Abstract
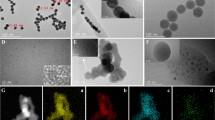
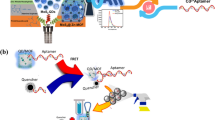
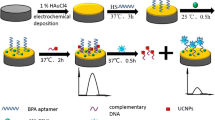
An “on–off-on”-type electrochemiluminescence (ECL) aptamer sensor based on Ru@Zn-oxalate metal–organic framework (MOF) composites is constructed for sensitive detection of sulfadimethoxine (SDM). The prepared Ru@Zn-oxalate MOF composites with the three-dimensional structure provide good ECL performance for the “signal-on.” The MOF structure with a large surface area enables the material to fix more Ru(bpy)32+. Moreover, the Zn-oxalate MOF with three-dimensional chromophore connectivity provides a medium which can accelerate excited-state energy transfer migration among Ru(bpy)32+ units, and greatly reduces the influence of solvent on chromophore, achieving a high-energy Ru emission efficiency. The aptamer chain modified with ferrocene at the end can hybridize with the capture chain DNA1 fixed on the surface of the modified electrode through base complementary pairing, which can significantly quench the ECL signal of Ru@Zn-oxalate MOF. SDM specifically binds to its aptamer to separate ferrocene from the electrode surface, resulting in a “signal-on” ECL signal. The use of the aptamer chain further improves the selectivity of the sensor. Thus, high-sensitivity detection of SDM specificity is realized through the specific affinity between SDM and its aptamer. This proposed ECL aptamer sensor has good analytical performance for SDM with low detection limit (27.3 fM) and wide detection range (100 fM–500 nM). The sensor also shows excellent stability, selectivity, and reproducibility, which proved its analytical performance. The relative standard deviation (RSD) of SDM detected by the sensor is between 2.39 and 5.32%, and the recovery is in the range 97.23 to 107.5%. The sensor shows satisfactory results in the analysis of actual seawater samples, which is expected to play a role in the exploration of marine environmental pollution.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Singh R, Sidhu SS, Zhang H, Huang Q (2015) Removal of sulfadimethoxine in soil mediated by extracellular oxidoreductases[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(21):16868–16874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4893-9
Park JY, Huwe B (2016) Sulfadimethoxine transport in soil columns in relation to sortable and non-sorbable tracers[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(12):12456–12466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6449-z
Okoth OK, Yan K, Liu Y, Zhang J (2016) Graphene-doped Bi2S3 nanorods as visible-light photoelectrochemical aptasensing platform for sulfadimethoxine detection[J]. Biosens Bioelectron 86:636–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.037
Liu Q, Shi T, Cheng Y, Wen Z, Ding C, Li Y, Wang K (2021) Amplified photocurrent signal for fabricating photoelectrochemical sulfadimethoxine aptasensor based on carbon nitride photosensitization with visible/near-infrared light responsive zinc phthalocyanine[J]. J Hazard Mater 406:124749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124749
You F, Zhu M, Ding L, Xu Y, Wang K (2019) Design and construction of Z-scheme Bi2S3/nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots: boosted photoelectric conversion efficiency for high-performance photoelectrochemical aptasensing of sulfadimethoxine[J]. Biosens Bioelectron 130:230–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.058
Dang X, Zhao H, Wang X, Sailijiang T, Chen S, Quan X (2018) Photoelectrochemical aptasensor for sulfadimethoxine using g-C3N4 quantum dots modified with reduced graphene oxide[J]. Microchim Acta 185(7):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2877-4
Li Y, Liu D, Meng S, Zhang J, Li L, You T (2022) Regulation of Ru (bpy)32+ electrochemiluminescence based on distance-dependent electron transfer of ferrocene for dual-signal readout detection of aflatoxin B1 with high sensitivity [J]. Anal Chem 94(2):1294–1301. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04501
Hao Q, Wang L, Niu S, Ding C, Luo X (2020) Ratiometric electrogenerated chemiluminescence sensor based on a designed anti-fouling peptide for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen [J]. Anal Chim Acta 1136:134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.09.033
Huang X, Deng X, Su K, Qi W (2021) Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of Au-Ag bimetallic nanocluster@ CNTs-TiO2 nanocomposites and its use in ultra-sensitive immunosensing for CEA [J]. New J Chem 45(29):13064–13069. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ01409A
Wei X, Qiao X, Fan J, Hao Y, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Xu M (2022) A label-free ECL aptasensor for sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen based on CdS QDs@MOF and TEOA@Au as bi-coreactants of Ru (bpy)32+ [J]. Microchem J 173:106910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106910
Hu Y, Chen Y, Tang Q, Liu H (2021) A sandwich-type ECL immunosensor for the sensitive determination of CEA content based on red emission carbon quantum dots as luminophores [J]. New J Chem 45(28):12613–12621. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ01002F
