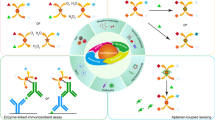
Abstract
Based on the highly specific interaction between concanavalin A (Con A) and glucose (Glu), a competitive electrochemiluminescence (ECL) biosensor was constructed for ultrasensitive detection of Con A. Nanocomposites with excellent electrocatalytic and photothermal properties were obtained by covalently bonding zinc oxide quantum dots (ZnO QDs) to vanadium carbide MXene (V2C MXene) surfaces. The modification of ZnO QDs hinders the aggregation of V2C MXene and increases the catalytic activity of oxygen reduction reaction, thus amplifying the luminol cathodic emission. In addition, the excellent photothermal performance of the V2C MXene-ZnO QDs can convert light energy into heat energy under the irradiation of 808 nm near infrared laser, thus increasing the temperature of the reaction system and accelerating the electron transfer process to realize the synergistic amplified homogeneous ECL system. This innovative work not only enriches the fundamental research on multifunctional MXene nanomaterials for biosensing, but also provides an effective strategy for ECL signal amplification.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharon N, Lis H (1972) Lectins: Cell-Agglutinating and Sugar-Specific Proteins: Lectins provide new tools for studying polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and cell surfaces, and for cancer research. Science. 177(4053):949-959. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.177.4053.949
Becker JW, Reeke GN, Cunningham BA, Edelman GM (1976) New evidence on the location of the saccharide-binding site of concanavalin A. Nature 259(5542):406–409. https://doi.org/10.1038/259406a0
Jang H, Lee C, Hwang Y, Lee SJ (2021) Concanavalin A: coordination diversity to xenobiotic metal ions and biological consequences. Dalton Trans 50:17817–17831. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1dt03501k
Sharon N, Lis H (1989) Lectins as cell recognition molecules. Science 246(4927):227–234. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2552581
Heymann F, Hamesch K, Weiskirchen R, Tacke F (2015) The concanavalin A model of acute hepatitis in mice. Lab Anim 49(1_suppl):12–20. https://doi.org/10.1177/0023677215572841
Huang CF, Yao GH, Liang RP, Qiu JD (2013) Graphene oxide and dextran capped gold nanoparticles based surface plasmon resonance sensor for sensitive detection of concanavalin A. Biosens Bioelectron 50:305–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.07.002
Wang T-H, Lee M-H, Su N-W (2009) Screening of lectins by an enzyme-linked adsorbent assay. Food Chem 113:1218–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.08.024
Gao Y, Wu Y, Di J (2017) Colorimetric detection of glucose based on gold nanoparticles coupled with silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 173:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.09.023
Sha Q, Guan R, Su H, Zhang L, Liu B-F, Hu Z, Liu X (2020) Carbohydrate-protein template synthesized high mannose loading gold nanoclusters: a powerful fluorescence probe for sensitive Concanavalin A detection and specific breast cancer cell imaging. Talanta 218:121130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121130
Liu X, Ou X, Lu Q, Chen S, Wei S (2014) A biorecognition system for concanavalin a using a glassy carbon electrode modified with silver nanoparticles, dextran and glucose oxidase. Microchimica Acta 182:797–803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1390-7
Sun C, Shen Y, Zhang Y, Du Y, Peng Y, Xie Q (2023) Sandwich photoelectrochemical biosensing of concanavalin A based on CdS/AuNPs/NiO Z-scheme heterojunction and lectin-sugar binding. Talanta 253:123882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123882
Fang C, Li H, Yan J, Guo H, Yifeng T (2017) Progress of the electrochemiluminescence biosensing strategy for clinical diagnosis with luminol as the sensing probe. ChemElectroChem 4:1587–1593. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201700465
Liu X, Qi W, Gao W, Liu Z, Zhang W, Gao Y, Xu G (2014) Remarkable increase in luminol electrochemiluminescence by sequential electroreduction and electrooxidation. Chem Commun (Camb) 50:14662–14665. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc06633b
Zhuo Y, Wang HJ, Lei YM, Zhang P, Liu JL, Chai YQ, Yuan R (2018) Electrochemiluminescence biosensing based on different modes of switching signals. Analyst 143:3230–3248. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8an00276b
Wang JX, Zhuo Y, Zhou Y, Wang HJ, Yuan R, Chai YQ (2016) Ceria doped zinc oxide nanoflowers enhanced luminol-based electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for amyloid-beta detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:12968–12975. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b00021
Wu FF, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Yuan R, Chai YQ (2018) Electrochemiluminescence peptide-based biosensor with hetero-nanostructures as coreaction accelerator for the ultrasensitive determination of tryptase. Anal Chem 90:2263–2270. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04631
