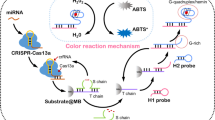
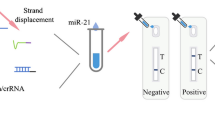
Abstract
A separation platform has been developed mediated by a combination of magnetic beads and the CRISPR/Cas12a system to achieve ultrasensitive and rapid detection of miRNA-21 at a low level. In this system, with the assistance of an auxiliary probe, the target miRNA-21 can be specifically combined with three-stranded probes to initiate the SDR reaction. Abundant aptamer A3 was added to the solution that can activate the CRISPR/Cas12a system and initiate the trans-cleavage reaction to recover the fluorescence signal. Using magnetic beads to mediate the separation considerably greatly improves the signal conversion efficiency and detection sensitivity. At the 492 nm excitation wavelength, and 502–650 nm scan range, through analyzing the fluorescence peak intensity at 520 nm, the biosensor’s determination range and limit of detection is 8 fM-250 nM and 2.42 fM, respectively, and the RSD is 19.03–37.80. Compared with other biosensors, the biosensor developed exhibited superior performance and the signal recovered excellently in 1% human serum and the LOD is 12.12 fM. This method provides a novel highly sensitive scheme for detecting miRNA .
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 4357043:834–838
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu C-G, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, Harris CC, Croce CM (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1037:2257–2261
Hampton T (2010) Scientists Probe MicroRNAs’ Role in Cancer. JAMA 30311:1025–1025
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 611:857–866
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O’Briant KC, Allen A, Lin DW, Urban N, Drescher CW, Knudsen BS, Stirewalt DL, Gentleman R, Vessella RL, Nelson PS, Martin DB, Tewari M (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 10530:10513–10518
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs — microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 64:259–269
Xiaolin W, Yong H, Bryan M, Bin G (2021) MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Gut 704:784
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu C-G, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Ménard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin GA, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) MicroRNA Gene Expression Deregulation in Human Breast Cancer. Can Res 6516:7065–7070
Lee J-W, Choi CH, Choi J-J, Park Y-A, Kim S-J, Hwang SY, Kim WY, Kim T-J, Lee J-H, Kim B-G, Bae D-S (2008) Altered MicroRNA Expression in Cervical Carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 149:2535–2542
Xu H, Zheng Y, Chen D, Cheng Y, Fang X, Zhong C, Huang X, Huang Q, Xu J, Xu J, Xue C (2023) Branch-Shaped Trapping Device Regulates Accelerated Catalyzed Hairpin Assembly and Its Application for MicroRNA In Situ Imaging. Anal Chem 952:1210–1218
Wang J, Sun J, Zhang J, Shen C, Zhang X, Xu J (2022) Engineered G-Quadruplex-Embedded Self-Quenching Probes Regulate Single Probe-Based Multiplex Isothermal Amplification to Light Road Lamp Probes for Sensitized Determination of microRNAs. Anal Chem 9410:4437–4445
Xue T, Liang W, Li Y, Sun Y, Xiang Y, Zhang Y, Dai Z, Duo Y, Wu L, Qi K, Shivananju B N, Zhang L A-O, Cui X, Zhang H A-O, Bao Q A-O X. Ultrasensitive detection of miRNA with an antimonene-based surface plasmon resonance sensor. 2041–1723 (Electronic):
Peng H, Newbigging AM, Reid MS, Uppal JS, Xu J, Zhang H, Le XC (2020) Signal Amplification in Living Cells: A Review of microRNA Detection and Imaging. Anal Chem 921:292–308
Chang H, Lv J, Zhang H, Zhang B, Wei W, Qiao Y (2017) Photoresponsive colorimetric immunoassay based on chitosan modified AgI/TiO2 heterojunction for highly sensitive chloramphenicol detection. Biosens Bioelectron 87:579–586
Lai W, Wei Q, Xu M, Zhuang J, Tang D (2017) Enzyme-controlled dissolution of MnO2 nanoflakes with enzyme cascade amplification for colorimetric immunoassay. Biosens Bioelectron 89:645–651
Lin X-C, Wang X-N, Liu L, Wen Q, Yu R-Q, Jiang J-H (2016) Surface Enhanced Laser Desorption Ionization of Phospholipids on Gold Nanoparticles for Mass Spectrometric Immunoassay. Anal Chem 8820:9881–9884
Otieno BA, Krause CE, Jones AL, Kremer RB, Rusling JF (2016) Cancer Diagnostics via Ultrasensitive Multiplexed Detection of Parathyroid Hormone-Related Peptides with a Microfluidic Immunoarray. Anal Chem 8818:9269–9275
