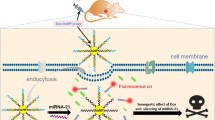
Abstract
MicroRNA-21 is an important biomarker of tumor early prediction and metastasis, and its accurate detection is of great significance for tumor diagnosis and treatment. It will be a meaningful work to combine the detection of RNA with chemotherapy and photothermal therapy on the same composite material. Herein, we designed a multifunctional nanocomposite based on gold nanorods (AuNRs), making use of microRNA-triggered drug release and near-infrared photothermal effect, which has been developed for cancer therapy and microRNA-21detection. Firstly, the AuNRs with photothermal effect were synthesized as carriers for drug delivery. Then the surface of gold nanorods was modified by functional DNA chains to provide an efficient site for doxorubicin (DOX) loading. Finally, folic acid was introduced to achieve the targeted treatment of MCF-7 cells. The microRNA competed with the double-stranded DNA, resulting in the release of DOX and the recovery of fluorescence signal located at 595 nm with an excitation of 488 nm effectively. The nano-biosensor could not only achieve dual-function of diagnosis and treatment of cancer cells, but also accomplish the detection of microRNA in tumor cells. It showed a high selectivity for microRNA-21 determination with a limit of detection (LOD) of 2.1 nM from the linear relationship from 1.0 × 10−5 M to 5.0 × 10−7 M. This scheme provides an outstanding strategy for cell imaging, treatment, and detection, which serves as a promising candidate in the field of biomedical research.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431(7006):350–355
Cissell K A, Shrestha S, Deo S K (2007) MicroRNA detection: Challenges for the analytical chemist. Anal Chem 79 (13), 4754–61
Dong H, Lei J, Ding L, Wen Y, Ju H, Zhang X (2013) MicroRNA: function, detection, and bioanalysis. Chem Rev 113(8):6207–6233
Ma J, Dong C, Ji C (2010) MicroRNA and drug resistance. Cancer Gene Ther 17(8):523–531
Kutanzi KR, Yurchenko OV, Beland FA, Checkhun VF, Pogribny IP (2011) MicroRNA-mediated drug resistance in breast cancer. Clin Epigenetics 2(2):171–185
Ji X, Wang Z, Niu S, Ding C (2020) DNAzyme-functionalized porous carbon nanospheres serve as a fluorescent nanoprobe for imaging detection of microRNA-21 and zinc ion in living cells. Mikrochim Acta 187(4):249
Xu W, Zhao A, Zuo F, Khan R, Hussain HMJ, Chang J (2020) Au@Ag core-shell nanoparticles for microRNA-21 determination based on duplex-specific nuclease signal amplification and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Mikrochim Acta 187(7):384
Zhang P, He Z, Wang C, Chen J, Zhao J, Zhu X, Li CZ, Min Q, Zhu JJ (2015) In situ amplification of intracellular microRNA with MNAzyme nanodevices for multiplexed imaging, logic operation, and controlled drug release. ACS Nano 9(1):789–798
Chen N, Li J, Feng X, Yang Y, Zhu L, Chen X, Liu X, Li Y, Wang C, Xia L (2020) Label-free and self-assembled fluorescent DNA nanopompom for determination of miRNA-21. Mikrochim Acta 187(8):432
Varallyay E, Burgyan J, Havelda Z (2008) MicroRNA detection by northern blotting using locked nucleic acid probes. Nat Protoc 3(2):190–196
Kim SW, Li Z, Moore PS, Monaghan AP, Chang Y, Nichols M, John B (2010) A sensitive non-radioactive northern blot method to detect small RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 38(7):e98
Liu CG, Calin GA, Volinia S, Croce CM (2008) MicroRNA expression profiling using microarrays. Nat Protoc 3(4):563–578
Tian T, Wang J, Zhou X (2015) A review: microRNA detection methods. Org Biomol Chem 13(8):2226–2238
Nelson PT, Baldwin DA, Scearce LM, Oberholtzer JC, Tobias JW, Mourelatos Z (2004) Microarray-based, high-throughput gene expression profiling of microRNAs. Nat Methods 1(2):155–161
Gewirtz DA (1991) Does bulk damage to DNA explain the cytostatic and cytotoxic effects of topoisomerase II inhibitors? Biochem Pharmacol 42(12):2253–2258
Wang F, Wang YC, Dou S, Xiong MH, Sun TM, Wang J (2011) Doxorubicin-tethered responsive gold nanoparticles facilitate intracellular drug delivery for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer cells. ACS Nano 5(5):3679–3692
