huntington (1850–1916) and hereditary chorea. J Hist Neurosci 9:76–89
Leon R, Wu H, Jin Y, Wei J, Buddhala C, Prentice H, Wu JY (2009) Protective function of taurine in glutamate-induced apoptosis in cultured neurons. J Neurosci Res 87:1185–1194
Lesne S, Koh MT, Kotilinek L, Kayed R, Glabe CG, Yang A, Gallagher M, Ashe KH (2006) A specific amyloid beta protein assembly in the brain impairs memory. Nature 440:352–357
Lima L, Cubillos S (1998) Taurine might be acting as a trophic factor in the retina by modulating phosphorylation of cellular proteins. J Neurosci Res 53:377–384
Lin H, Bhatia R, La R (2001) Amyloid b protein forms ion channels: implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. FASEB J 15:2433–2444
Loo DT, Copani A, Pike CJ, Whittemore ER, Walencewicz AJ, Cotman CW (1993) Apoptosis is induced by B-amyloid in cultured central nervous system neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7951–7955
López-Colomé AM, Fragoso G, Salceda R (1991) Taurine receptors in membranes from retinal pigment epithelium cells in culture. Neuroscience 41:791–796
Louzada PR, Paula-Lima AC, Mendonca-Silva DL, Noel F, De Mello FG, Ferreira ST (2004) Taurine prevents the neurotoxicity of beta-amyloid and glutamate receptor agonists: activation of GABA receptors and possible implications for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological disorders. FASEB J 18:511–518
Ludolph AC, He F, Spencer PS, Hammerstad J, Sabri M (1990) 3-Nitropropionic acid: exogenous animal neurotoxin and possible human striatal toxin. Can J Neurol Sci 18:492–498
Lustbader JW, Cirilli M, Lin C, Xu HW, Takuma K, Wang N, Caspersen C, Chen X, Pollak S, Chaney M, Trinchese F, Liu S, Gunn-Moore F, Lue LF, Walker DG, Kuppusamy P, Zewier ZL, Arancio O, Stern D, Yan SS, Wu H (2004) ABAD directly links Abeta to mitochondrial toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 304:448–452
Macaione S, Ruggeri P, DeLuca F, Tucci G (1974) Free amino acids in developing rat retina. J Neurochem 22:887–891
MacDermott AB, Dale BN (1987) Receptors, ion channels and synaptic potentials underlying the integrative actions of excitatory amino acids. Trend Neurosci 10:280–284
Magnusson KR, Clements JR, Wu JY, Beitz AJ (1989) Colocalization of taurine and cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase-like immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of the rat. Synapse 4:55–69
Maguire-Zeiss KA, Short DW, Federoff HJ (2005) Synuclein, dopamine and oxidative stress: co-conspirators in Parkinson’s disease? Brain Res Mol Brain Res 134:18–23
Mankovskaya IN, Serebrovskaya TV, Swanson RJ, Vavilova GL, Kharlamova ON (2000) Mechanisms of taurine antihypoxic and antioxidant action. High Alt Med Biol 1:105–110
Martin DL (1992) Synthesis and release of neuroactive substances by glial cells. Glia 5:81–94
Martindale D, Hackam A, Wieczorek A, Ellerby L, Wellington C, McCutcheon K, Singaraja R, Kazemi-Esfarjani P, Devon R, Kim SU, Bredesen DE, Tufaro F, Hayden MR (1998) Length of huntingtin and its polyglutamine tract influences localization and frequency of intracellular aggregates. Nat Genet 18:150–154
Masliah E, Mallory M, Alford M, Tanaka S, Hansen LA (1998) Caspase dependent DNA fragmentation might be associated with excitotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neuro 57:1041–1052
Mattson MP (1997) Advances fuel Alzheimer’s conundrum. Nat Genet 17:254–256
Mazziotta JC, Phelps ME, Pahl JJ, Huang SC, Baxter LR, Riege WH, Hoffman JM, Kuhl DE, Lanto AB, Wapenski JA, Markham CH (1987) Reduced cerebral glucose metabolism in asymptomatic patients at risk for Huntington’s disease. New Eng J Med 316:357–362
Miao J, Zhang J, Zheng L, Yu X, Zhu W, Zou S (2012) Taurine attenuates Streptococcus uberis-induced mastitis in rats by increasing T regulatory cells. Amino Acids 42:2417–2428
Mikhailov V, Mikhailova M, Pulkrabek DJ, Dong Z, Venkatachalam MA, Saikumar P (2001) Bcl-2 Prevents Bax oligomerization in the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Biol Chem 276:18361–18374
Milakovic T, Johnson GV (2005) Mitochondrial respiration and ATP production are significantly impaired in striatal cells expressing mutant huntingtin. J Biol Chem 280:30773–30782
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B, Reed JC (1994) Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and Bax gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 9:1799–1805