Kurt H, Yüce M, Hussain B, Budak H (2016) Dual-excitation upconverting nanoparticle and quantum dot aptasensor for multiplexed food pathogen detection. Biosens Bioelectron 81:280–286
Ngo HT, Gandra N, Fales AM, Taylor SM, Vo-Dinh T (2016) Sensitive DNA detection and SNP discrimination using ultrabright SERS nanorattles and magnetic beads for malaria diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron 81:8–14
Oishi M, Sugiyama S (2016) An Efficient Particle-Based DNA Circuit System: Catalytic Disassembly of DNA/PEG-Modified Gold Nanoparticle-Magnetic Bead Composites for Colorimetric Detection of miRNA. Small 1237:5153–5158
Li X, Chen B, He M, Hu B (2021) A dual-functional magnetic microsphere for ICP-MS quantification and fluorescence imaging of matrix metalloproteinase 2 in cell secretion. Anal Chim Acta 1161:338479
Zhou J, Cheng M, Zeng L, Liu W, Zhang T, Xing D (2016) Specific capture of the hydrolysate on magnetic beads for sensitive detecting plant vacuolar processing enzyme activity. Biosens Bioelectron 79:881–886
Barrangou R, Fremaux C, Deveau H, Richards M, Boyaval P, Moineau S, Romero DA, Horvath P (2007) CRISPR Provides Acquired Resistance Against Viruses in Prokaryotes. Science 3155819:1709–1712
Gootenberg JS, Abudayyeh OO, Kellner MJ, Joung J, Collins JJ, Zhang F (2018) Multiplexed and portable nucleic acid detection platform with Cas13, Cas12a, and Csm6. Science 3606387:439–444
Koonin EV, Makarova KS, Zhang F (2017) Diversity, classification and evolution of CRISPR-Cas systems. Curr Opin Microbiol 37:67–78
Li Y, Teng X, Zhang K, Deng R, Li J (2019) RNA Strand Displacement Responsive CRISPR/Cas9 System for mRNA Sensing. Anal Chem 916:3989–3996
Marraffini LA, Sontheimer EJ (2008) CRISPR Interference Limits Horizontal Gene Transfer in Staphylococci by Targeting DNA. Science 3225909:1843–1845
Petri K, Pattanayak V (2018) SHERLOCK and DETECTR Open a New Frontier in Molecular Diagnostics. CRISPR J 13:209–211
Chen JS, Ma E, Harrington LB, Da Costa M, Tian X, Palefsky JM, Doudna JA (2018) CRISPR-Cas12a target binding unleashes indiscriminate single-stranded DNase activity. Science 3606387:436–439
Li S-Y, Cheng Q-X, Liu J-K, Nie X-Q, Zhao G-P, Wang J (2018) CRISPR-Cas12a has both cis- and trans-cleavage activities on single-stranded DNA. Cell Res 284:491–493
Zhang D, Yan Y, Que H, Yang T, Cheng X, Ding S, Zhang X, Cheng W (2020) CRISPR/Cas12a-Mediated Interfacial Cleaving of Hairpin DNA Reporter for Electrochemical Nucleic Acid Sensing. ACS Sensors 52:557–562
Yuan C, Tian T, Sun J, Hu M, Wang X, Xiong E, Cheng M, Bao Y, Lin W, Jiang J, Yang C, Chen Q, Zhang H, Wang H, Wang X, Deng X, Liao X, Liu Y, Wang Z, Zhang G, Zhou X (2020) Universal and Naked-Eye Gene Detection Platform Based on the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/Cas12a/13a System. Anal Chem 925:4029–4037
Li H, Zhao W, Pu J, Zhong S, Wang S, Yu R (2022) Combining functional hairpin probes with disordered cleavage of CRISPR/Cas12a protease to screen for B lymphocytic leukemia. Biosens Bioelectron 201:113941
Zhao W, Liu M, Li H, Wang S, Tang S, Kong R-M, Yu R (2019) Ultra-sensitive label-free electrochemical detection of the acute leukaemia gene Pax-5a based on enzyme-assisted cycle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 143:111593
Shen Z-F, Li F, Jiang Y-F, Chen C, Xu H, Li C-C, Yang Z, Wu Z-S (2018) Palindromic Molecule Beacon-Based Cascade Amplification for Colorimetric Detection of Cancer Genes. Anal Chem 905:3335–3340
Shen H, Qileng A, Yang H, Liang H, Zhu H, Liu Y, Lei H, Liu W (2021) “Dual-Signal-On” Integrated-Type Biosensor for Portable Detection of miRNA: Cas12a-Induced Photoelectrochemistry and Fluorescence Strategy. Anal Chem 9334:11816–11825
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No: 22164011, 21565015, 21663014), and the State Key Laboratory of Chemical Biosensing & Chemometrics.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China,22164011,hongbo li
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, H., Zhao, W. et al. Development of a separation platform comprising magnetic beads combined with the CRISPR/Cas12a system enabling ultrasensitive and rapid detection of miRNA-21. Microchim Acta 190, 458 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06038-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06038-w