Abstract
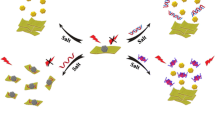
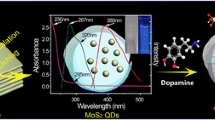
The authors describe a fluorometric strategy for the determination of dopamine (DA). It is based on the use of aptamer-functionalized MoS2 quantum dots (QDs) and MoS2 nanosheets (NSs). The QDs and NSs were extensively characterized with regard to their physical and chemical properties using methods such as TEM, XRD, FT-IR, EDX and molecular spectroscopies. The aptamer against dopamine was labeled with QDs acting as the energy donor in an energy transfer system, while the NSs serve as the energy acceptor. Under the optimal conditions, the fluorescence (FL) intensity (best measured at excitation/emission peaks of 315/412 nm) increases with increasing DA concentration in the range from 0.1 nM to 1000 nM, with a lower detection limit of 45 pM. The method was successfully applied to the determination of DA in complex matrices. In our perception, the method has a wide scope in that it may be extended to other biomolecules for which respective aptamer are available. The QDs show excellent optical properties, good stability, low cytotoxicity, and may also be applied to fluorometric imaging of live cells.

A “turn-on” fluorometric aptasensor for the determination of dopamine (DA) was established based on aptamer-functionalized molybdenum disulfide quantum dots (MoS2 QDs) and MoS2 nanosheets. This assay exhibits high selectivity and sensitivity with a detection limit as low as 45 pM.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818–822
Tan W, Donovan MJ, Jiang J (2013) Aptamers from cell-based selection for bioanalytical applications. Chem Rev 113:2842–2862
Huang Y, Chen J, Zhao S, Shi M, Chen ZF, Liang H (2013) Label-free colorimetric aptasensor based on nicking enzyme assisted signal amplification and DNAzyme amplification for highly sensitive detection of protein. Anal Chem 88:1455–1461
Liu J, Lu Y (2006) Preparation of aptamer-linked gold nanoparticle purple aggregates for colorimetric sensing of analytes. Nat Protoc 1:246–252
Song S, Wang L, Li J, Fan C, Zhao J (2008) Aptamer-based biosensors. Trends Anal Chem 27:108–117
Chen T, Shukoor MI, Chen Y, Yuan Q, Zhu Z, Zhao Z, Gulbakan B, Tan W (2011) Aptamer-conjugated nanomaterials for bioanalysis and biotechnology applications. Nanoscale 3:546–556
Kong R, Zhang X, Chen Z, Tan W (2011) Aptamer-assembled nanomaterials for biosensing and biomedical applications. Small 7:2428–2436
Lan L, Yao Y, Ping J, Ying Y (2017) Recent progress in nanomaterial-based optical aptamer assay for the detection of food chemical contaminants. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:23287–23301
Zhu L, Xu G, Song Q, Tang T, Wang X, Wei F, Hu Q (2016) Highly sensitive determination of dopamine by a turn-on fluorescent biosensor based on aptamer labeled carbon dots and nano-graphite. Sens Actuators B Chem 231:506–512
Chhowalla M, Shin H, Eda G, Li L, Loh K, Zhang H (2013) The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Nat Chem 5:263–275
Wang H, Li C, Fang P, Zhang Z, Zhang J (2018) Synthesis, properties, and optoelectronic applications of two-dimensional MoS2 and MoS2-based hetero structures. Chem Soc Rev 47:6101–6127
Yao Y, Tolentino L, Yang Z, Song X, Zhang W, Chen Y, Wong CP (2013) High-concentration aqueous dispersions of MoS2. Adv Funct Mater 23:3577–3583
Li Y, Wang H, Xie L, Liang Y, Hong G, Dai H (2011) MoS2 nanoparticles grown on graphene: an advanced catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Am Chem Soc 133:7296–7299
Kalantar-zadeh K, Ou JZ (2016) Biosensors based on two-dimensional MoS2. ACS Sens 1:5–16
Dai W, Dong H, Fugetsu B, Cao Y, Lu H, Ma X, Zhang X (2015) Tunable fabrication of molybdenum disulfide quantum dots for intracellular microRNA detection and multiphoton bioimaging. Small 11:4158–4164
Zhu C, Zeng Z, Li H, Li F, Fan C, Zhang H (2013) Single-layer MoS2-based nanoprobes for homogeneous detection of biomolecules. J Am Chem Soc 135:5998–6001
Wang Y, Ma T, Ma S, Liu Y, Tian Y, Wang R, Jiang Y, Hou D, Wang J (2017) Fluorometric determination of the antibiotic kanamycin by aptamer-induced FRET quenching and recovery between MoS2 nanosheets and carbon dots. Microchim Acta 184:203–210