Wei Y, Chen Q, Wu B, Zhou A, Xing D (2012) High-sensitivity in vivo imaging for tumors using a spectral up-conversion nanoparticle NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ in cooperation with a microtubulin inhibitor. Nanoscale 4(13):3901–3909
Liu J, Zhang L, Lei J, Ju H (2015) MicroRNA-responsive cancer cell imaging and therapy with functionalized gold nanoprobe. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(34):19016–19023
Grabinski C, Schaeublin N, Wijaya A, D’Couto H, Baxamusa SH, Hamad-Schifferli K, Hussain SM (2011) Effect of gold nanorod surface chemistry on cellular response. ACS Nano 5(4):2870–2879
Zijlstra P, Paulo PM, Orrit M (2012) Optical detection of single non-absorbing molecules using the surface plasmon resonance of a gold nanorod. Nat Nanotechnol 7(6):379–382
Kong G, Braun R, Dewhirst M (2000) Hyperthermia enables tumor-specific nanoparticle delivery: effect of particle size. Cancer Res 60:4440–4445
Zhao P, Zheng M, Yue C, Luo Z, Gong P, Gao G, Sheng Z, Zheng C, Cai L (2014) Improving drug accumulation and photothermal efficacy in tumor depending on size of ICG loaded lipid-polymer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 35(23):6037–6046
Kong G, Dewhirst MW (1999) Review hyperthermia and liposomes. Int J Hyperth 15(5):345–370
Karino T, Koga S, Maeta M (1988) Experimental studies of the effects of local hyperthermia on blood flow, oxygen pressure and pH in tumors. Jpn J Surg 18(3):276–283
Wang H, Zhao R, Li Y, Liu H, Li F, Zhao Y, Nie G (2016) Aspect ratios of gold nanoshell capsules mediated melanoma ablation by synergistic photothermal therapy and chemotherapy. Nanomedicine 12(2):439–448
Cheng L, Liu J, Gu X, Gong H, Shi X, Liu T, Wang C, Wang X, Liu G, Xing H, Bu W, Sun B, Liu Z (2014) PEGylated WS(2) nanosheets as a multifunctional theranostic agent for in vivo dual-modal CT/photoacoustic imaging guided photothermal therapy. Adv Mater 26(12):1886–1893
Song XR, Wang X, Yu SX, Cao J, Li SH, Li J, Liu G, Yang HH, Chen X (2015) Co(9) Se(8) nanoplates as a new theranostic platform for photoacoustic/magnetic resonance dual-modal-imaging-guided chemo-photothermal combination therapy. Adv Mater 27(21):3285–3291
Wen L, Chen L, Zheng S, Zeng J, Duan G, Wang Y, Wang G, Chai Z, Li Z, Gao M (2016) Ultrasmall biocompatible WO3− x nanodots for multi-modality imaging and combined therapy of cancers. Adv Mater 28(25):5072–5079
Zhou Y, Zhang Z, Xu Z, Yin H, Ai S (2012) MicroRNA-21 detection based on molecular switching by amperometry. New J Chem 36(10):1985–1991
Azzouzi S, Fredj Z, Turner APF, Ali MB, Mak WC (2019) Generic neutravidin biosensor for simultaneous multiplex detection of microRNAs via electrochemically encoded responsive nanolabels. ACS Sens 4(2):326–334
Zhao H, Qu Y, Yuan F, Quan X (2016) A visible and label-free colorimetric sensor for miRNA-21 detection based on peroxidase-like activity of graphene/gold-nanoparticle hybrids. Anal Methods 8:2005–2012
Zuo C, Guo Y, Li J, Peng Z, Bai S, Yang S, Wang D, Chen H, Xie G (2021) A nanoprobe for fluorescent monitoring of microRNA and targeted delivery of drugs. RSC Adv 11:8871–8878
Wang A, Yang X, Wang K, Huang J (2021) Orderly assembled, self-powered FRET flares for microRNA imaging in live cells. Anal Chem 93(15):6270–6277
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21904077, 22074074, 22004078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
Experimental section, TEM image and zeta potential of the nanoprobe (Fig. S1), comparison of fluorescence recovery (Fig. S2), cell cytotoxicity of AuNRs-DNA/FA (Fig. S3), the effect of pH in vitro (Fig. S4), living cell images at different pH values (Fig. S5) and flow cytometry measurement (Fig. S6). (DOCX 1191 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Y., Yuan, W., Guo, X. et al. Fluorescent detection of microRNA-21 in MCF-7 cells based on multifunctional gold nanorods and the integration of chemotherapy and phototherapy. Microchim Acta 188, 253 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04917-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04917-8