Abstract
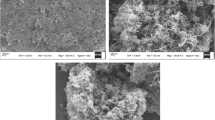
The work describes a voltammetric method for the recognition of tryptophan (Trp) enantiomers. A glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was modified with polydopamine-coated multiwalled carbon nanotubes and subsequently loaded with copper(II) ions. The morphology and structure of the material were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy and electrochemical methods. The recognition of Trp enantiomers by the modified GCE was investigated by differential pulse voltammetry. Under optimum conditions, the sensor revealed a linear range from 1.0 to 100.0 μM with the limit of detection values of 0.15 μM and 0.20 μM for D-Trp and L-Trp, respectively. The recognition efficiency for the Trp enantiomers (with a chiral separation factor of 5.4 for L-Trp over D-Trp) is much higher than that of other electrodes. This is assumed to be due to the unique features of MWCNTs, PDA and Cu(II). After optimizing various experimental conditions, the method was successfully applied to chiral sensing of Trp isomers in a racemic mixture. The potential application to chiral separation of the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine was also evaluated, with a chiral separation factor of 2.14 and 1.33 for L−/D-phenylalanine and L−/D-tyrosine, respectively.

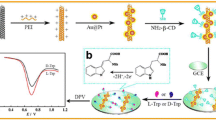
Schematic presentation of the synthesis of a multi-walled carbon nanotubes@polydopamine composite loaded with copper(II), and its application in electrochemical enantiorecognition of tryptophan enantiomers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tao Y, Chu F, Gu X, Kong Y, Lv Y, Deng L (2018) A novel electrochemical chiral sensor for tyrosine isomers based on a coordination-driven self-assembly. Sensors Actuators B Chem 255:255–261
Liang W, Rong Y, Fan L, Dong W, Dong Q, Yang C, Zhong Z, Dong C, Shuang S, Wong W-Y (2018) 3D graphene/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin nanocomposite as an electrochemical chiral sensor for the recognition of tryptophan enantiomers. J Mater Chem C 6:12822–12829
Han C, Li H (2008) Chiral recognition of amino acids based on cyclodextrin-capped quantum dots. Small 4:1344–1350
Slama I, Dufresne C, Fahrat EJF, Villet A, Ravel A, Grosset C, Peyrin E (2002) Vancomycin dimerization and chiral recognition studied by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Chem 74:5205–5211
Su H, Zheng Q, Li H (2012) Colorimetric detection and separation of chiral tyrosine based on N-acetyl-l-cysteine modified gold nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 22:6546–6548
Lammers I, Buijs J, Ariese F, Gooijer C (2010) Sensitized enantioselective laser-induced phosphorescence detection in chiral capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem 82:9410–9417
Nie R, Bo X, Wang H, Zeng L, Guo L (2013) Chiral electrochemical sensing for tyrosine enantiomers on glassy carbon electrode modified with cysteic acid. Electrochem Commun 27:112–115
Liang H-J, Ling T-R, Rick JF, Chou T-C (2005) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor able to enantroselectivly recognize d and l-tyrosine. Anal Chim Acta 542:83–89
Muñoz J, González-Campo A, Riba-Moliner M, Baeza M, Mas-Torrent M (2018) Chiral magnetic-nanobiofluids for rapid electrochemical screening of enantiomers at a magneto nanocomposite graphene-paste electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 105:95–102
Zor E, Morales-Narváez E, Alpaydin S, Bingol H, Ersoz M, Merkoçi A (2016) Graphene-based hybrid for enantioselective sensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron 87:410–416
Song J, Yang C, Ma J, Han Q, Ran P, Fu Y (2018) Voltammetric chiral discrimination of tryptophan using a multilayer nanocomposite with implemented amino-modified beta-cyclodextrin as recognition element. Microchim Acta 185:230
Saini AK, Saraf M, Kumaric P, Mobin SM (2018) A highly selective and sensitive chemosensor for L-tryptophan by employing a Schiff based cu(II) complex. New J Chem 42:3509–3518
Zhao M, Deng C, Zhang X (2013) Synthesis of polydopamine-coated magnetic graphene for Cu2+ immobilization and application to the enrichment of low-concentration peptides for mass spectrometry analysis. ACS Appl Mat Interfaces 5:13104–13112
Goulart LA, Gonçalves R, Correa AA, Pereira EC, Mascaro LH (2017) Synergic effect of silver nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes on the simultaneous voltammetric determination of hydroquinone, catechol, bisphenol a and phenol. Microchim Acta 185:12
Barsan MM, Ghica ME, Brett CMA (2015) Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on redox polymer/carbon nanotube modified electrodes: a review. Anal Chim Acta 881:1–23
Yi Y, Zhang D, Ma Y, Wu X, Zhu G (2019) Dual-signal electrochemical enantiospecific recognition system via competitive supramolecular host–guest interactions: the case of phenylalanine. Anal Chem 91:2908–2915
