Abstract
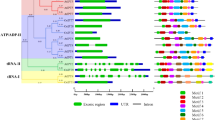
Sulfur (S) is an essential macronutrient required by plants. Plants absorb and transport S through sulfate transporters (SULTRs). In this study, we cloned 8 SULTR genes (CsSULTR1;1/1;2/2;1/3;1/3;2/3;3/3;5/4;1) from tea plant (Camellia sinensis), all of which contain a typical sulfate transporter and antisigma factor antagonist (STAS) conserved domain. Phylogenetic tree analysis further divided the CsSULTRs into four main groups. Many cis-acting elements related to hormones and environmental stresses were found within the promoter sequence of CsSULTRs. Subcellular localization results showed that CsSULTR4;1 localized in the vacuolar membrane and that other CsSULTRs localized to the cellular membrane. The tissue-specific expression of the 8 CsSULTR genes showed different expression patterns during the active growing period and dormancy period. In particular, the expression of CsSULTR1;1 was highest in the roots, but that of CsSULTR1;2 was lowest in the dormancy period. The expression of CsSULTR1;1/1;2/2;1/3;2 was stimulated under different concentrations of selenium (Se) and S; moreover, CsSULTR1;2/2;1/3;3/3;5 was upregulated in response to different valences of Se.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- S:
-
Sulfur
- Se:
-
Selenium
- SULTRs:
-
Sulfate transporters
- CsSULTRs:
-
Sulfate transporters of tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- h-GSH:
-
Homo-GSH
- PCs:
-
Phytochelatins
- TMDs:
-
Transmembrane domains
- STAS:
-
Sulfate transporter and antisigma factor antagonist
References
Adhikari S, Ghosh S, Azahar I, Adhikari A, Hossain Z (2008) Sulfate improves cadmium tolerance by limiting cadmium accumulation, modulation of sulfur metabolism and antioxidant defense system in maize. Environ Exp Bot 153:143–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.05.008
Akiko MN, Yumiko N, Akiko WT, Tomoyuki Y, Hideki T (2004) Induction of SULTR1;1 sulfate transporter in Arabidopsis roots involves protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation circuit for transcriptional regulation. Plant Cell Physiol 45:340–345. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pch029
Anjum NA, Ritu G, Manjeri K, Mirza H, Eduarda P, Iqbal A, Narendra T, Gill SS (2015) ATP-sulfurylase, sulfur-compounds, and plant stress tolerance. Front Plant Sci 6:210. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00210
Arvy MP (1993) Selenate and selenite uptake and translocation in bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris). J Exp Bot 44:1083–1087. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/44.6.1083
Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2019) Role of selenium in plants against abiotic stresses: phenological and molecular aspects. Mol Plant Abiot Stress:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119463665.ch7
Barberon M, Berthomieu P, Clairotte M, Shibagaki N, Davidian JC, Gosti F (2008) Unequal functional redundancy between the two Arabidopsis thaliana high-affinity sulphate transporters SULTR1;1 and SULTR1;2. New Phytol 180:608–619. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02604.x
Buchner P, Parmar S, Kriegel A, Carpentier M, Hawkesford MJ (2010) The sulfate transporter family in wheat: tissue-specific gene expression in relation to nutrition. Mol Plant 3:374–389. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssp119
Cao MJ, Wang Z, Wirtz M, Hell R, Xiang CB (2012) SULTR3;1 is a chloroplast-localized sulfate transporter in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 73:607–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12059
El Kassis E, Cathala N, Rouached H, Fourcroy P, Berthomieu P, Terry N, Davidian JC (2007) Characterization of a selenate-resistant Arabidopsis mutant. Root growth as a potential target for selenate toxicity. Plant Physiol 143:1231–1241. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.091462
Feng RW, Wei CY, Tu SX (2013) The roles of selenium in protecting plants against abiotic stresses. Environ Exp Bot 87:58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.09.002
Galeas ML, Zhang LH, Freeman JL, Wegner M, Pilon-Smits EAH (2006) Seasonal fluctuations of selenium and sulfur accumulation in selenium hyperaccumulators and related nonaccumulators. New Phytol 173:517–525. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01943.x
