Abstract
Mutual interactions between plant and rhizosphere bacteria facilitate plant growth and reduce risks of biotic and abiotic stresses. The present study demonstrates alleviation of salt stress in Brassica rapa L. ssp. perkinensis (Chinese cabbage) by Herbaspirillum sp. strain GW103 isolated from rhizosphere soil of Phragmites australis. The strain was capable of producing plant beneficial factors, such as auxin, siderophore, and 1-aminocylopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase. Treatment of strain GW103 on Chinese cabbage under salt stress increased K+/Na+ ratio in roots generating balance in the ratio of ion homeostasis and consequently contributed to the increase of biomass. In addition, root colonization potential of the strain was observed by green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagging approach. These results strongly suggest the beneficial impact of strain GW103 by inducing the alleviation of salt stress and development of stress tolerance in Chinese cabbage via plant-microbe interaction.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Azeem SAM, Elwan MWM, Sung JK, Ok YS (2012) Alleviation of salt stress in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) by plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 43:1303–1315
Bao Y, Lies DP, Fu H, Roberts GP (1991) An improved Tn7-based system for the single-copy insertion of cloned genes into chromosomes of Gram-negative bacteria. Gene 109:167–168
Bleecker AB, Kende H (2000) Ethylene: a gaseous signal molecule in plants. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:1–18
Chen Z, Newman I, Zhou M, Mendham N, Zhang G, Shabala S (2005) Screening plants for salt tolerance by measuring K+ flux: a case study for barley. Plant Cell Environ 28:1230–1246
Cheng Z, Park E, Glick BR (2007) 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase from Pseudomonas putida UW4 facilitates the growth of canola in the presence of salt. Can J Microbiol 53:912–918
Choi KH, Schweizer HP (2006) Mini-Tn7 insertion in bacteria with single attTn7 sites: example Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat Protoc 1:153–161
Figurski DH, Helinski DR (1979) Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1648–1652
Glick BR (2005) Modulation of plant ethylene levels by the bacterial enzyme ACC deaminase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 251:1–7
Glick BR, Penrose DM, Li J (1998) A model for the lowering of plant ethylene concentrations by plant growth-promoting bacteria. J Theor Biol 190:63–68
Gordon SA, Weber RP (1951) Colorimetric estimation of indoleacetic acid. Plant Physiol 26:192–195
Greenway H, Munns R (1980) Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 31:149–190
James EK, Olivares FL (1998) Infection and colonization of sugar cane and other graminaceous plants by endophytic diazotrophs. Crit Rev Plant Sci 17:77–119
Karthikeyan S et al (2004) Structural analysis of Pseudomonas 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase complexes: insight into the mechanism of a unique pyridoxal-5′-phosphate dependent cyclopropane ring-opening reaction. Biochemistry 43:13328–13339
Kessler B, de Lorenzo V, Timmis KN (1992) A general system to integrate lacZ fusions into the chromosomes of Gram-negative eubacteria: regulation of the Pm promoter of the TOL plasmid studied with all controlling elements in monocopy. Mol Gen Genet 233:293–301
Koch B, Jensen LE, Nybroe O (2001) A panel of Tn7-based vectors for insertion of the gfp marker gene or for delivery of cloned DNA into Gram-negative bacteria at a neutral chromosomal site. J Microbiol Methods 45:187–195
Kohler J, Hernández JA, Caravaca F, Roldán A (2009) Induction of antioxidant enzymes is involved in the greater effectiveness of a PGPR versus AM fungi with respect to increasing the tolerance of lettuce to severe salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 65:245–252
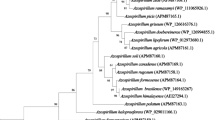
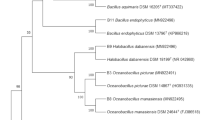
Lee GW, Lee KJ, Chae JC (2012) Genome sequence of Herbaspirillum sp. strain GW103, a plant growth-promoting bacterium. J Bacteriol 194:4150
Moradi F, Ismail AM (2007) Responses of photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence and ROS-scavenging systems to salt stress during seedling and reproductive stages in rice. Ann Bot 99:1161–1173
Morgan PW, Drew MC (1997) Ethylene and plant responses to stress. Physiol Plant 100:620–630
Penrose DM, Glick BR (2001) Levels of ACC and related compounds in exudate and extracts of canola seeds treated with ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting bacteria. Can J Microbiol 47:368–372
Penrose DM, Glick BR (2003) Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol Plant 118:10–15
Rajendran G, Sing F, Desai AJ, Archana G (2008) Enhanced growth and nodulation of pigeon pea by co-inoculation of Bacillus strains with Rhizobium spp. Bioresour Technol 99:4544–4550
Rhoades JD, Loveday J (1990) Salinity in irrigated agriculture. In: Stewart BA and Nielsen DR (ed) Irrigation of agricultural crops. Agron Monogr, 30, Madison, WI, p 1089–1142,
Roncato-Maccari LD et al (2003) Endophytic Herbaspirillum seropedicae expresses nif genes in gramineous plants. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45:39–47
Shilev S, Sancho ED, Benlloch-Gonzalez M (2012) Rhizospheric bacteria alleviate salt-produced stress in sunflower. J Environ Manage 95(Suppl):S37–41
Shukla PS, Agarwal PK, Jha B (2012) Improved salinity tolerance of Arachis hypogaea (L.) by the interaction of halotolerant plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. J Plant Growth Regul 31:195–206
Siddikee MA, Glick BR, Chauhan PS, Yim W, Sa T (2011) Enhancement of growth and salt tolerance of red pepper seedlings (Capsicum annuum L.) by regulating stress ethylene synthesis with halotolerant bacteria containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase activity. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:427–434
Singh JS, Pandey VC, Singh DP (2011) Efficient soil microorganisms: a new dimension for sustainable agriculture and environmental development. Agr Ecosyst Environ 140:339–353
Skoog DA, West DM, Holler FJ, Crouch SR (1999) Analytical chemistry: an introduction, 7th edn. Brooks Cole, Philadelphia, pp 594–631, Chapter 23
Upadhyay SK, Singh JS, Singh DP (2011) Exopolysaccharide-producing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria under salinity condition. Pedosphere 21:214–222
Yao L, Wu Z, Zheng Y, Kaleem I, Li C (2010) Growth promotion and protection against salt stress by Pseudomonas putida Rs-198 on cotton. Eur J Soil Biol 46:49–54
Yildrim E, Donmez MF, Turan M (2008) Use of bioinoculants in ameliorative effects on radish plants under salinity stress. J Plant Nutr 31:2059–2074
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out with the support of “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ009801)” Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling Editor: Bhumi Nath Tripathi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, G.W., Lee, KJ. & Chae, JC. Herbaspirillum sp. strain GW103 alleviates salt stress in Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis . Protoplasma 253, 655–661 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0872-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0872-8