Abstract
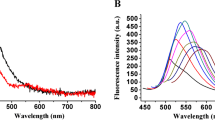
A method is described for the determination of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPα) which is a regulator in adipocyte differentiation. The method is based on quenching of the red fluorescence (with excitation/emission maxima at 548/562 nm) of Cy3-labeled DNA if it becomes adsorbed on positively charged gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Fluorescently labeled dsDNA that can bind C/EBPα is introduced as a fluorescent probes. The dsDNA is electrostatically adsorbed on the positively charged AuNPs to quench their fluorescence. In the presence of C/EBPα, it will bind dsDNA which then diffuses away. The fluorescence of the AuNPs becomes restored. The fluorescent signal increases linearly in the 0.05 to 600 ng·mL−1 μM C/EBPα concentration range, and the detection limit is 29 pg·mL−1. The method is specific and was applied to analyze cell lysates and in-situ.

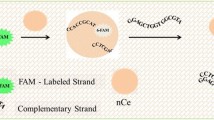
Schematic representation of a fluorometric method for determination of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPα). Fluorescently labeled dsDNA that can bind C/EBPα is introduced as a fluorescent probes. The dsDNA is electrostatically adsorbed on the positively charged AuNPs to quench their fluorescence. In the presence of C/EBPα, it will bind dsDNA which then diffuses away. The fluorescence of the AuNPs becomes restored.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashwell MGP, Gibson S (2012) Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 13:275–286
Collaborators GBDO, Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, Reitsma MB, Sur P, Estep K, Lee A, Marczak L, Mokdad AH, Moradi-Lakeh M, Naghavi M, Salama JS, Vos T, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Ahmed MB, Al-Aly Z, Alkerwi A, Al-Raddadi R, Amare AT, Amberbir A, Amegah AK, Amini E, Amrock SM, Anjana RM, Arnlov J, Asayesh H, Banerjee A, Barac A, Baye E, Bennett DA, Beyene AS, Biadgilign S, Biryukov S, Bjertness E, Boneya DJ, Campos-Nonato I, Carrero JJ, Cecilio P, Cercy K, Ciobanu LG, Cornaby L, Damtew SA, Dandona L, Dandona R, Dharmaratne SD, Duncan BB, Eshrati B, Esteghamati A, Feigin VL, Fernandes JC, Furst T, Gebrehiwot TT, Gold A, Gona PN, Goto A, Habtewold TD, Hadush KT, Hafezi-Nejad N, Hay SI, Horino M, Islami F, Kamal R, Kasaeian A, Katikireddi SV, Kengne AP, Kesavachandran CN, Khader YS, Khang YH, Khubchandani J, Kim D, Kim YJ, Kinfu Y, Kosen S, Ku T, Defo BK, Kumar GA, Larson HJ, Leinsalu M, Liang X, Lim SS, Liu P, Lopez AD, Lozano R, Majeed A, Malekzadeh R, Malta DC, Mazidi M, McAlinden C, McGarvey ST, Mengistu DT, Mensah GA, Mensink GBM, Mezgebe HB, Mirrakhimov EM, Mueller UO, Noubiap JJ, Obermeyer CM, Ogbo FA, Owolabi MO, Patton GC, Pourmalek F, Qorbani M, Rafay A, Rai RK, Ranabhat CL, Reinig N, Safiri S, Salomon JA, Sanabria JR, Santos IS, Sartorius B, Sawhney M, Schmidhuber J, Schutte AE, Schmidt MI, Sepanlou SG, Shamsizadeh M, Sheikhbahaei S, Shin MJ, Shiri R, Shiue I, Roba HS, Silva DAS, Silverberg JI, Singh JA, Stranges S, Swaminathan S, Tabares-Seisdedos R, Tadese F, Tedla BA, Tegegne BS, Terkawi AS, Thakur JS, Tonelli M, Topor-Madry R, Tyrovolas S, Ukwaja KN, Uthman OA, Vaezghasemi M, Vasankari T, Vlassov VV, Vollset SE, Weiderpass E, Werdecker A, Wesana J, Westerman R, Yano Y, Yonemoto N, Yonga G, Zaidi Z, Zenebe ZM, Zipkin B, Murray CJL (2017) Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med 377(1):13–27. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1614362
Martin KA, Mani MV, Mani A (2015) New targets to treat obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Eur J Pharmacol 763 (Pt a):64-74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.03.093
Srivastava GCMA (2018) Current pharmacotherapy for obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 14(1):12–24
Colman E (2005) Anorectics on trial: a half century of federal regulation of prescription appetite suppressants. Ann Intern Med 143(5):380–385
Guo L, Li X, Tang QQ (2015) Transcriptional regulation of adipocyte differentiation: a central role for CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) beta. J Biol Chem 2:755–761
Millward CA, Heaney JD, Sinasac DS, Chu EC, Bederman IR, Gilge DA, Previs SF, Croniger CM (2007) Mice with a deletion in the gene for CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta are protected against diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 56(1):161–167. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-0310
Heath VSH, Holman M, Renn K, Gooya JM, Parkin S, Klarmann KD, Ortiz M, Johnson P, Keller J (2004) C/EBPalpha deficiency results in hyperproliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells and disrupts macrophage development in vitro and in vivo. Blood 104:1639–1647