Gigolashvili T, Kopriva S (2014) Transporters in plant sulfur metabolism. Front Plant Sci 5:442. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00442
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2011) Cadmium stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Signal Behav 6:215–222. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.6.2.14880
Gupta M, Gupta S (2016) An overview of selenium uptake, metabolism, and toxicity in plants. Front Plant Sci 7:2074. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.02074
Han W, Hu D, Shi Y, Ma L (2004) Sulphur nutrition of tea plant: a review of present studies and research prospects. Tea Sci 04:227–234. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2004.04.001
Hankuil Yi, Geoffrey E. Ravilious, Ashley Galant, Hari B. Krishnan, Joseph M. Jez, (2010) From sulfur to homoglutathione: thiol metabolism in soybean. Amino Acids 39 (4):963-978
Hao X, Horvath D, Chao W, Yang Y, Wang X, Xiao B (2014) Identification and evaluation of reliable reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Int J Mol Sci 15:22155–22172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222155
Hu YR, Yue C, Zhou C, Huang YT, Cao HL, Hao XY, Wang XC, Zeng JM (2015) Cloning and expression analysis of sulfate transporter CsSUL3.5 gene in tea plant. Acta Horticulturae Sin, (in Chinese with English abstract) 42:208–216. https://doi.org/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0513
Huang Q, Wang M, Xia Z (2018) The SULTR gene family in maize (Zea mays L.): gene cloning and expression analyses under sulfate starvation and abiotic stress. J Plant Physiol 220:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2017.10.010
Kataoka T (2004) Root-to-shoot transport of sulfate in Arabidopsis. Evidence for the role of SULTR3;5 as a component of low-affinity sulfate transport system in the root vasculature. Plant Physiol 136:4198–4204. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.045625
Kataoka T, Watanabe-Takahashi A, Hayashi N, Ohnishi M, Mimura T, Buchner P, Hawkesford MJ, Yamaya T, Takahashi H (2004) Vacuolar sulfate transporters are essential determinants controlling internal distribution of sulfate in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2693–2704. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.023960
Kumar S, Asif MH, Chakrabarty D, Tripathi RD, Trivedi PK (2011) Differential expression and alternative splicing of rice sulphate transporter family members regulate sulphur status during plant growth, development and stress conditions. FunctIntegrative Genomics 11:259–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-010-0207-y
Li HF, Mcgrath SP, Zhao FJ (2008) Selenium uptake, translocation and speciation in wheat supplied with selenate or selenite. New Phytol 178:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02343.x
Nazar R, Iqbal N, Masood A, Syeed S, Khan NA (2011) Understanding the significance of sulfur in improving salinity tolerance in plants. Environ Exp Bot 70:80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.09.011
Otte ML, (2004). Sulfur transport and assimilation in plants: regulation, interaction and signaling. * Davidian J-C, Grill D, De Kok L. J, Stulen I, Hawkesford MJ, Schnug E, Rennenberg H, eds. 2003. * Leiden: Backhuys Publishers. 96 (hardback). 393 pp. Annals of Botany 94: 480. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mch145
Pilon-Smits EAH (2015) Selenium in Plants. In: Lüttge U, Beyschlag W. (eds) Progress in Botany. Progress in Botany (Genetics - Physiology - Systematics - Ecology), vol 76. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08807-5_4
Pilon-Smits EA, Quinn CF, Tapken W, Malagoli M, Schiavon M (2009) Physiological functions of beneficial elements. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.04.009
Pommerrenig B, Diehn TA, Bienert GP (2015) Metalloido-porins: essentiality of Nodulin 26-like intrinsic proteins in metalloid transport. Plant Sci Int J Exp Plant BioL 238:212–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.06.002
Quinn CF, Galeas ML, Freeman JL, Pilon-Smits EAH (2010) Selenium: deterrence, toxicity, and adaptation. Integr Environ Assess Manag 3:460–462. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.5630030317
Rennenberg H, Herschbach C, Haberer K, Kopriva S (2007) Sulfur metabolism in plants: are trees different? Plant Biol 9:620–637. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-965248
