Summary.
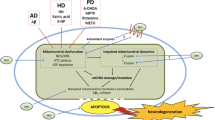
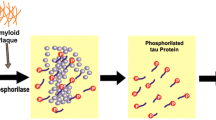
This review summarizes recent advancements in our understanding of the potential role of the amyloid β protein in Alzheimer's disease. It also discusses the significance of amyloid β in initiating the generation of partially reduced oxygen species and points out their role in damaging essential macromolecules in the CNS which leads to neuronal dysfunction and loss. Recently acquired experimental data links these destructive oxidative processes with some neurodegenerative aspects of Alzheimer's disease. The experimental findings related to the free radical scavenging and antioxidative properties of melatonin are tabulated and its efficacy and the likely mechanisms involved in its ability to reduce neuronal damage mediated by oxygen-based reac-tive species in experimental models of Alzheimer's disease are summarized. Besides the direct scavenging properties and indirect antioxidant actions of melatonin, its ability to protect neurons probably also stems from its antiamyloidogenic properties. Melatonin is also unique because of the ease with which it passes through the blood-brain barrier.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received June 28, 1999, accepted August 12, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pappolla, M., Chyan, YJ., Poeggeler, B. et al. An assessment of the antioxidant and the antiamyloidogenic properties of melatonin: implications for Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm 107, 203–231 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050018
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050018