Zhao XH, Shang L, Zhang W, Jia LP, Ma RN, Wang HS (2021) Sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen based on a low-potential-triggered electrochemiluminescence of tris (2,2’-bipyridine) ruthenium(II) with oxalate as coreactant [J]. J Electroanal Chem 895:115392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115392
Jiang D, Du X, Chen D, Zhou L, Chen W, Li Y, Hao N, Qian J, Liu Q, Wang K (2016) One-pot hydrothermal route to fabricate nitrogen doped graphene/Ag-TiO2: Efficient charge separation, and high-performance “on-off-on” switch system based photoelectrochemical biosensing [J]. Biosens Bioelectron 83:149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.04.042
Zhao M, Zhuo Y, Chai YQ, Yuan R (2015) Au nanoparticles decorated C60 nanoparticle-based label-free electrochemiluminesence aptasensor via a novel “on-off-on” switch system [J]. Biomaterials 52:476–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.02.058
Fan Y, Chen S, Wei S, Guo G, Li Y (2020) A simple “on–off–on” ECL sensor for glucose determination based on Pd nanowires and Ag doped gC3N4 nanosheets [J]. Anal Methods 12(1):8–17. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AY02357G
Xu R, Du Y, Ma H, Wu D, Ren X, Sun X, Wei Q, Ju H (2021) Photoelectrochemical aptasensor based on La2Ti2O7/Sb2S3 and V2O5 for effectively signal change strategy for cancer marker detection [J]. Biosens Bioelectron 192:113528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113528
Kitte SA, Bushira FA, Li H, Jin Y (2021) Electrochemiluminescence of Ru (bpy)32+/thioacetamide and its application for the sensitive determination of hepatotoxic thioacetamide [J]. Analyst 146(16):5198–5203. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AN00862E
Asif M, Aziz A, Ashraf G, Wang Z, Wang J, Azeem M, Chen X, Xiao F, Liu H (2018) Facet-inspired core-shell gold nanoislands on metal oxide octadecahedral heterostructures: high sensing performance toward sulfide in biotic fluids [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(43):36675–36685. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b12186
Asif M, Aziz A, Wang Z, Ashraf G, Wang J, Luo H, Chen X, Xiao F, Liu H (2019) Hierarchical CNTs@ CuMn layered double hydroxide nanohybrid with enhanced electrochemical performance in H2S detection from live cells [J]. Anal Chem 91(6):3912–3920. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04685
Asif M, Aziz A, Ashraf G, Shuang D, Aziz A, Zhang G, Xiao F, Liu H (2018) Facet-inspired core–shell gold nanoislands on metal oxide octadecahedral heterostructures: high sensing performance toward sulfide in biotic fluids [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(43):36675–36685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.010
Asif M, Liu H, Aziz A, Wang H, Wang Z, Ajmal M, Xiao F, Liu H (2017) Core-shell iron oxide-layered double hydroxide: high electrochemical sensing performance of H2O2 biomarker in live cancer cells with plasma therapeutics [J]. Biosens Bioelectron 97:352–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.05.057
Asif M, Aziz A, Ashraf G, Iftikhar T, Sun Y, Xiao F, Liu H (2022) Unveiling microbiologically influenced corrosion engineering to transfigure damages into benefits: A textile sensor for H2O2 detection in clinical cancer tissues [J]. Chem Eng J 427:131398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131398
Asif M, Aziz A, Wang H, Wang Z, Wang W, Ajmal M, Xiao F, Chen X, Liu H (2019) Superlattice stacking by hybridizing layered double hydroxide nanosheets with layers of reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid [J]. Microchim Acta 186:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3158-y
Hu GB, Xiong CY, Liang WB, Zeng XS, Xu HL, Yang Y, Yao LY, Yuan R, Xiao DR (2018) Highly stable mesoporous luminescence-functionalized MOF with excellent electrochemiluminescence property for ultrasensitive immunosensor construction [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(18):15913–15919. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b05038
Yang HY, Wang HJ, Xiong CY, Chai YQ, Yuan R (2017) Intramolecular self-enhanced nanochains functionalized by an electrochemiluminescence reagent and its immunosensing application for the detection of urinary β2-microglobulin [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(41):36239–36246. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b12011
Farah K, Müller-Plathe F, Böhm MC (2012) Classical reactive molecular dynamics implementations: state of the art [J]. ChemPhysChem 13(5):1127–1151. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201100681
Vojoudi H, Bastan B, Ghasemi JB, Badiei A (2019) An ultrasensitive fluorescence sensor for determination of trace levels of copper in blood samples [J]. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:5593–5603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01940-w
Mohammadi ZG (2020) Green method for the synthesis of indeno [1, 2-B] pyridines using Fe3O4@sio2@ pr-So3H as nanomagnetic catalyst [J]. Iranian Journal of Catalysis 10(1):65–70
Vojoudi H, Ghasemi JB, Hajihosseinloo A, Bastan B, Badiei A (2021) One-pot synthesis of hematite-alumina hollow sphere composite by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique with high adsorption capacity toward PAHs [J]. Adv Powder Technol 32(4): 1060–1069.Bastan, B., & Badiei, A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2021.02.015
