Abstract
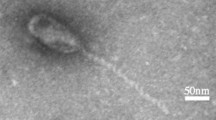
This work describes the characterization and genome annotation of a new lytic Enterococcus faecalis siphovirus, vB_EfaS_AL3 (referred to as AL3), isolated from wastewater samples collected in Liaoning Province, China. The genome of phage AL3 is composed of linear double-stranded DNA that is 40,789 bp in length with a G + C content of 34.84% and 61 putative protein-coding genes. Phylogenetic and comparative genomic analyses indicate that phage AL3 should be considered a novel phage.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias CA, Murray BE (2012) The rise of the Enterococcus: beyond vancomycin resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:266–278
Bebeacua C, Lorenzo Fajardo JC, Blangy S, Spinelli S, Bollmann S, Neve H, Cambillau C, Heller KJ (2013) X-ray structure of a superinfection exclusion lipoprotein from phage TP-J34 and identification of the tape measure protein as its target. Mol Microbiol 89:152–165
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Cheng M, Zhang Y, Li X, Liang J, Hu L, Gong P, Zhang L, Cai R, Zhang H, Ge J, Ji Y, Guo Z, Feng X, Sun C, Yang Y, Lei L, Han W, Gu J (2017) Endolysin LysEF-P10 shows potential as an alternative treatment strategy for multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecalis infections. Sci Rep 7:10164
Liang L, Zhao H, An B, Tang L (2018) High-resolution structure of podovirus tail adaptor suggests repositioning of an octad motif that mediates the sequential tail assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:313–318
Livornese LL Jr, Dias S, Samel C, Romanowski B, Taylor S, May P, Pitsakis P, Woods G, Kaye D, Levison ME et al (1992) Hospital-acquired infection with vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium transmitted by electronic thermometers. Ann Intern Med 117:112–116
Pell LG, Kanelis V, Donaldson LW, Howell PL, Davidson AR (2009) The phage lambda major tail protein structure reveals a common evolution for long-tailed phages and the type VI bacterial secretion system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:4160–4165
Penades JR, Chen J, Quiles-Puchalt N, Carpena N, Novick RP (2015) Bacteriophage-mediated spread of bacterial virulence genes. Curr Opin Microbiol 23:171–178
Schattner P, Brooks AN, Lowe TM (2005) The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W686–W689
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Yuksel SA, Thompson KD, Ellis AE, Adams A (2001) Purification of Piscirickettsia salmonis and associated phage particles. Dis Aquat Organ 44:231–235
Zhang W, Mi Z, Yin X, Fan H, An X, Zhang Z, Chen J, Tong Y (2013) Characterization of Enterococcus faecalis phage IME-EF1 and its endolysin. PLoS One 8:e80435
Zhang X, Wang Y, Li S, An X, Pei G, Huang Y, Fan H, Mi Z, Zhang Z, Wang W, Chen Y, Tong Y (2015) A novel termini analysis theory using HTS data alone for the identification of Enterococcus phage EF4-like genome termini. BMC Genomics 16:414
Acknowledgements
The authors thank members of Professor Yigang Tong’s group at the Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology for help with sequence analysis.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean (Grant no. 201405003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Johannes Wittmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Y., Zhao, F., Wang, L. et al. Complete genome analysis of the novel Enterococcus faecalis phage vB_EfaS_AL3. Arch Virol 164, 2599–2603 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04341-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04341-7