Singh P, Gupta R, Sinha M, Kumar R, Bhalla V (2016) MoS2 based digital response platform for aptamer based fluorescent detection of pathogens. Microchim Acta 183:1501–1506
Tang J, Huang Y, Cheng Y, Huang L, Zhuang J, Tang D (2018) Two-dimensional MoS2 as a nano-binder for ssDNA: ultrasensitive aptamer based amperometric detection of Ochratoxin a. Microchim Acta 185:162
Wang Y, Ni Y (2015) Molybdenum disulfide quantum dots as a photoluminescence sensing platform for 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol detection. Anal Chem 86: 7463–7470
Hu L, Zhang Q, Gan X, Ying W, Fu W (2018) Switchable fluorescence of MoS2 quantum dots: a multifunctional probe for sensing of chromium (VI), ascorbic acid, and alkaline phosphatase activity. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:7551–7557
Zhang A, Neumeyer JL, Baldessarini RJ (2007) Recent progress in development of dopamine receptor subtype-selective agents: potential therapeutics for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Chem Rev 107:274–302
Rasheed PA, Lee JS (2017) Recent advances in optical detection of dopamine using nanomaterials. Microchim Acta 184:1239–1266
Qian T, Yu CF, Zhou X, Wu SS, Shen J (2014) Au nanoparticles decorated polypyrrole/reduced graphene oxide hybrid sheets for ultrasensitive dopamine detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 193:759–763
Liu S, Xing X, Yu J, Lian W, Li J, Cui M, Huang J (2012) A novel label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on graphene–polyaniline composite film for dopamine determination. Biosens Bioelectron 36:186–191
Štengl V, Henych J (2013) Strongly luminescent monolayered MoS2 prepared by effective ultrasound exfoliation. Nanoscale 5: 3387–3394
Huang KJ, Wang L, Liu YJ, Liu YM, Wang HB, Gan T, Wang LL (2013) Layered MoS2–graphene composites for supercapacitor applications with enhanced capacitive performance. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:14027–14034
Lai L, Chen L, Zhan D, Sun L, Liu J, Lim SH, Poh CK, Shen Z, Lin J (2011) One-step synthesis of NH2-graphene from in situ graphene-oxide reduction and its improved electrochemical properties. Carbon 49:3250–3257
Koroteev VO, Bulusheva LG, Asanov IP, Shlyakhova EV, Vyalikh DV, Okotrub AV (2011) Charge transfer in the MoS2/carbon nanotube composite. J Phys Chem C 115:21199–21204
Turner NH, Single AM (1990) Determination of peak positions and areas from wide-scan XPS spectra. Surf Interface Anal 15:215–222
Sáenz HSC, Hernández-Saravia LP, Selva JSG, Sukeri A (2018) Electrochemical dopamine sensor using a nanoporous gold microelectrode: a proof-of-concept study for the detection of dopamine release by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Microchim Acta 185:367
Tao Y, Lin YH, Ren JS, Qu XG (2013) A dual fluorometric and colorimetric sensor for dopamine based on BSA-stabilized au nanoclusters. Biosens Bioelectron 42:41–46
Li SJ, Deng DH, Shi Q, Liu SR (2012) Electrochemical synthesis of a graphene sheet and gold nanoparticle-based nanocomposite, and its application to amperometric sensing of dopamine. Microchim Acta 177:325–331
Khoobi A, Ghoreishi SM, Behpour M, Masoum S (2014) Three-dimensional voltammetry: a chemometrical analysis of electrochemical data for determination of dopamine in the presence of unexpected interference by a biosensor based on gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 86(18):8967–8973
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21822407, 21405163), the Funds for Distinguished Young Scientists of Gansu (1506RJDA281) and the top priority program of “One-Three-Five” Strategic Planning of Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2616 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Li, Y., Huang, Y. et al. Fluorometric dopamine assay based on an energy transfer system composed of aptamer-functionalized MoS2 quantum dots and MoS2 nanosheets. Microchim Acta 186, 58 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3143-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3143-5