Molina JA, Jiménez-Jiménez FJ, Gomez P, Vargas C, Navarro JA, Ortí-Pareja M, Gasalla T, Benito-León J, Bermejo F, Arenas J (1997) Decreased cerebrospinal fluid levels of neutral and basic amino acids in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 150:123–127
Morales I, Dopico JG, Sabate M, Gonzalez-Hernandez T, Rodriguez M (2007) Substantia nigra osmoregulation: taurine and ATP involvement. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C1934–C1941
Moran J, Salazar P, Pasantes-Morales H (1988) Effect of tocopherol and taurine on membrane fluidity of retinal rod outer segments. Exp Eye Res 45:769–776
Mytilineou C, Kramer BC, Yabut JA (2002) Glutathione depletion and oxidative stress. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 8:385–387
Navneet AK, Appukuttan TA, Pandey M, Mohanakumar KP (2008) Taurine fails to protect against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced striatal dopamine depletion in mice. Amino Acids 35:457–461
Neumann M, Tolnay M, Mackenzie IR (2009) The molecular basis of frontotemporal dementia. Exp Rev Mol Med. doi:10.1017/S1462399409001136
Nicklas WJ, Yougster SK, Kindt MV, Heikkila RE (1987) MPTP, MPP+ and mitochondrial function. Life Sci 40:721–729
Novelli A, Reilly JA, Lysko PG, Henneberry RC (1988) Glutamate becomes neurotoxic via the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor when intracellular energy levels are reduced. Brain Res 451:205–212
O’Byrne MB, Tipton KF (2000) Taurine-induced attenuation of MPP1 neurotoxicity in vitro: a possible role for the GABAA subclass of GABA receptors. Neurochem 74:2087–2093
Oddo S, LaFerla FM (2006) The role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. J Physiol 99:172–179
Oja SS, Lahdesmaki P (1974) Is taurine an inhibitory neurotransmitter? Med Biol 52:138–143
Oja SS, Saransaari P (2007) Pharmacology of taurine. Proc West Pharmacol 50:8–15
Oja SS, Ahtee L, Kontro P, Paasonen MK (1985) Taurine biological actions and clinical perspectives. Alan R Liss Inc, New York
Okamoto K, Kimura H, Sakai Y (1983) Taurine-induced increase of the Cl conductance of cerebellar Purkinje cell dendrites in vitro. Brain Res 259:319–323
Oliveira JM (2010) Mitochondrial bioenergetics and dynamics in Huntington’s disease: tripartite synapses and selective striatal degeneration. J Bioenerg Biomembr 42:227–234
Palkovits M, Elekes I, Lang T, Patthy A (1986) Taurine levels in discrete brain nuclei of rats. J Neurochem 47:1333–1335
Pan C, Giraldo GS, Prentice H, Wu JY (2010) Taurine protection of PC12 cells against endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by oxidative stress. J Biomed Sci 1:S17
Pan C, Prentice H, Price AL, Wu JY (2011) Beneficial effect of taurine on hypoxia- and glutamate-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways in primary neuronal culture. Amino Acid 43:1141–1146
Parker WD, Boyson SJ, Parks JK (1989) Abnormalities of the electron transport chain in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 26:719–723
Paula-Lima AC, De Felice FG, Brito-Moreira J, Ferreira ST (2005) Activation of GABAA receptors by taurine and muscimol blocks the neurotoxicity of beta-amyloid in rat hippocampal and cortical neurons. Neuropharmacology 49:1140–1148
Pedersen WA, Kloczewiak MA, Blusztajn JK (1996) Amyloid beta-protein reduces acetyl-choline synthesis in a cell line derived from cholinergic neurons of the basal forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8068–8071
Philibert RA, Rogers KL, Dutton GR (1989) Stimulus-coupled taurine efflux from cerebellar neuronal cultures: on the roles of Ca++ and Na+. J Neurosci Res 22:167–171
Pion PD, Kittleson MD, Rogers QR, Morris JG (1987) Myocardial failure in cats associated with low plasma taurine: a reversible cardiomyopathy. Science 237:764–768
Procter AW (2000) Abnormalities in non-cholinergic neurotransmitter systems in Alzheimer’s disease. In: O’Brien J, Ames D, Burns A (eds) Dementia, 2nd edn. Edward Arnold, Oxford, pp 433–442
Rao RV, Bredesen DE (2004) Misfolded proteins, endoplasmic reticulum stress and neurodegeneration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16:653–662
Reichelt KL, Edminson PD (1974) Biogenic amine specificity of cortical peptide synthesis in monkey brain. FEBS Lett 47:185–189
