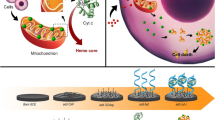
Abstract
A new electrochemiluminescence (ECL) cytosensor is proposed for the simultaneous determination of phosphatidylserine (PS) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) based on the ECL signals of metal-organic framework-5 (MOF-5) loaded CdS quantum dots and N-(aminobutyl)-N-(ethylisoluminol)-polyethylenimine capped Au and Ag nanoparticles. Apoptosis promotes the exposure of PS and reduces the expression of EGFR in cell membranes. Two spatially resolved areas on dual-disk glassy carbon electrodes were designed to eliminate the interference from different ECL probes. Using HepG2 cells treated with resveratrol to induce apoptosis, the cytosensor exhibited high sensitivity, simplicity, and high reproducibility, demonstrating its potential in drug screening and rapid apoptotic cell detection. The strategy reported provides a promising platform for the highly sensitive cytosensing and convenient screening of clinically relevant anticancer drugs.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou B, Qiu Y, Wen Q, Zhu M, Yang P (2017) Dual electrochemiluminescence signal system for in situ and simultaneous evaluation of multiple cell-surface receptors. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:2074–2083. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12411
Yavas S, Macha´n R, Wohland T (2016) The epidermal growth factor receptor forms location-dependent complexes in resting cells. Biophys J 111:2241–2254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2016.09.049
Koseska A, Bastiaens PIH (2022) Processing temporal growth factor patterns by an epidermal growth factor receptor network dynamically established in space. Annu Rev Cell Dev Bi 36:359–383. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-013020-103810
Qiu Y, Wen Q, Zhang L, Yang P (2016) Label-free and dynamic evaluation of cell-surface epidermal growth factor receptor expression via an electrochemiluminescence cytosensor. Talanta 150:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.12.019
Nagata S, Suzuki J, Segawa K, Fujii T (2016) Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the cell surface. Cell Death Differ 23:952–961. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.7
Park M, Kang K (2019) Phosphatidylserine receptor-targeting therapies for the treatment of cancer. Arch Pharm Res 42:617–628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-019-01167-4
Pillai-Kastoori L, Schutz-Geschwender AR, Harford JA (2020) A systematic approach to quantitative western blot analysis. Anal Biochem 593:113608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2020.113608
Ma Y, Lee Y, Best-Popescu C, Gao L (2021) High-speed compressed-sensing fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy of live cells. P Natl Acad Sci USA 118:e2004176118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2004176118
Salmond N, Khanna K, Owen GR, Williams KC (2021) Nanoscale flow cytometry for immunophenotyping and quantitating extracellular vesicles in blood plasma. Nanoscale 13:2012–2025. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr05525e
Zhang X, Wang Z, Wang X, Zhang Y, Qu Z, Ding S (2022) Band-edge effect-induced electrochemiluminescence signal amplification based on inverse opal photonic crystals for ultrasensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Anal Chem 94:9919–9926. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01986
Wang L, Wang B, Kang K, Ji X, Wang B, Li C, Ren J (2022) Electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer system between ruthenium-based nanosheets and CdS quantum dots for detection of chlorogenic acid. Microchim Acta 189:323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05428-w
Li S, Wu Y, Pang C, Ma X, Wang M, Luo J, Zhi X, Li B (2022) Reusable molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence assay for kanamycin based on ordered mesoporous carbon loaded with indium oxide nanoparticles and carbon quantum dots. Microchim Acta 189:431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05527-8
Kong X, Wang C, Pu L, Gai P, Li F (2021) Self-photocatalysis boosted electrochemiluminescence signal amplification via in situ generation of the coreactant. Anal Chem 93:12441–12446. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c02605
Hao N, Wang K (2016) Recent development of electrochemiluminescence sensors for food analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:7035–7048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9548-2