Modheji M, Emadi H, Vojoudi H (2020) Efficient pre-concentration of As (III) in food samples using guanidine-modified magnetic mesoporous silica [J]. J Porous Mater 27:971–978. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-020-00873-5
Vojoudi H, Badiei A, Vojoudi E (n.d.) System and method for treating chemical byproducts using ultrasonic irradiation: U.S. Patent Application 16/600,459[P]. 2021–4–15
Adil K, Belmabkhout Y, Pillai RS, Cadiau A, Bhatt PM, Assen AH, Maurin G, Eddaoudi M (2017) Gas/vapour separation using ultra-microporous metal-organic frameworks: insights into the structure/separation relationship [J]. Chem Soc Rev 46(11):3402–3430. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS00153C
Qiao X, Su B, Liu C, Song Q, Luo D, Mo G, Wang T (2018) Selective surface enhanced Raman scattering for quantitative detection of lung cancer biomarkers in superparticle@ MOF structure [J]. Adv Mater 30(5):1702275. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201702275
Hu PP (2017) Recent advances in aptamers targeting immune system [J]. Inflammation 40(1):295–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0437-9
You H, Bai L, Yuan Y, Zhou J, Bai Y, Mu Z (2018) An amperometric aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of sulfadimethoxine based on exonuclease-assisted target recycling and new signal tracer for amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 117:706–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.06.011
Zhao G, Wang Y, Li X, Yue Q, Dong X, Du B, Cao W, Wei Q (2019) Dual-quenching electrochemiluminescence strategy based on three-dimensional metal-organic frameworks for ultrasensitive detection of amyloid-β [J]. Anal Chem 91(3):1989–1996. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04332
Bai W, Cui A, Liu M, Qiao X, Li Y, Wang T (2019) Signal-off electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensing platform based on the quenching effect between ferrocene and Ru(bpy)32+-functionalized metal-organic frameworks for the detection of methylated RNA [J]. Anal Chem 91(18):11840–11847. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02569
Kent CA, Liu D, Ito A, Zhang T, Brennaman MK, Meyer TJ, Lin W (2013) Rapid energy transfer in non-porous metal-organic frameworks with caged Ru (bpy)32+ chromophores: oxygen trapping and luminescence quenching [J]. J Mater Chem A 1(47):14982–14989. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14009A
Feng Y, Sun F, Wang N, Lei J, Ju H (2017) Ru (bpy) 32+ incorporated luminescent polymer dots: double-enhanced electrochemiluminescence for detection of single-nucleotide polymorphism[J]. Anal Chem 89(14):7659–7666. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01603
Xu Z, Chang Y, Chai Y, Wang H, Yuan R (2019) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for speedy detection of microRNA based on a DNA rolling machine and target recycling [J]. Anal Chem 91(7):4883–4888. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00728
Turco A, Corvaglia S, Mazzotta E (2015) Electrochemical sensor for sulfadimethoxine based on molecularly imprinted polypyrrole: study of imprinting parameters [J]. Biosens Bioelectron 63:240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.07.045
Bai Z, Chen Y, Li F, Zhou Y, Yin H, Ai S (2019) Electrochemical aptasensor for sulfadimethoxine detection based on the triggered cleavage activity of nuclease P1 by aptamer-target complex [J]. Talanta 204:409–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.06.035
Yang Z, Ding X, Guo Q, Wang Y, Lu Z, Ou H, Luo Z, Luo X (2017) Second generation of signaling-probe displacement electrochemical aptasensor for detection of picomolar ampicillin and sulfadimethoxine [J]. Sens Actuators B Chem 253:1129–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.119
Wang A, Zhao H, Chen X, Tan B, Zhang Y, Quan X (2017) A colorimetric aptasensor for sulfadimethoxine detection based on peroxidase-like activity of graphene/nickel@palladium hybrids [J]. Anal Biochem 525:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2017.03.006
Song KM, Jeong E, Jeon W, Jo H, Ban C (2012) A coordination polymer nanobelt (CPNB)-based aptasensor for sulfadimethoxine [J]. Biosens Bioelectron 33(1):113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.12.034
Razmi N, Baradaran B, Hejazi M, Hasanzadeh M, Mosafer J, Mokhtarzadeh A, de la Guardia M (2018) Recent advances on aptamer-based biosensors to detection of platelet-derived growth factor. Biosens Bioelectron 113:58–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.04.048
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51973102), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong (ZR2022MB042, ZR2019MB067), Qinghai Provincial Basic Research Program (2021-ZJ-710), Innovation Ability Improvement Project of Science and Technology Small and Medium-Size Enterprise in Shandong Province (2022TSGC1121) and Talent Fund of QUST (2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Xu, X., Zheng, L. et al. A signal “on–off-on”-type electrochemiluminescence aptamer sensor for detection of sulfadimethoxine based on Ru@Zn-oxalate MOF composites. Microchim Acta 190, 131 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05701-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05701-6