Reijonen S, Putkonen N, Nørremølle A, Lindholm D, Korhonen L (2008) Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress counteracts neuronal cell death and protein aggregation caused by N-terminal mutant huntingtin proteins. Exp Cell Res 14:950–960
Reiner A, Albin RL, Anderson KD, D’Amato CJ, Penney JB, Young AB (1988) Differential loss of striatal projection neurons Huntington disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5733–5737
Richfield EK, Maguire-Zeiss KA, Cox C, Gilmore J, Voorn P (1995) Reduced expression of preproenkephalin in striatal neurons from Huntington’s disease patients. Ann Neurol 37:335–343
Rivas-arancibia S, Alba I, Rodríguez AI, Tanja Zigova T, Willing AE, Brown WD, Cahill DW, Sanberg PR (2001) Taurine increases rat survival and reduces striatal damage caused by 3-nitropropionic acid. Int J Neurosci 108:55–67
Roselli F, Tirard M, Lu J, Hutzler P, Lamberti P, Livrea P, Morabito M, Almeida OF (2005) Soluble beta-amyloid 1–40 induces NMDA-dependent degradation of postsynaptic density-95 at glutamatergic synapses. J Neurosci 25:11061–11070
Ruotsalainen M, Ahtee L (1996) Intrastriatal taurine increases striatal extracellular dopamine in a tetrodotoxin-sensitive manner in rats. Neurosci Let 212:175–178
Santa-Maria I, Hernandez F, Moreno FJ, Avial J (2007) Taurine, an inducer of tau polymerization and a weak inhibitor for amyloid-beta-peptide aggregation. Neurosci Lett 429:91–94
Saransaari P, Oja SS (2000) Taurine and neural cell damage. Amino Acids 19:509–526
Schaffer SW, Azuma J, Matura JD (1995) Mechanisms underlying taurine-mediated alterations in membrane function. Amino Acids 18:231–246
Schaffer SW, Takahashi K, Azuma J (2000) Role of osmoregulation in the actions of taurine. Amino Acids 19:527–546
Schaffer SW, Azuma J, Mozaffari M (2009) Role of antioxidant activity of taurine in diabetes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 87:91–99
Schapira AH, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Clark JB, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1990) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 54:823–827
Schliebs R, Arendt T (2006) The significance of the cholinergic system in the brain during aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 113:1625–1644
Schulz S, Siemer H, Krug M, Höllt V (1999) Direct evidence for biphasic cAMP responsive element-binding protein phosphorylation during long-term potentiation in the rat dentate gyrus in vivo. J Neurosci 19:5683–5692
Selkoe DJ (2002) Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science 298:789–791
Shankar GM, Bloodgood BL, Townsend M, Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ, Sabatini BL (2007) Natural oligomers of the Alzheimer amyloid-beta protein induces reversible synapse loss by modulating an NMDA-type glutamate receptor-dependent signaling pathway. J Neurosci 27:2866–2875
Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz A, Shepardson NE, Smith I, Brett FM, Farrell MA, Rowan MJ, Lemere CA, Regan CM, Walsh DM, Sabatini BL, Selkoe DJ (2008) Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer’s brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med 14:837–842
Shimo Y, Wichmann T (2009) Neuronal activity in the subthalamic nucleus modulates the release of dopamine in the monkey striatum. Eur J Neurosci 29:104–113
Size C, Bi H, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Filley CM, Martin LJ (2001) N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit. Proteins and their phosphorylation status are altered selectively in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 182:151–159
Smith Y, Charara A, Parent A (1996) Synaptic innervation of midbrain dopaminergic neurons by glutamate-enriched terminals in the squirrel monkey. J Comp Neurol 364:231–253
Smith WW, Jiang H, Pei Z, Tanaka Y, Morita H, Sawa A, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Ross CA (2005) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial cell death pathways mediate A53T mutant alpha-synuclein-induced toxicity. Hum Mol Genet 14:3801–3811
Spencer JP, Jenner P, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Marsden DC, Halliwell B (1998) Conjugates of catecholamines with cysteine and GSH in Parkinson’s disease: possible mechanisms of formation involving reactive oxygen species. J Neurochem 71:2112–2122
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Hasegawa M (1998) Alpha synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6469–6473