Mo G, He X, Qin D, Meng S, Wu Y, Deng B (2021) Spatially-resolved dual-potential sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for the simultaneous determination of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 and carbohydrate antigen 24-2. Biosens Bioelectron 178:113024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113024
Wang F, Liu Y, Fu C, Li N, Du M, Zhang L, Ge S, Yu J (2021) Paper-based bipolar electrode electrochemiluminescence platform for detection of multiple miRNAs. Anal Chem 93:1702–1708. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04307
Kurup CP, Mohd-Naim NF, Ahmed MU (2022) A solid state electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for β lactoglobulin using Ru AuNP/GNP/Naf nanocomposite modified printed sensor. Microchim Acta 189:165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05275-9
Lu J, Shan XY, Wu Q, Sun Z, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Tian L (2022) Solid-state electrochemiluminescence sensor based on zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 electrospinning nanofibers for chlorpyrifos detection. Microchim Acta 189:298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05398-z
Chen Y, Gou X, Ma C, Jiang D, Zhu J (2021) A synergistic coreactant for single-cell electrochemiluminescence imaging: guanine-rich ssDNA-loaded high-index faceted gold nanoflowers. Anal Chem 93:7682–7689. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c00602
Dong J, Lu Y, Xu Y, Chen F, Yang J, Chen Y, Feng J (2021) Direct imaging of single-molecule electrochemical reactions in solution. Nature 596:244–249. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03715-9
Liu Y, Zhang H, Li B, Liu J, Jiang D, Liu B, Sojic N (2021) Single biomolecule imaging by electrochemiluminescence. J Am Chem Soc 143:17910–17914. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c06673
Cao J, Wang Y, Zhang J, Dong Y, Liu F, Ren S, Liu Y (2018) Immuno-electrochemiluminescent imaging of a single cell based on functional nanoprobes of heterogeneous Ru(bpy)32+@SiO2/Au nanoparticles. Anal Chem 90:10334–10339. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02141
Wang C, Pei Y, Liu P, Li Y, Wang Z (2022) Donor–acceptor structure-dependent electrochemiluminescence sensor for accurate uranium detection in drinking water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10:14665–14670. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c05561
Fan M, Yu H, Fu P, Su Z, Li X, Hu X, Gao F, Pan Q (2021) Luminescent Cd(II) metal-organic frameworks with anthracene nitrogen-containing organic ligands as novel multifunctional chemosensors for the detection of picric acid, pesticides, and ferric ions. Dyes Pigments 185:108834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108834
Liang Z, Qiu T, Gao S, Zhong R, Zou R (2022) Multi-scale design of metal-organic framework-derived materials for energy electrocatalysis. Adv Energy Mater 12:2003410. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202003410
Wang M, Dong R, Feng X (2021) Two-dimensional conjugated metal-organic frameworks (2D c-MOFs): chemistry and function for MOFtronics. Chem Soc Rev 50:2764–2793. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2cs90005j
Qin D, Meng S, Wu Y, Luo Z, Deng B (2022) Construction of efficient electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer sensor based on SnO2/SnS2QDs-Ru@IRMOF-3 composite for sensitive detection of procalcitonin. Microchim Acta 189:430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05519-8
Mo G, Qin D, Jiang X, Zheng X, Mo W, Deng B (2020) A sensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on metal-organic framework and imprinted polymer for squamous cell carcinoma antigen detection. Sensor Actuat B 310:127852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127852
Wang Y, Zhao G, Chi H, Yang S, Niu Q, Wu D, Cao W, Li T, Ma H, Wei Q (2021) Self-luminescent lanthanide metal-organic frameworks as signal probes in electrochemiluminescence immunoassay. J Am Chem Soc 143:504–512. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c12449
Noby H, El-Shazly AH, Elkady MF, Ohshima M (2019) Strong acid doping for the preparation of conductive polyaniline nanoflowers, nanotubes, and nanofibers. Polymer 182:121848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2019.121848
Khosrozadeh A, Darabi MA, Wang Q, Xing M (2017) Polyaniline nanoflowers grown on vibrationisolator-mimetic polyurethane nanofibers for flexible supercapacitors with prolonged cycle life. J Mater Chem A 5:7933–7943. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta00591a
