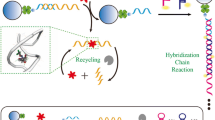
Abstract
An ultrasensitive fluorescence sensing strategy for kanamycin (KANA) determination using endonuclease IV (Endo IV)-powered DNA walker, and hybridization chain reaction (HCR) amplification was reported. The sensing system consists of Endo IV-powered 3D DNA walker using for the specific recognition of KANA and the formation of the initiators, two metastable hairpin probes as the substrates of HCR and a tetrahydrofuran abasic site (AP site)-embeded fluorescence-quenched probe for fluorescence signal output. On account of this skilled design of sensing system, the specific binding between KANA and its aptamer activates DNA walker, in which the swing arm can move autonomously along the 3D track via Endo IV-mediated hydrolysis of the anchorages, inducing the formation of initiators that initiates HCR and the following Endo IV-assisted cyclic cleavage of fluorescence reporter probes. The use of Endo IV offers the advantages of simplified and accessible design without the need of specific sequence in DNA substrates. Under the optimal experimental conditions, the fluorescence biosensor shows excellent sensitivity toward KANA detection with a detection limit as low as 1.01 pM (the excitation wavelength is 486 nm). The practical applicability of this strategy is demonstrated by detecting KANA in spiked milk samples with recovery in the range of 98 to 102%. Therefore, this reported strategy might create an accurate and robust fluorescence sensing platform for trace amounts of antibiotic residues determination and related safety analysis.

Highly efficient fluorescence sensing of kanamycin using Endo IV-powered DNA Walker and hybridization chain, reaction amplification, Xiaonan Qu, Jingfeng Wang, Rufeng Zhang, Yihan Zhao, Shasha Li, Yu Wang, Su Liu*, Jiadong Huang, and Jinghua Yu, an ultrasensitive fluorescence sensing strategy for kanamycin determination using endonuclease IV-powered DNA walker, and hybridization chain reaction amplification is reported.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen ZC, Xiong F, Yu AM, Lai GS (2019) Aptamer biorecognition-triggered DNAzyme liberation and Exo III-assisted target recycling for ultrasensitive homogeneous colorimetric bioassay of kanamycin antibiotic. Chem Commun 55:3959–3662
Bai Z, Chen Y, Li F, Zhou Y, Yin H, Ai S (2019) Electrochemical aptasensor for sulfadimethoxine detection based on the triggered cleavage activity of nuclease P1 by aptamer-target complex. Talanta 204:409–414
Liao QG, Wei BH, Luo LG (2017) Aptamer based fluorometric determination of kanamycin using double-stranded DNA and carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 184:627–632
Robati RY, Arab A, Ramezani M, Langroodi FA, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM Aptasensors for quantitative detection of kanamycin. Biosens Bioelectron 82:162–172
Zeng RJ, Zhang LJ, Luo ZB, Tang DP (2019) Palindromic fragment-mediated single-chain amplification: an innovative mode for photoelectrochemical bioassay. Anal Chem 91:7835–7841
Zhang K, Gan N, Shen ZP, Cao JX, Hu FT, Li TH (2019) Microchip electrophoresis based aptasensor for multiplexed detection of antibiotics in foods via a stir-bar assisted multi-arm junctions recycling for signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 130:139–146
Mcwhinney BC, Wallis SC, Tara H, Roberts JA, Jeffrey L, Ungerer JPJ (2010) Analysis of 12 beta-lactam antibiotics in human plasma by HPLC with ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr B 878:2039–2043
Liu JX, Zhao MZ, Deng Y, Tie C, Chen HX, Zhou YL, Zhang XX (2013) The coating of smart pH-responsive polyelectrolyte brushes in capillary and its application in CE. Electrophoresis 34:1352–1358
Turner NW, Subrahmanyam S, Piletsky SA (2009) Analytical methods for determination of mycotoxins: a review. Anal Chim Acta 632:168–180
Wenxiao J, Zhanhui W, Beier RC, Haiyang J, Yongning W, Jianzhong S (2013) Simultaneous determination of 13 fluoroquinolone and 22 sulfonamide residues in milk by a dual-colorimetric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal Chem 85:1995–1999
Watson TL, Pearson J, Clifford CWG (2004) Perceptual grouping of biological motion promotes binocular rivalry. Curr Biol 14:1670–1674
Cha TG, Pan J, Chen HR, Salgado J, Li X, Mao CD, Choi JH (2014) A synthetic DNA motor that transports nanoparticles along carbon nanotubes. Nat Nanotechnol 9:39–43
Yaniv A, Eldad BI, Daniel L, Shmulik I, Almogit AH, Ido B (2014) Universal computing by DNA origami robots in a living animal. Nat Nanotechnol 9:353–357
Liu M, Fu J, Hejesen C, Yang Y, Woodbury NW, Gothelf K, Liu Y, Yan H (2013) A DNA tweezer-actuated enzyme nanoreactor. Nat Commun 24:2127
Zhao L, Sun R, He P, Zhang X (2019) Ultrasensitive detection of exosomes by target-triggered three-dimensional DNA walking machine and exonuclease III-assisted electrochemical ratiometric biosensing. Anal Chem 91:14773–14779
Tian Y, He Y, Chen Y, Yin P, Mao C (2005) A DNAzyme that walks processively and autonomously along a one-dimensional track. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:4355–4358