Stokes AH, Hastings TG, Vrana KE (1999) Cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of dopamine. J Neurosci Res 55:659–665
Sturman JA (1993) Taurine in development. Physiol Rev 73:119–147
Su JH, Anderson AJ, Cummings B, Cotman CW (1994) Immunocytochemical evidence for apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroReport 5:2529–2533
Sulaiman SA, Suliman FE, Barghouthi S (2003) Kinetic studies on the inhibition of GABA-T by gamma-vinyl GABA and taurine. Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 18:297–301
Sun M, Gu Y, Zhao Y, Xu C (2011) Protective functions of taurine against experimental stroke through depressing mitochondria-mediated cell death in rats. Amino Acids 40:1419–1429
Sun M, Zhao Y, Gu Y, Xu C (2012) Anti-inflammatory mechanism of taurine against ischemic stroke is related to down-regulation of PARP and NF-kappaB. Amino Acids 42:1735–1747
Sung DY, Walthall WW, Derby CD (1996) Identification and partial characterization of putative taurine receptor proteins from the olfactory organ of the spiny lobster. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 115:19–26
Tadros MG, Khalifa AE, Abdel-Naim AB, Arafa HM (2005) Neuroprotective effect of taurine in 3-nitropropionic acid-induced experimental animal model of Huntington’s disease phenotype. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82:574–582
Takatani T, Takahashi K, Uozumi Y, Shikata E, Yamamoto Y, Ito T, Matsuda T, Schaffer SW, Fujio Y, Azuma J (2004) Taurine inhibits apoptosis by preventing formation of the Apaf-1/caspase-9 apoptosome. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287:C949–C953
Takuma K, Yan SS, Stern DM, Yamada K (2005) Mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Pharmacol Sci 97:312–316
Tang XW, Deupree DL, Sun Y, Wu JY (1996) Biphasic effect of taurine on excitatory amino acid-induced neurotoxicity. In: Huxtable RJ, Azuma J, Kuriyama K, Nakagawa M, Baba A (eds) Taurine 2: basic and clinical aspects in advances in experimental medicine and biology, vol 43. Plenum Press, New York, pp 499–505
Teaktong T, Graham AJ, Court JA, Perry RH, Jaros E, Johnson M, Hall R, Perry EK (2004) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor immunohistochemistry in Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies: differential neuronal and astroglial pathology. J Neurol Sci 225:39–49
Texidó L, Martín-Satué M, Alberdi E, Solsona C, Matute C (2011) Amyloid β peptide oligomers directly activate NMDA receptors. Cell Calcium 49:184–190
Trushina E, Dyer RB, Badger JD, Ure D, Eide L, Tran DD, Vrieze BT, Legendre-Guillemin V, McPherson PS, Mandavilli BS, Van Houten B, Zeitlin S, McNiven M, Aebersold R, Hayden M, Parisi JE, Seeberg E, Dragatsis I, Doyle K, Bender A, Chacko C, McMurray CT (2004) Mutant huntingtin impairs axonal trafficking in mammalian neurons in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell Biol 24:8195–8209
Vaucher E, Aumont N, Pearson D, Rowe W, Poirier J, Kar S (2001) Amyloid peptide levels and its effects on hippocampal acetylcholine release in aged, cognitively-impaired and unimpaired rats. J Chem Neuroanat 21:323–329
Venkatraman P, Wetzel R, Tanaka M, Nukina N, Goldberg AL (2004) Eukaryotic proteasomes cannot digest polyglutamine sequences and release them during degradation of polyglutamine containing proteins. Mol Cell 14:95–104
Verner A, Craig S, McGuire W (2007) Effect of taurine supplementation on growth and development in preterm or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 17:CD006072
Vohra BP, Hui X (2001) Taurine protects against carbon tetrachloride toxicity in the cultured neurons and in vivo. Arch Physiol Biochem 109:90–94
Wan FS, Li GH, Zhang J, Yu LH, Zhao XM (2008) Protective effects of taurine on myocardial mitochondria and their enzyme activities in rate with severe burn. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi 24:171–174
Warskulat U, Flögel U, Jacoby C, Hartwig HG, Thewissen M, Merx MW, Molojavyi A, Heller-Stilb B, Schrader J, Häussinger D (2004) Taurine transporter knockout depletes muscle taurine levels and results in severe skeletal muscle impairment but leaves cardiac function uncompromised. FASEB J 18:577–579
Wertkin AM, Turner RS, Pleasure SJ, Golde TE, Younkin SG, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (1993) Human neurons derived from a teratocarcinoma cell line express solely the 695-amino acid amyloid precursor protein and produce intracellular β-amyloid or A4 peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9513–9517
