Abstract
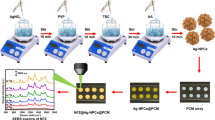
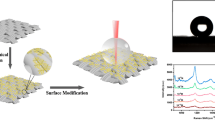
Silver nanocubes monolayer-modified polydimethylsiloxane (Ag NC/PDMS) flexible SERS substrates have been prepared by a three-phase interface self-assembly procedure. The combination of this method with membrane technology brings nanoparticles in close proximity, densely, and regularly arranged in monolayers over a large area, leading to excellent SERS properties. Considering the complexity of practical detection, molecular imprinted polymers (MIPs) were anchored on the surface of SERS substrate and applied to selective detection of microcystin-LR (MC-LR). It is worth mentioning that the SERS imprinted membranes (AP-MIMs) were still clearly detected at a concentration of 0.1 µg·L−1 of MC-LR in drinking water, and the detection limit was as low as 0.0067 µg·L−1. The substrate exhibited excellent uniformity with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of 6.1%. In the presence of interference molecules, AP-MIMs exhibited excellent selectivity for MC-LR. Furthermore, in the spiking and recovery tests of practical lake water samples, the method showed excellent recoveries ranging from 96.47 to 105.31%. It has been demonstrated that the prepared AP-MIMs can be applied to sensitive and specific detection of trace amounts of MC-LR in drinking water.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
He SX, Xie WY, Fang SX, Zhou DM, Djebbi K, Zhang ZY, Du JL, Du CL, Wang DQ (2018) Label-free identification of trace microcystin-LR with surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectra. Talanta 195:401–406
Zegura B, Straser A, Filipic M (2011) Genotoxicity and potential carcinogenicity of cyanobacterial toxins-a review. Mutat Res-Fund Mol M 727:16–41
Birbeck JA, Westrick JA, O’Neill GM, Spies B, Szlag DC (2019) Comparative analysis of microcystin prevalence in Michigan lakes by online concentration LC/MS/MS and ELISA. Toxins 11(1):13
Shen F, Xu YJ, Wang Y, Chen J, Shi JZ (2021) Rapid determination of microcystins and nodularin in surface water by on-line solid-phase extraction (SPE) with ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Instrum Sci Technol 49:233–243
Zhang H, Li YS, Abdallah MF, Tan HG, Li JX, Liu SY, Zhang R, Sun FF, Li Y, Yang SP (2023) Novel one-point calibration strategy for high-throughput quantitation of microcystins in freshwater using LC-MS/MS. Sci Total Environ 858:159345
Talamini L, Zanato N, Zapp E, Brondani D, Vieira IC (2018) Direct electrochemical nano-immunosensor for microcystin-LR in seawater. Electroanal 30:819–827
Ding SY, Yi J, Li JF, Ren B, Wu DY, Panneerselvam R, Tian ZQ (2016) Nanostructure-based plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for surface analysis of materials. Nat Rev Mater 1:16021
Santos LP, Kinnear C, Juste JP, Mulvaney P, Liz-Marzán LM (2018) Plasmonic polymer nanocomposites. Nat Rev Mater 3:375–391
Jiang CY, Wu T, Liu JX, Wang YP (2020) Application of a thermo-sensitive imprinted SERS substrate to the rapid trace detection of ofloxacin. Anal Methods-UK 12(39):4783–4788
Gao MS, Miao P, Han XJ, Sun C, Ma Y, Gao YL, Xu P (2019) Hollow transition metal hydroxide octahedral microcages for single particle surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Inorg Chem Front 6(9):2318–2324
Wang KQ, Sun DW, Pu HB, Wei QY (2021) Polymer multilayers enabled stable and flexible Au@Ag nanoparticle array for nondestructive SERS detection of pesticide residues. Talanta 223:121782
Yang YY, Li YT, Li XJ, Zhang L, Fodjo EK, Han S (2020) Controllable in situ fabrication of portable AuNP/mussel-inspired polydopamine molecularly imprinted SERS substrate for selective enrichment and recognition of phthalate plasticizers. Chem Eng J 402:125179
Luo XJ, Zhao XJ, Wallace GQ, Brunet MH, Wilkinson KJ, Wu P, Cai CX, Bazuin CG, Masson JF (2021) Multiplexed SERS detection of microcystins with aptamer-driven core-satellite assemblies. ACS App Mater Interfaces 13(5):6545–6556
Wang H, Li KB, Xu C, Xu SC, Li GH (2019) Large-scale solvothermal synthesis of Ag nanocubes with high SERS activity. J Alloy Compd 772:150–156
Barveen NR, Wang TJ, Chang YH (2021) Photochemical synthesis of Ag/Au/AgCl heterostructure from Ag nanowires as a reusable SERS substrate for ultrasensitive detection of analgesics and antibiotics. Chem Eng J 423:130191
Yadav S, Senapati S, Desai D, Gahlaut SH, Kulkarni S, Singh JP (2021) Portable and sensitive Ag nanorods based SERS platform for rapid HIV-1 detection and tropism determination. Colloid Surfaces B 198:111477
