Abstract
Background
There is still no clear guideline for surgical treatment for patients with medically refractory trigeminal neuralgia (TN). When it comes to which surgical treatment to choose, microvascular decompression (MVD) or Gamma Knife surgery (GKS), we should know the long-term outcome of each treatment.
Methods
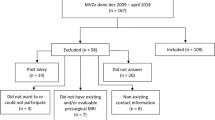
We analyzed 179 patients undergoing MVD and 52 patients undergoing GKS followed for 1 year or longer. We evaluated the patient’s neurological status including pain relief, complications and recurrence. Results were assessed with Barrow Neurological Institute (BNI) pain intensity and facial numbness scores. Overall outcomes were compared between the two groups based on pain relief and complications.
Results
BNI pain intensity and facial numbness scores at the final visit were significantly lower in the MVD group than in the GKS group (P < 0.001, P = 0.04, respectively). Overall outcomes were superior following MVD than following GKS (P < 0.001). Following whichever treatment, there were initially high rates of pain-free status “without medication”: 96.6% in the MVD group and 96.2% in the GKS group. However, 6.1% in the MVD group and 51.9% in the GKS group fell into a “with medication” state within median periods of 1.83 and 3.92 years, respectively (P < 0.001). Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that pain recurred more often and later in the GKS group than in the MVD group (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Considering the long-term outcomes, MVD should be chosen as the initial surgical treatment for patients with medically refractory TN.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker FG 2nd, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD (1996) The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med 334:1077–1083
Berger I, Nayak N, Schuster J, Lee J, Stein S, Malhotra NR (2017) Microvascular decompression versus stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a decision analysis. Cureus 9:e1000
Brisman R (2007) Microvascular decompression vs. Gamma Knife radiosurgery for typical trigeminal neuralgia: preliminary findings. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85:94–98
Dai ZF, Huang QL, Liu HP, Zhang W (2016) Efficacy of stereotactic Gamma Knife surgery and microvascular decompression in the treatment of primary trigeminal neuralgia: a retrospective study of 220 cases from a single center. J Pain Res 26:535–542
Hayashi M, Chernov M, Tamura N, Taira T, Izawa M, Yomo S, Nagai M, Chang CS, Ivanov P, Tamura M, Muragaki Y, Okada Y, Iseki H, Takakura K (2011) Stereotactic radiosurgery of essential trigeminal neuralgia using Leksell Gamma Knife model C with automatic positioning system: technical nuances and evaluation of outcome in 130 patients with at least 2 years follow-up after treatment. Neurosurg Rev 34:497–508
Hitchon PW, Holland M, Noeller J, Smith MC, Moritani T, Jerath N, He W (2016) Options in treating trigeminal neuralgia: experience with 195 patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 149:166–170
Inoue T, Hirai H, Shimizu T, Tsuji M, Shima A, Suzuki F, Matsuda M (2012) Ocular neuromyotonia treated by microvascular decompression: usefulness of preoperative 3D imaging: case report. J Neurosurg 117:1166–1169
Inoue T, Hirai H, Shima A, Suzuki F, Fukushima T, Matsuda M (2017) Diagnosis and management for trigeminal neuralgia caused solely by venous compression. Acta Neurochir 159:681–688
Kalkanis SN, Eskandar EN, Carter BS, Barker FG 2nd (2003) Microvascular decompression surgery in the United States, 1996 to 2000: mortality rates, morbidity rates, and the effects of hospital and surgeon volumes. Neurosurgery 52:1251–1261
Kondo A, Date I, Endo S, Fujii K, Fujii Y, Fujimaki T, Hasegawa M, Hatayama T, Hongo K, Inoue T, Ishikawa M, Ito M, Kayama T, Kohmura E, Matsushima T, Munemoto S, Nagahiro S, Ohno K, Okamura T, Ryu H, Shigeno T, Shirane R, Tagusagawa Y, Tanabe H, Yamada K, Yamakami I (2012) A proposal for standardized analysis of the results of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia and hemifacial spasm. Acta Neurochir 154:773–778
Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC, Young RF, Vermeulen S, Duma CM, Jacques DB, Rand RW, Regis J, Peragut JC, Manera L, Epstein MH, Lindquist C (1996) Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a multiinstitutional study using the gamma unit. J Neurosurg 84:940–945
Linskey ME, Ratanatharathorn V, Peñagaricano J (2008) A prospective cohort study of microvascular decompression and Gamma Knife surgery in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 109:160–172
Martínez Moreno NE, Gutiérrez-Sárraga J, Rey-Portolés G, Jiménez-Huete A, Martínez Álvarez R (2016) Long-term outcomes in the treatment of classical trigeminal neuralgia by Gamma Knife radiosurgery: a retrospective study in patients with minimum 2-year follow-up. Neurosurgery 79:879–888
Matsuda S, Serizawa T, Nagano O, Ono J (2008) Comparison of the results of 2 targeting methods in Gamma Knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 109:185–189
Matsushima T, Yamaguchi T, Inoue TK, Matsukado K, Fukui M (2000) Recurrent trigeminal neuralgia after microvascular decompression using an interposing technique. Teflon felt adhesion and the sling retraction technique. Acta Neurochir 142:557–561
Nanda A, Javalkar V, Zhang S, Ahmed O (2015) Long term efficacy and patient satisfaction of microvascular decompression and Gamma Knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia. J Clin Neurosci 22:818–822
Oesman C, Mooij JJA (2011) Long-term follow-up of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Skull Base 21:313–322
Pollock BE, Schoeberl KA (2010) Prospective comparison of posterior fossa exploration and stereotactic radiosurgery dorsal root entry zone target as primary surgery for patients with idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 67:633–638
Régis J, Metellus P, Hayashi M, Roussel P, Donnet A, Bille-Turc F (2006) Prospective controlled trial of Gamma Knife surgery for essential trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 104:913–924
Régis J, Tuleasca C, Resseguier N, Carron R, Donnet A, Gaudart J, Levivier M (2016) Long-term safety and efficacy of Gamma Knife surgery in classical trigeminal neuralgia: a 497-patient historical cohort study. J Neurosurg 124:1079–1087
Rogers CL, Shetter AG, Fiedler JA, Smith KA, Han PP, Speiser BL (2000) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: the initial experience of the Barrow Neurological Institute. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:1013–1019
Sindou M, Leston J, Decullier E, Chapuis F (2007) Microvascular decompression for primary trigeminal neuralgia: long-term effectiveness and prognostic factors in a series of 362 consecutive patients with clear-cut neurovascular conflicts who underwent pure decompression. J Neurosurg 107:1144–1153
Sindou M, Leston JM, Decullier E, Chapuis F (2008) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: the importance of a noncompressive technique—Kaplan-Meier analysis in a consecutive series of 330 patients. Neurosurgery 63:341–350
Sindou M, Leston J, Howeidy T, Decullier E, Chapuis F (2006) Micro-vascular decompression for primary trigeminal neuralgia (typical or atypical). Long-term effectiveness on pain; prospective study with survival analysis in a consecutive series of 362 patients. Acta Neurochir 148:1235–1245
Tatli M, Satici O, Kanpolat Y, Sindou M (2008) Various surgical modalities for trigeminal neuralgia: literature study of respective long-term outcomes. Acta Neurochir 150:243–255
Wang DD, Raygor KP, Cage TA, Ward MM, Westcott S, Barbaro NM, Chang EF (2017) Prospective comparison of long-term pain relief rates after first-time microvascular decompression and stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 24:1–10
Zhang H, Lei D, You C, Mao BY, Wu B, Fang Y (2013) The long-term outcome predictors of pure microvascular decompression for primary trigeminal neuralgia. World Neurosurg 79:756–762
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Satomi Fujimura and Ms. Lori Radcliffe for assistance with data collection and English language editing.
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, T., Hirai, H., Shima, A. et al. Long-term outcomes of microvascular decompression and Gamma Knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a retrospective comparison study. Acta Neurochir 159, 2127–2135 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3325-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3325-7