Wei Ren JG, Jiang F, Lu J, Ding Y, Li A, Liang X, Jia W (2014) CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α is a crucial regulator of human fat mass and obesity associated gene transcription and expression. Biomed Res Int 2014:406909
Nguyen KDQY, Cui X, Goh YP, Mwangi J, David T, Mukundan L, Brombacher F, Locksley RM, Chawla A (2011) Alternatively activated macrophages produce catecholamines to sustain adaptive thermogenesis. Nature 480:104–108
Chen B, Lam KS, Wang Y, Wu D, Lam MC, Shen J, Wong L, Hoo RL, Zhang J, Xu A (2006) Hypoxia dysregulates the production of adiponectin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 independent of reactive oxygen species in adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341(2):549–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.004
Yang XYL, Li T, Chen Z (2014) Green tea extracts reduce adipogenesis by decreasing expression of transcription factors C/EBPα and PPARγ. Int J Clin Exp Med 7(12):4906–4914
Mayer KMHJ (2011) Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem Rev 111(6):3828–3857
Giannini VF-DA, Heck SC, Maier SA (2011) Plasmonic nanoantennas: fundamentals and their use in controlling the radiative properties of nanoemitters. Chem Rev 111(6):3888–3912
Cao XYY, Liu S (2011) Gold nanoparticle-based signal amplification for biosensing. Anal Biochem 417:1–16
Degliangeli FKP, Brunetti V, Pompa PP, Fiammengo R (2014) Absolute and direct microRNA quantification using DNA-gold nanoparticle probes. J Am Chem Soc 136(6):2264–2267
Zhu FFPJ, Huang Z, Hu LM, Zhang GG, Liu DF, Xing KY, Zhang KY, Lai WH (2018) Specific colorimetric ELISA method based on DNA hybridization reaction and non-crosslinking gold nanoparticles aggregation for the detection of amantadine. Food Chem 257:382–387
Lim SY, Kim JH, Lee JS, Park CB (2009) Gold nanoparticle enlargement coupled with fluorescence quenching for highly sensitive detection of analytes. Langmuir 25(23):13302–13305. https://doi.org/10.1021/la903248w
May S, Hirsch C, Rippl A, Bohmer N, Kaiser JP, Diener L, Wichser A, Burkle A, Wick P (2018) Transient DNA damage following exposure to gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr03612h
Kang KAWJ, Jasinski JB, Achilefu S (2011) Fluorescence manipulation by Gold nanoparticles: from complete quenching to extensive enhancement. J Nanobiotechnology 9:16
Matveeva EGST, Gryczynski I, Akopova I, Gryczynski Z (2008) Fluorescence quenching/enhancement surface assays: signal manipulation using silver-coated Gold nanoparticles. Chem Phys Lett 454(1–3):85–90
Lecrenier MC, Baeten V, Taira A, Abbas O (2018) Synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy for detecting blood meal and blood products. Talanta 189:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.06.076
Oza GKK, Merupo VI, Bracamontes KAC, Olmos PC, Garrido E, Velumani S, Sridharan M, Sharma A, Arriaga LG, Ramirez JT (2019) Gold-iron oxide yolk-shell nanoparticles (YSNPs) as magnetic probe for fluorescence-based detection of 3 base mismatch DNA. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 176:431–438
Miao XCZ, Ma H, Li Z, Xue N, Wang P (2018) Label-free platform for MicroRNA detection based on the fluorescence quenching of positively charged Gold nanoparticles to silver Nanoclusters. Anal Chem 90(2):1098–1103
Sridhar RTH, Syed R, Kobayashi IS, Hui LB, Kamal A, Tenen DG, Kobayashi SS (2018) Styryl Quinazolinones as potential inducers of myeloid differentiation via Upregulation of C/EBPα. Molecules 23(8)
Harada N, Hirano I, Inui H, Yamaji R (2018) Stereoselective effects of lactate enantiomers on the enhancement of 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 498(1):105–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.198
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81770866, 81670773, 81770837, 81600687), Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Team (CXTDA2017001), Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent (QNRC2016108), 333 high level talents training project of Jiangsu Province, Jiangsu Province “six talent peak” personal training project (YY-081) and Nanjing Technological Development Program(201715054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2394 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Li, J., Cui, X. et al. Fluorometric determination of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha by using gold nanoparticles and a labeled protein-binding DNA. Microchim Acta 187, 22 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4025-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4025-1