Zou R, Xie R, Peng Y, Guan W, Lin Y, Lu C (2022) Ag–O–Co interface modulation-amplified luminol cathodic electrogenerated chemiluminescence. Anal Chem 94(11):4813–4820. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00050
Gaillard F, Sung YE, Bard AJ (1999) Hot electron generation in aqueous solution at oxide-covered tantalum electrodes. Reduction of methylpyridinium and electrogenerated chemiluminescence of Ru(bpy)(3)(2+). J Phys Chem B 103:667–674. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp982821k
Kankare J, Fäldén K, Kulmala S, Haapakka K (1992) Cathodically induced time-resolved lanthanide(III) electroluminescence at stationary aluminium disc electrodes. Anal Chim Acta 256(1):17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2670(92)85320-6
Wang X, Shang L, Zhang W, Jia LP, Ma RN, Jia WL, Wang HS (2019) An ultrasensitive luminol cathodic electrochemiluminescence probe with highly porous Pt on ionic liquid functionalized graphene film as platform for carcinoembryonic antigen sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 141:111436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111436
Haghighi B, Tavakoli A, Bozorgzadeh S (2015) Cathodic electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol on glassy carbon electrode modified with cobalt nanoparticles decorated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Electrochim Acta 154:259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.175
Cao Y, Yuan R, Chai Y, Liu H, Liao Y, Zhuo Y (2013) Amplified cathodic electrochemiluminescence of luminol based on Pd and Pt nanoparticles and glucose oxidase decorated graphene as trace label for ultrasensitive detection of protein. Talanta 113:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.03.018
Xu S, Liu Y, Wang T, Li J (2011) Positive potential operation of a cathodic electrogenerated chemiluminescence immunosensor based on luminol and graphene for cancer biomarker detection. Anal Chem 83:3817–3823. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac200237j
Ho DH, Choi YY, Jo SB, Myoung J-M, Cho JH (2021) Sensing with MXenes: progress and prospects. Adv Mater 33(47):2005846. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202005846
Li K, Liang M, Wang H, Wang X, Huang Y, Coelho J, Pinilla S, Zhang Y, Qi F, Nicolosi V, Xu Y (2020) 3D MXene architectures for efficient energy storage and conversion. Adv Funct Mater 30(47):2000842. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202000842
Zhong Q, Li Y, Zhang G (2021) Two-dimensional MXene-based and MXene-derived photocatalysts: recent developments and perspectives. Chem Eng J 409:128099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.128099
Wu X, Ma P, Sun Y, Du F, Song D, Xu G (2021) Application of MXene in electrochemical sensors: a review. Electroanalysis 33:1827–1851. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202100192
Zhu X, Zhang Y, Liu M, Liu Y (2021) 2D titanium carbide MXenes as emerging optical biosensing platforms. Biosens Bioelectron 171:112730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112730
Ji Hyun C, Don Hui L, Won-Yong L (2023) Enhanced cathodic electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol at a MXene–Nafion composite-modified electrode in neutral aqueous solution. J Electroanal Chem 936:117389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2023.117389
Liu A, Liang X, Ren X, Guan W, Gao M, Yang Y, Yang Q, Gao L, Li Y, Ma T (2020) Recent progress in MXene-based materials: potential high-performance electrocatalysts. Adv Funct Mater 30(38):2003437. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202003437
Fang D, Ren H, Huang Y, Dai H, Huang D, Lin Y (2020) Photothermal amplified cathodic ZnO quantum dots/Ru(bpy)32+/S2O82- ternary system for ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence detection of thyroglobulin. Sens Actuators B 312:127950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127950
Park Y, Yoo R, Park S, Lee JH, Jung H, Lee H-S, Lee W (2019) Highly sensitive and selective isoprene sensing performance of ZnO quantum dots for a breath analyzer. Sens Actuators B 290:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.03.118
Cai G, Yu Z, Tong P, Tang D (2019) Ti(3)C(2) MXene quantum dot-encapsulated liposomes for photothermal immunoassays using a portable near-infrared imaging camera on a smartphone. Nanoscale 11:15659–15667. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr05797h
Zeng R, Wang W, Chen M, Wan Q, Wang C, Knopp D, Tang D (2021) CRISPR-Cas12a-driven MXene-PEDOT:PSS piezoresistive wireless biosensor. Nano Energy 82:105711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105711
Shahzad F, Alhabeb M, Hatter CB, Anasori B, Man Hong S, Koo CM, Gogotsi Y (2016) Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science 353(6304):1137–1140. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aag2421
