Abstract.
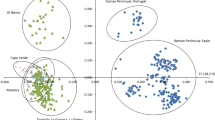
Genetic variation and structure of ten wild, three domesticated and one wild-cultivated populations of pepper (Capsicum annuum) from northwestern Mexico were studied in order to find out if the domestication process has reduced the genetic variation of the modern cultivars of this species. The analysis was based on 12 polymorphic loci from nine isozymes. Wild populations were sampled in different habitats along a latitudinal gradient of ca. 500 km. All populations had high genetic variation (i.e. wild: A = 2.72, P = 90.8%, He = 0.445; wild-cultivated: A = 2.50, P = 92.3%, He = 0.461; domesticated: A = 2.60, P = 84.6%, He = 0.408), indicating little genetic erosion in modern cultivars of pepper. Genetic diversity estimated by Nei's method showed that most genetic variation is found within, rather than among populations. However, genetic differentiation is greater among cultivated (G ST=0.167) than among wild (G ST=0.056) populations. Wild populations had an average genetic identity (I) of 0.952, indicating little differentiation and high gene flow (Nm=4.21) among these populations. Average genetic identity between wild and domesticated populations was of I=0.818, revealing that the domestication process has modified the genetic composition of commercial varieties of pepper. Changes in genetic composition among commercial varieties seem to have occurred in different directions, as indicated by the average value of I = 0.817 among these populations. The high level of diversity found in wild populations of C. annuum suggests that the wild relatives of cultivated peppers are a valuable genetic resource which must be conserved.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received May 5, 1999 Accepted October 30, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández-Verdugo, S., Luna-Reyes, R. & Oyama, K. Genetic structure and differentiation of wild and domesticated populations of Capsicum annuum (Solanaceae) from Mexico. Plant Syst. Evol. 226, 129–142 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s006060170061
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s006060170061