Rouached H, Berthomieu P, Kassis EE, Cathala N, Catherinot V, Labesse G, Fourcroy P (2005) Structural and functional analysis of the C-terminal STAS (sulfate transporter and anti-sigma antagonist) domain of the Arabidopsis thaliana sulfate transporter SULTR1.2. J Biol Chem 280:15976–15983. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M501635200
Rouached H, Wirtz M, Alary R, Hell R, Arpat AB, Davidian J-C, Fourcroy P, Berthomieu P (2008) Differential regulation of the expression of two high-affinity sulfate transporters, SULTR1.1 and SULTR1.2, in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 147:897–911. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.118612
Saithong T, Saerue S, Kalapanulak S, Sojikul P, Narangajavana J, Bhumiratana S (2015) Gene co-expression analysis inferring the crosstalk of ethylene and gibberellin in modulating the transcriptional acclimation of cassava root growth in different seasons. PLoS One 10:e0137602. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137602
Shibagaki N, Grossman AR (2006) The role of the STAS domain in the function and biogenesis of a sulfate transporter as probed by random mutagenesis *. J Biol Chem 281:22964–22973. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m603462200
Shibagaki N, Rose A, McDermott JP, Fujiwara T, Hayashi H, Yoneyama T, Davies JP (2010) Selenate-resistant mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana identify Sultr1;2, a sulfate transporter required for efficient transport of sulfate into roots. Plant J 29:475–486. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0960-7412.2001.01232.x
Smith FW, Ealing PM, Hawkesford MJ, Clarkson DT (1995) Plant members of a family of sulfate transporters reveal functional subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:9373–9377. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.20.9373
Takahashi H (2019) Sulfate transport systems in plants: functional diversity and molecular mechanisms underlying regulatory coordination. J Exp Bot 70:4075–4087. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz132
Takahashi H, Watanabe-Takahashi A, Smith FW, Blake-Kalff M, Saito K (2001) The roles of three functional transporters involved in uptake and translocation of sulphate in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 23:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00768.x
Terry N, Souza MP, Am TAZ (2000) Selenium in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:401–432. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.51.1.401
Thiry C, Ruttens A, Temmerman LD, Schneider Y-J, Pussemier L (2012) Current knowledge in species-related bioavailability of selenium in food. Food Chem 130:767–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.102
Tolu J, Thiry Y, Bueno MT Jolivet C, Potin-Gautier M, Le Hécho I, (2014). Distribution and speciation of ambient selenium in contrasted soils, from mineral to organic rich. Sci Total Environ 93-101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.079
Tombuloglu H, Filiz E, Aydın M, Koc I (2017) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of sulphate transporter (SULTR) genes under sulfur deficiency in Brachypodium distachyon. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 26:263–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-016-0388-0
Urr J, Ucking H, Mult S, Wildhagen H, Palme K, Rennenberg H, Ditengou F, Herschbach C (2010) Seasonal and cell type specific expression of sulfate transporters in the phloem of Populus reveals tree specific characteristics for SO4 (2-) storage and mobilization. Plant Mol Biol 72:499–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9587-6
Vatansever R, Koc I, Ozyigit II, Sen U, Filiz E (2016) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of sulfate transporter (SULTR) genes in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Planta 244:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2575-6
Wan Y, Yu Y, Wang Q, Qiao Y, Li H (2016) Cadmium uptake dynamics and translocation in rice seedling: influence of different forms of selenium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.07.001
Wang XY (2011) Subcellular localization of the sulfate transporter gene OsST in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Anhui Agric Sci 39:10190–10191. https://doi.org/10.13989/j.cnki.0517-6611.2011.17.179