Feng X, Gao W, Zhou S, Shi H, Huang H, Song W (2013) Discrimination and simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol by tunable polymerization of imidazolium-based ionic liquid on multi-walled carbon nanotube surfaces. Anal Chim Acta 805:36–44
Ambrico M, Ambrico PF, Cardone A, Della Vecchia NF, Ligonzo T, Cicco SR, Talamo MM, Napolitano A, Augelli V, Farinola GM, d'Ischia M (2013) Engineering polydopamine films with tailored behaviour for next-generation eumelanin-related hybrid devices. J Mater Chem C 1:1018–1028
Kima H, Leec J-W, Byunb D, Choia W (2018) Coaxial-nanostructured MnFe2O4 nanoparticles on polydopaminecoated MWCNT for anode materials in rechargeable batteries. Nanoscale 10:18949–18960
Zhou H, Huang T, Chen D, Li S, Yu H, Li Y, Song Q (2017) Copper nanoparticles modified nitrogen doped reduced graphene oxide 3-D superstructure for simultaneous determination of dihydroxybenzene isomers. Sensors Actuators B Chem 249:405–413
Zhou H, Ran G, Masson JF, Wang C, Zhao Y, Song Q (2018) Rational design of magnetic micronanoelectrodes for recognition and ultrasensitive quantification of cysteine dnantiomers. Anal Chem 90:3374–3381
Huang N, Zhang S, Yang L, Liu M, Li H, Zhang Y, Yao S (2015) Multifunctional electrochemical platforms based on the michael addition/schiff base reaction of polydopamine modified reduced graphene oxide: construction and application. ACS Appl Mat Interfaces 7:17935–17946
Lee H, Rho J, Messersmith PB (2009) Facile conjugation of biomolecules onto surfaces via mussel adhesive protein inspired coatings. Adv Mater 21:431–434
Lee H, Dellatore SM, Miller WM, Messersmith PB (2007) Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 318:426–430
Yari A, Derki S (2016) New MWCNT-Fe3O4@PDA-ag nanocomposite as a novel sensing element of an electrochemical sensor for determination of guanine and adenine contents of DNA. Sensors Actuators B Chem 227:456–466
Huang K-J, Xu C-X, Xie W-Z, Wang W (2009) Electrochemical behavior and voltammetric determination of tryptophan based on 4-aminobenzoic acid polymer film modified glassy carbon electrode. Colloids Surf, B 74:167–171
Tao Y, Dai J, Kong Y, Sha Y (2014) Temperature-sensitive electrochemical recognition of tryptophan enantiomers based on β-cyclodextrin self-assembled on poly(l-glutamic acid). Anal Chem 86:2633–2639
Yorita H, Otomo K, Hiramatsu H, Toyama A, Miura T, Takeuchi H (2008) Evidence for the cation-π interaction between Cu2+ and tryptophan. J AmChem Soc 130:15266–15267
Yu Y, Tao Y, Yang B, Wu D, Qin Y, Kong Y (2017) Smart chiral sensing platform with alterable enantioselectivity. Anal Chem 89:12930–12937
Gu X, Tao Y, Pan Y, Deng L, Bao L, Kong Y (2015) DNA-inspired electrochemical recognition of tryptophan isomers by electrodeposited chitosan and sulfonated chitosan. Anal Chem 87:9481–9486
Tao Y, Gu X, Deng L, Qin Y, Xue H, Kong Y (2015) Chiral recognition of d-tryptophan by confining high-energy water molecules inside the cavity of copper-modified β-cyclodextrin. J Phys Chem C 119:8183–8190
Anu Prathap MU, Srivastava R (2013) Tailoring properties of polyaniline for simultaneous determination of a quaternary mixture of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid, and tryptophan. Sensors Actuators B Chem 177:239–250
Wang H, Zhou Y, Guo Y, Liu W, Dong C, Wu Y, Li S, Shuang S (2012) β-Cyclodextrin/Fe3O4 hybrid magnetic nano-composite modified glassy carbon electrode for tryptophan sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 163:171–178
Zhao G, Zhou X, Ran X, Tan X, Li T, Cao M, Yang L, Du G (2018) Layer-by-layer assembly of anionic−/cationic-pillar[5]arenes multilayer films as chiral interface for electrochemical recognition of tryptophan isomers. Electrochim Acta 277:1–8
Bao L, Chen X, Yang B, Tao Y, Kong Y (2016) Construction of electrochemical chiral interfaces with integrated polysaccharides via amidation. ACS Appl Mat Interfaces 8:21710–21720
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21607061), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20190543)the Opening Project of State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics of Hunan University (2018019), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, Collaborative Innovation Center of Technology and Material of Water Treatment, and the Program of Young Backbone Teachers in Jiangsu University (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 531 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, J., Yi, Y., Zhang, D. et al. Electrochemical recognition of tryptophan enantiomers using a multi-walled carbon nanotube@polydopamine composite loaded with copper(II). Microchim Acta 186, 358 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3469-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3469-7