Huang L, Chen J, Yu Z, Tang D (2020) Self-powered temperature sensor with seebeck effect transduction for photothermal-thermoelectric coupled immunoassay. Anal Chem 92:2809–2814. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05218
Yu Z, Gong H, Xu J, Li Y, Xue F, Zeng Y, Liu X, Tang D (2022) Liposome-embedded Cu(2-x)Ag(x)S nanoparticle-mediated photothermal immunoassay for daily monitoring of cTnI protein using a portable thermal imager. Anal Chem 94:7408–7416. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01133
Li Y, Zhang S, Zhang Q, Xu G, Dai H, Lin Y (2016) Binding-induced internal-displacement of signal-on photoelectrochemical response: a glyphosate detection platform based on graphitic carbon nitride. Sens Actuators B 224:798–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.10.111
Dai H, Gong L, Xu G, Li Y, Li X, Zhang Q, Lin Y (2015) Double-amplified photoelectrochemical response of hematin on carbon nanohorns superstructure support for ultrasensitive detection of roxarsone. Sens Actuators B 215:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.03.027
Yu Z, Gong H, Li M, Tang D (2022) Hollow prussian blue nanozyme-richened liposome for artificial neural network-assisted multimodal colorimetric-photothermal immunoassay on smartphone. Biosens Bioelectron 218:114751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114751
Muhammad F, Guo M, Qi W, Sun F, Wang A, Guo Y, Zhu G (2011) pH-Triggered controlled drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles via intracelluar dissolution of ZnO nanolids. J Am Chem Soc 133:8778–8781. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja200328s
Hong Z, Zhou K, Zhang J, Huang Z, Wei M (2015) Facile synthesis of rutile TiO2 mesocrystals with enhanced sodium storage properties. J Mater Chem A 3:17412–17416. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta04232a
Qian Y, Wei H, Dong J, Du Y, Fang X, Zheng W, Sun Y, Jiang Z (2017) Fabrication of urchin-like ZnO-MXene nanocomposites for high-performance electromagnetic absorption. Ceram Int 43:10757–10762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.05.082
Guo S, Kang S, Feng S, Lu W (2020) MXene-enhanced deep ultraviolet photovoltaic performances of crossed Zn2GeO4 nanowires. J Phys Chem C 124:4764–4771. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c01032
Yu Z, Qiu C, Huang L, Gao Y, Tang D (2023) Microelectromechanical Microsystems-supported photothermal immunoassay for point-of-care testing of Aflatoxin B1 in foodstuff. Anal Chem 95:4212–4219. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05617
Mohrhusen L, Grebien M, Al-Shamery K (2020) Electron transfer in oxide–oxide cocatalysts: interaction of tungsten oxide clusters with Ti3+ states in rutile TiO2. J Phys Chem C 124:23661–23673. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c06591
Chen W-J, Kandasamy K, Chen Y-C (2019) Functional gold nanoparticles as sensing probes for concanavalin A and as imaging agents for cancer cells. ACS Appl Energy Mater 2(6):3348–3357. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b00220
Ma X, Li J, Liu Y, Yuan Y, Xu G (2017) Construction of a concanavalin A electrochemical sensor base on a novel sandwich capture mode. Sens Actuators B 248:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.03.172
Erdoğan Y, Çimen D, Onur MA, Denizli A (2023) Preparation of concanavalin A imprinted surface plasmon resonance based biosensors. IEEE Sensors J 23:11566–11573. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2023.3266286
Xie M, Chen J, Wang Y, Liu B, Song R-B, Meng H-M, Li Z (2023) Ratiometric fluorescence probe for accurate detection of concanavalin A by coupling fluorescent microsphere with boric acid functionalized carbon dots. Chin Chem Lett:108575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2023.108575
Zhao S, Shi C, Hu H, Li Z, Xiao G, Yang Q, Sun P, Cheng L, Niu W, Bi J, Yue Z (2020) ISFET and Dex-AgNPs based portable sensor for reusable and real-time determinations of concanavalin A and glucose on smartphone. Biosens Bioelectron 151:111962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111962
Tang T, Yang F, Wang L, Zhao C, Nie F, GuopingYang (2020) A sandwich electrochemiluminescent assay for determination of concanavalin A with triple signal amplification based on MoS(2)NF@MWCNTs modified electrode and Zn-MOF encapsulated luminol. Mikrochim Acta 187:523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04472-8
Funding
This project was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21877012, 21575024), the National Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2020J02034, 2019J01052063), and the Health-Education Joint Research Project of Fujian Province (2019-WJ-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Huang, Y., Gao, L. et al. Versatile MXene composite probe–mediated homogeneous electrochemiluminescence biosensor with integrated signal transduction and near-infrared modulation strategy for concanavalin A detection. Microchim Acta 190, 372 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05941-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05941-6