Wang L, Yao L, Hao X, Li N, Qian W, Yue C, Ding C, Zeng J, Yang Y, Wang X (2018) Tea plant SWEET transporters: expression profiling, sugar transport, and the involvement of CsSWEET16 in modifying cold tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 96:577–592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-018-0716-y
White PJ (2004) Interactions between selenium and sulphur nutrition in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 55:1927–1937. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh192
Wipf D, Mongelard GL, van Tuinen D, Gutierrez L, Casieri L (2014) Transcriptional responses of Medicago truncatula upon sulfur deficiency stress and arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Front Plant Sci 5:680. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00680
Xing, K., (2015). Studies on soil - plant selenium content and migration in Shi Tai mountain village, Chi Zhou. Anhui normal university (Doctoral dissertation) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yamaguchi, C.; Maruyamanakashita, A., (2017). Sulfate transporters involved in Cd-induced changes of sulfate uptake and distribution in Arabidopsis thaliana.199-205. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56526-2_20
Yan G, Tian Q, Zhang WH (2013) Systemic regulation of sulfur homeostasis in Medicago truncatula. Planta 239:79–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1958-1
Yoshimoto N (2003) Phloem-localizing sulfate transporter, sultr1;3, mediates re-distribution of sulfur from source to sink organs in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 131:1511–1517. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.014712
Yoshimoto N, Inoue E, Watanabe-Takahashi A, Saito K, Takahashi H (2007) Posttranscriptional regulation of high-affinity sulfate transporters in Arabidopsis by sulfur nutrition. Plant Physiol 145:378–388. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.105742
Yu Y, Zhuang Z, Luo L, Wang Y, Li H (2019) Difference between selenite and selenate in selenium transformation and the regulation of cadmium accumulation in Brassica chinensis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:24532–24541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05705-x
Yue C, Cao HL, Wang L, Zhou YH, Huang YT, Hao XY, Wang YC, Wang B, Yang YJ, Wang XC (2015) Effects of cold acclimation on sugar metabolism and sugar-related gene expression in tea plant during the winter season. Plant Mol Biol 88:591–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0345-7
Zawislanski PT, Benson SM, TerBerg R, Borglin SE (2003) Selenium speciation, solubility, and mobility in land-disposed dredged sediments. Environ Sci Technol 37:2415–2420. https://doi.org/10.1021/es020977z
Zhang JJ, Qian WJ, Hao XY, Wang L, Ding CQ, Yao LN, Wang XC, Zeng JM (2018) Cloning and expression analysis of CsSULTR3.1 implicated in sulfate and selenate treatments in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Acta Horticulturae Sin, (in Chinese with English abstract) 45:321–332. https://doi.org/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0792
Zhao XQ, Mitani N, Yamaji N, Shen RF, Ma JF (2010) Involvement of silicon influx transporter OsNIP2;1 in selenite uptake in rice. Plant Physiol 153:1871–1877. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.157867
Funding
This work was supported by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (1610212016001), the Agricultural Sciences and Technology Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (ASTIP), the Special R & D Program Project of Chinese Academy of Se-enriched Industry (2019QCY-1.2), and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-XTCX20190025-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JMZ, XH, and LW conceived and designed the experiments. HZ, JJZ, and LG performed the experiments. HZ, JJZ, and YW analyzed the data and prepared some figures and tables. NL, XH, and HR provided advice on the analysis and interpretation of the data. HZ, JJZ, and YW prepared some figures and tables. HZ and XH wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Néstor Carrillo
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Hao, X., Zhang, J. et al. Genome-wide identification of SULTR genes in tea plant and analysis of their expression in response to sulfur and selenium. Protoplasma 259, 127–140 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-021-01643-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-021-01643-z