Leis AG, Arreba IR, Cortes SS (2017) Morphological tuning of plasmonic silver nanostars by controlling the nanoparticle growth mechanism: application in the SERS detection of the amyloid marker Congo red. Colloid Surface A 535:49–60
Li KG, Wang Y, Jiang K, Ren Y, Dai YQ, Lu YH, Wang P (2017) Free-standing Ag triangle arrays with configurable vertical gap for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanotechnology 28:385401
Liu YQ, Guan HY, Lin S, Dong HY, Hasi WL, Dong B (2022) Plasmonic nanosensor based on Ag nanocubes of high purification by extraction filtration strategy for SERS determination of malachite green in aquaculture water. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 358:131515
Zhan HR, Cheng FS, Chen YQ, Wong KW, Mei J, Hui D, Lau WM, Liu Y (2016) Transfer printing for preparing nanostructured PDMS film as flexible SERS active substrate. Compos Part B-Eng 84:222–227
Xia DC, Jiang PP, Cai ZW, Zhou R, Tu B, Gao N, Chang G, He HP, He YB (2022) Ag nanocubes monolayer-modified PDMS as flexible SERS substrates for pesticides sensing. Microchim Acta 189:232
Lin X, Fang GQ, Liu YL, He YY, Wang L, Dong B (2020) Marangoni effect-driven transfer and compression at three-phase interfaces for highly reproducible nanoparticle monolayers. J Phys Chem Lett 11:3573–3581
Carneiro MCCG, Castillo AS, Duarte MAC, Sales MGF (2019) Dual biorecognition by combining molecularly-imprinted polymer and antibody in SERS detection. Application to carcinoembryonic antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 146:111761
Zhu YY, Wu L, Yan H, Lu ZC, Yin WM, Han HY (2020) Enzyme induced molecularly imprinted polymer on SERS substrate for ultrasensitive detection of patulin. Anal Chim Acta 1101:111–119
Ren XH, Cheshari EC, Qi JY, Li X (2018) Silver microspheres coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer as a SERS substrate for sensitive detection of bisphenol A. Microchim Acta 185:242
Li YT, Yang YY, Sun YX, Cao Y, Huang YS, Han S (2020) Electrochemical fabrication of reduced MoS2-based portable molecular imprinting nanoprobe for selective SERS determination of theophylline. Microchim Acta 187:203
Saxena S, Lakshmi GBVS, Chauhan D, Solanki PR (2020) Molecularly imprinted polymer-based novel electrochemical sensor for the selective detection of aldicarb. Phys Status Solidi A 217:1900599
Karthika P, Shanmuganathan S, Viswanathan S, Matos CD (2021) Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensor for the determination of endocrine disruptor bisphenol-A in bovine milk. Food Chem 363:130287
Hu R, Tang R, Xu JY, Lu F (2018) Chemical nanosensors based on molecularly-imprinted polymers doped with silver nanoparticles for the rapid detection of caffeine in wastewater. Anal Chim Acta 1034:176–183
Jiang CY, Wu T, He X, Wang YP, Lian HZ (2022) Preparation of thermo-sensitive molecular imprinted SERS substrate with robust recyclability for detection of ofloxacin. Chemosensors 10(11):437
Li QQ, Gong SS, Zhang H, Huang FZ, Zhang LN, Li SK (2019) Tailored necklace-like [email protected] core/shell heterostructure nanowires for high-performance plasmonic SERS detection. Chem Eng J 371:26–33
Siekkinen AR, McLellan JM, Chen JY, Xia YN (2006) Rapid synthesis of small silver nanocubes by mediating polyol reduction with a trace amount of sodium sulfide or sodium hydrosulfide. Chem Phys Lett 432:491–496
Li HJ, Wang JF, Fang HQ, Xu HD, Yu HC, Zhou TY, Liu CB, Che GB, Wang DD (2022) Hydrophilic modification of PVDF-based SERS imprinted membrane for the selective detection of L-tyrosine. J Environ Manage 304:114260
Hu BX, Pu HB, Sun DW (2023) Flexible Au@AgNRs/CMC/qPCR film with enhanced sensitivity, homogeneity and stability for in-situ extraction and SERS detection of thiabendazole on fruits. Food Chem 423:135840
Yang HY, Song H, Suo ZQ, Li FN, Jin QY, Zhu X, Chen Q (2022) A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on surface imprinted polymerization and boric acid affinity for selective and sensitive detection of P-glycoproteins. Anal Chim Acta 1207:339797
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 21906062), the Natural Science Foundation Project of Jilin Province (YDZJ202201ZYTS356, YDZJ202101ZYTS073), and the Project of Education Department of Jilin Province (JJKH20230807CY, JJKH20230508KJ, JJKH20220431KJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Zhang, L., Sun, L. et al. Self-assembly flexible SERS imprinted membrane based on Ag nanocubes for selective detection of microcystin-LR. Microchim Acta 191, 19 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06096-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06096-0