Winder DG, Mansuy LM, Osman M, Moallem TM, Kandel ER (1998) Genetic and pharmacological evidence for a novel, intermediate phase of long term potentiation suppressed by calcineurin. Cell 92:25–37
Wogulis M, Wright S, Cunningham D, Chilcote T, Powell K, Rydel RE (2005) Nucleation-dependent polymerization is an essential component of amyloid-mediated neuronal cell death. J Neurosci 25:1071–1080
Wu JY (1982) Purification and characterization of cysteic/cysteine sulfinic acids decarboxylase and l-glutamate decarboxylase in bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4270–4274
Wu JY, Prentice H (2010) Role of taurine in the central nervous system. J Biomed Sci 17:S1
Wu JY, Moss LG, Chen MS (1979) Tissue and regional distribution of cysteic acid decarboxylase in bovine brain. A new assay method. Neurochem Res 4:201–212
Wu JY, Johansen FF, Lin CT, Liu JW (1987) Taurine system in the normal and ischemic rat hippocampus. Adv Exp Med Biol 217:265–274
Wu JY, Liao C, Lin CJ, Lee YH, Ho JY, Wu HT (1990) Taurine receptor in the mammalian brain. Prog Clin Biol Res 351:147–156
Wu JY, Tang XW, Tsai WH (1992a) Taurine receptor: kinetic analysis and pharmacological studies. Adv Exp Med Biol 315:263–268
Wu QD, Wang JH, Fennessy F, Redmond HP, Bouchier-Hayes HD, Wu JY, Tang XW, Tsai WH (1992b) Taurine receptor: kinetic analysis and pharmacological studies. Adv Exp Med Biol 315:263–268
Wu JY, Chen W, Tang XW, Jin H, Foos T, Schloss JV, Davis K, Faiman MD, Hsu CC (2000) Mode of action of taurine and regulation dynamics of its synthesis in the CNS. Adv Exp Med Biol 483:35–44
Wu H, Jin Y, Wei J, Jin H, Sha D, Wu JY (2005) Mode of action of taurine as a neuroprotector. Brain Res 1038:123–131
Wu J, Kohno T, Georgiev SK, Ikoma M, Ishii H, Petrenko AB, Baba H (2008) Taurine activates glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors in rat substantia gelatinosa neurons. Neuro Report 19:333–337
Wu JY, Wu H, Jin Y, Wei J, Sha D, Howarad P, Lee HH, Lin CH, Lee YH, Yang LL (2009) Mechanism of neuroprotective function of taurine. Adv Exp Med Biol 643:169–179
Xu H, Greengard P, Gandy S (1995) Regulated formation of Golgi secretory vesicles containing Alzheimer β-amyloid precursor protein. J Biol Chem 270:23243–23245
Yan SD, Fu J, Soto C, Chen X, Zhu H, Al-Mohanna F, Collison K, Zhu A, Stern E, Saido T, Tohyama M, Ogawa S, Roher A, Stern D (1997) An intracellular protein that binds amyloid-beta peptide and mediates neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 389:689–695
Ye G, Tse AC, Yung W (1997) Taurine inhibits rat substantia nigra pars reticulata neurons by activation of GABA- and glycine-linked chloride conductance. Brain Res 749:175–179
Youdim MB, Ben Shachar D, Riederer P (1989) Is Parkinson’s disease a progressive siderosis of substantia nigra resulting in iron and melanin induced neurodegeneration? Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 126:47–54
Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (2001) PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell 7:673–682
Zhang Y, McLaughlin R, Goodyer C, LeBlanc A (2002) Selective cytotoxicity of intracellular amyloid beta peptide-42 through p53 and Bax in cultured primary human neurons. J Cell Biol 156:519–529
Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, Lincoln S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Uitti RJ, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ, Pfeiffer RF, Patenge N, Carbajal IC, Vieregge P, Asmus F, Müller-Myhsok B, Dickson DW, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Wszolek ZK, Gasser T (2004) Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant Parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 44:601–607
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by the James and Esther King Biomedical Research Program, Florida Department of Health (grant #: 09KW-11), and the Schmidt Foundation, Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine, Florida Atlantic University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menzie, J., Pan, C., Prentice, H. et al. Taurine and central nervous system disorders. Amino Acids 46, 31–46 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1382-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1382-z