Dai C, Yang J, Hussein WM, Zhao L, Wang X, Khalil ZG, Capon RJ, Toth I, Stephenson RJ (2022) Polyethylenimine: an intranasal adjuvant for liposomal peptide based subunit vaccine against group a streptococcus. ACS Infect Dis 6:2502–2512. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00452
Yang H, Wang H, Xiong C, Chai Y, Yuan R (2017) Intramolecular self-enhanced nanochains functionalized by an electrochemiluminescence reagent and its immunosensing application for the detection of urinary β2-microglobulin. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:36239–36246. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b12011
Zhou B, Zhu M, Hao Y, Yang P (2017) Potential-resolved electrochemiluminescence for simultaneous determination of triple latent tuberculosis infection markers. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:30536–30542. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b10343
Du D, Shu J, Guo M, Haghighatbin MA, Yang D, Bian Z, Cui H (2020) Potential-resolved differential electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for cardiac troponin I based on MOF-5-wrapped CdS quantum dot nanoluminophores. Anal Chem 92:14113–14121. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03131
Zhang L, Jiang J, Luo J, Zhang L, Cai J, Teng J, Yang P (2013) A label-free electrochemiluminescence cytosensors for specific detection of early apoptosis. Biosens Bioelectron 49:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.04.032
Shivaji K, Mani S, Ponmurugan P, Suenne C, Castro SD, Davies ML, Balasubramanian MG, Pitchaimuthu S (2018) Green-synthesis-derived CdS quantum dots using tea leaf extract: antimicrobial, bioimaging, and therapeutic applications in lung cancer cells. ACS Appl Nano Mater 1:1683–1693. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b00147
Pakolpakc A, Draczynski ZJ (2021) Preparation and characterization of the advanced alginate-Based nanofibrous nonwoven using EDC/NHS coupling agent by electrospinning. J Text Inst:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405000.2021.1954806
Liu Y, Schubert DJ (1997) Cytotoxic amyloid peptides inhibit cellular 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction by enhancing MTT formazan exocytosis. J Neurochem 69:2285–2293. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.69062285.x
Zhang X, Li W, Zhou Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2019) An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for microRNA detection based on luminol-functionalized Au NPs@ZnO nanomaterials as signal probe and dissolved O2 as coreactant. Biosens Bioelectron 135:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.04.004
Liu G, Jin B, Ma C, Chen Z, Zhu J (2019) Potential-resolved electrochemiluminescence nanoprobes for visual apoptosis evaluation at single-cell level. Anal Chem 91:6363–6370. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01401
Li X, Chen B, He M, Wang H, Xiao G, Yang B, Hu B (2017) Simultaneous detection of MCF-7 and HepG2 cells in blood by ICP-MS with gold nanoparticles and quantum dots as elemental tags. Biosens Bioelectron 90:343–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.11.030
Liu D, Wang L, Ma S, Jiang Z, Yang B, Han X, Liu S (2015) A novel electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on CdS-coated ZnO nanorods array for HepG2 cell detection. Nanoscale 7:3627–3633. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr06946c
Wu Y, Zhou H, Wei W, Hua X, Wang L, Zhou Z, Liu S (2012) Signal amplification cytosensor for evaluation of drug-induced cancer cell apoptosis. Anal Chem 84:1894–1899. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac202672x
Wu M, Yuan D, Xu J, Chen H (2013) Sensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on Au-ITO hybrid bipolar electrode amplification system for cell surface protein detection. Anal Chem 85:11960–11965. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac402889z
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22164004) and the Guangxi Science Foundation of China (2022GXNSFDA035069).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
The online version contains supplementary material available at (DOCX 4501 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, G., Qin, D., Wu, Y. et al. Dual-potential electrochemiluminescence cytosensor based on a metal-organic framework and ABEI-PEI-Au@AgNPs for the simultaneous determination of phosphatidylserine and epidermal growth factor receptors on an apoptotic cell surface. Microchim Acta 190, 347 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05934-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05934-5