Yao Q, Wang YQ, Wang J, Chen SM, Liu HY, Jiang ZR, Zhang XE, Liu SM, Yuan Q, Zhou X (2018) An ultrasensitive diagnostic biochip based on biomimetic periodic nanostructure-assisted rolling circle amplification. ACS Nano 12:6777–6783
Song W, Zhang Q, Sun W (2015) Ultrasensitive detection of nucleic acids by template enhanced hybridization followed by rolling circle amplification and catalytic hairpin assembly. Chem Commun 51:2392–2395
Zhang HG, Li FY, Chen HL, Ma YH, Qi SD, Chen XG, Zhou L (2015) AuNPs colorimetric sensor for detecting platelet-derived growth factor-BB based on isothermal target-triggering strand displacement amplification. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 207:748–755
Gu Y, Song J, Li MX, Zhang TT, Zhao W, Xu JJ (2017) Ultrasensitive microRNA assay via surface plasmon resonance responses of Au@Ag nanorods etching. Anal Chem 89:10585–10591
Wu Z, Liu GQ, Yang XL, Jiang JH (2015) Electrostatic nucleic acid nanoassembly enables hybridization chain reaction in living cells for ultrasensitive mRNA imaging. J Am Chem Soc 137:6829–6836
Zhang K, Cao JX, Wu YX, Hu FT, Li TH, Wang Y, Gan N (2019) A fluorometric aptamer method for kanamycin by applying a dual amplification strategy and using double Y-shaped DNA probes on a gold bar and on magnetite nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186:120
Xue C, Zhang SX, Ouyang CH, Chang D, Salena BJ, Li Y, Wu ZS (2018) Target-induced catalytic assembly of Y-shaped DNA and its application for in situ imaging of microRNAs. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:9739–9743
Manzanares-Palenzuela CL, De-Los-Santos-Álvarez N, Lobo-Castañón MJ, López-Ruiz B (2015) Multiplex electrochemical DNA platform for femtomolar-level quantification of genetically modified soybean. Biosens Bioelectron 68:259–265
Lee NY (2018) A review on microscale polymerase chain reaction based methods in molecular diagnosis, and future prospects for the fabrication of fully integrated portable biomedical devices. Microchim Acta 185:22
Xu C, Zhang F, Wang K, Xu E, Liu Y, Wei W et al (2019) A three-dimensional DNAzyme motor for sensitive imaging of telomerase activity in living cells. Sensor Actuat B Chem 298:126930
Cryer AM, Chan C, Eftychidou A, Maksoudian C, Mahesh M, Tetley TD, Spivey AC, Thorley AJ (2019) Tyrosine kinase inhibitor gold Nanoconjugates for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:16336–16346
Liu X, Liu P, Tang Y, Yang L, Li L, Qi Z et al (2018) A photoelectrochemical aptasensor based on a 3D flower-like TiO2-MoS2-gold nanoparticle heterostructure for detection of kanamycin. Biosens Bioelectron 112:193–201
Han S, Li B, Song Z, Pan S, Zhang Z, Yao H et al (2016) A kanamycin sensor based on an electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted poly-o-phenylenediamine film on a single-walled carbon nanohorn modified glassy carbon electrode. Analyst 142:218–223
Nguyen TA, Park S, Kim JB, Kim TK, Seong GH, Choo J et al (2011) Polycrystalline tungsten oxide nanofibers for gas-sensing applications. Sensors Actuators B Chem 160:549–554
Wu Z, Hui L, Liu Z (2015) An aptasensor for carcinoembryonic antigen based on upconversion fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Biosens Bioelectron 206:531–537
Chong KC, Thang LY, Quirino JP, Hong HS (2017) Monitoring of vancomycin in human plasma via portable microchip electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detector and multi-stacking strategy. J Chromatogr A 1485:142
Zhou N, Zhang J, Tian Y (2014) Aptamer-based spectrophotometric detection of kanamycin in milk. Anal Methods 6:1569
Leung KH, He HZ, Chan SH, Fu WC, Leung CH, Ma DL (2013) An oligonucleotide-based switch-on luminescent probe for the detection of kanamycin in aqueous solution. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 177:487–492
Xin Y, Li Z, Zhang Z (2015) Photoelectrochemical aptasensor for the sensitive and selective detection of kanamycin based on Au nanoparticle functionalized self-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays. Chem Commun 51:15498–15501
Ramezani M, Danesh NM, Lavaee P, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM (2016) A selective and sensitive fluorescent aptasensor for detection of kanamycin based on catalytic recycling activity of exonuclease III and gold nanoparticles. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 222:1–7
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471644), the Primary Research & Development Plan of Shandong Province (2017GSF220009) and the Program for Taishan Scholer of Shandong Province (TS201712048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1254 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, X., Wang, J., Zhang, R. et al. Highly efficient fluorescence sensing of kanamycin using Endo IV-powered DNA walker and hybridization chain reaction amplification. Microchim Acta 187, 193 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4167-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4167-1