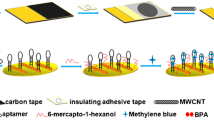
Abstract
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were electrodeposited on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) and then treated with a mixture of a thiolated DNA sequence (p-63; with high affinity for bisphenol A) and free bisphenol A (BPÀ). Pyrrole was then electropolymerizaed on the surface of the GCE to entrap the BPA@p-63 complex. BPA is then extracted with acetic acid solution to obtain MIP cavities where the embedded DNA sequence acts as the binding site for BPA. Scanning electron microscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and cyclic voltammetry were employed to characterize the surface of the modified GCE. Under the optimum conditions, the assay has a dynamic range that covers the 0.5 fM to 5 pM BPA concentration range and an 80 aM detection limit. It was applied to the quantitation of BPA in (spiked) milk, milk powder and water samples and gave acceptable recoveries.

Schematic of the procedure for aptamer-based detection of BPA using unique features of the aptamer-based modified electrodes and MIP-based sensors. This assay has high sensitivity and good selectivity. It can presumably be transferred to other detection schemes for small molecules.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenfeld CS (2017) Neuroendocrine disruption in animal models due to exposure to bisphenol A analogues. Front Neuroendocrinol 47:123–133
Zhou W, Sun C, Zhou Y, Yang X, Yang W (2014) A facial electrochemical approach to determinate bisphenol A based on graphene-hypercrosslinked resin MN202 composite. Food Chem 158:81–87
Lin Y, Liu K, Liu C, Yin L, Kang Q, Li L, Li B (2014) Electrochemical sensing of bisphenol A based on polyglutamic acid/amino-functionalised carbon nanotubes nanocomposite. Electrochim Acta 133:492–500
Ma M, Tu X, Zhan G, Li C, Zhang S (2014) Electrochemical sensor for bisphenol A based on a nanoporous polymerized ionic liquid interface. Microchim Acta 181:565–570
Hou C, Tang WX, Zhang C, Wang YF, Zhu NN (2014) A novel and sensitive electrochemical sensor for bisphenol A determination based on carbon black supporting ferroferric oxide nanoparticles. Electrochim Acta 144:324–331
Hakova M, Chocholousova HL, Chvojka J, Solich P, Satinsky D (2018) An on-line coupling of nanofibrous extraction with column-switching high performance liquid chromatography – a case study on the determination of bisphenol A in environmental water samples. Talanta 178:141–146
Hu Y, Liu Z, Zhan H, Hu L, Cui L, Wang K (2017) A novel electrochemiluminescence sensor for bisphenol A determination based on graphene–palladium nanoparticles/polyvinyl alcohol hybrids. Anal Methods 9:3870–3875
Nicolucci C, Errico S, Federico A, Dallio M, Loguercio C, Diano N (2017) Human exposure to Bisphenol A and liver health status: quantification of urinary and circulating levels by LC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed 140:105–112
Spagnuolo ML, Marini F, Sarabia LA, Ortiz MC (2017) Migration test of Bisphenol A from polycarbonate cups using excitation-emission fluorescence data with parallel factor analysis. Talanta 167:367–378
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhu W, Wang J, Yue X, Liu W, Zhang D, Wang J (2017) Simultaneous colorimetric determination of bisphenol A and bisphenol S via a multi-level DNA circuit mediated by aptamers and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184:951–959
Wang Q, Zhu L, Chen M, Ma X, Wang X, Xia J (2017) Simultaneously determination of bisphenol A and its alternatives in sediment by ultrasound-assisted and solid phase extractions followed by derivatization using GC-MS. Chemosphere 169:709–715
Kim SG, Lee JS, Jun J, Shin DH, Jang J (2016) Ultrasensitive bisphenol a field-effect transistor sensor using an aptamer-modified multichannel carbon nanofiber transducer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:6602–6610
Zhou L, Wang J, Li D, Li Y (2014) An electrochemical aptasensor based on gold nanoparticles dotted graphene modified glassy carbon electrode for label-free detection of bisphenol A in milk samples. Food Chem 162:34–40
Zhu Y, Zhou C, Yan X, Yan Y, Wang Q (2015) Aptamer-functionalized nanoporous gold film for high-performance direct electrochemical detection of bisphenol A in human serum. Anal Chim Acta 883:81–89
Yu P, Yunqing L, Zhang X, Zhou J, Xiong X, Li X, Chen J (2016) A novel electrochemical aptasensor for bisphenol A assay based on triple-signaling strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 79:22–28
Liu Y, Liu Y, Liu B (2016) A dual-signaling strategy for ultrasensitive detection of bisphenol A by aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor. J Electroanal Chem 781:265–271
Peng C, Pan N, Xie Z, Liu L, Xiang J, Liu C (2016) Determination of bisphenol A by a gold nanoflower enhanced enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal Lett 49:1492–1501
Qiao Y, Li J, Li H, Fang H, Fan D, Wang W (2016) A label-free photoelectrochemical aptasensor for bisphenol A based on surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticle-sensitized ZnO nanopencils. Biosens Bioelectron 86:315–320
Yang F, Xu L, Zhu L, Zhang Y, Meng W, Liu R (2016) Competitive immunoassay for analysis of bisphenol A in children’s sera using a specific antibody. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:10714–10721
Ensafi AA, Amini M, Rezaei B, Talebi M (2016) A novel diagnostic biosensor for distinguishing immunoglobulin mutated and unmutated types of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Biosens Bioelectron 77:409–415
Heydari-Bafrooei E, Shamszadeh NS (2017) Electrochemical bioassay development for ultrasensitive aptasensing of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 91:284–292
Huang Y, Li X, Zheng S (2016) A novel and label-free immunosensor for bisphenol A using rutin as the redox probe. Talanta 160:241–246
Baghayeri M, Amiri A, Alizadeh Z, Veisi H, Hasheminejad E (2018) Non-enzymatic voltammetric glucose sensor made of ternary NiO/Fe3O4-SH/para-amino hippuric acid nanocomposite. J Electroanal Chem 810:69–77
Baghayeri M, Veisi H, Ghanei-Motlagh M (2017) Amperometric glucose biosensor based on immobilization of glucose oxidase on a magnetic glassy carbon electrode modified with a novel magnetic nanocomposite. Sensors Actuators B 249:321–330
Baghayeri M, Sedrpoushan A, Mohammadi A, Heidari M (2017) A non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on NiO nanoparticles/functionalized SBA 15/MWCNT-modified carbon paste electrode. Ionics 23:1553–1562
Baghayeri M (2017) Pt nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide nanosheets as a sensing platform: application to determination of droxidopa in presence of phenobarbital. Sensors Actuators B 240:255–263
Tan F, Cong L, Li X, Zhao Q, Zhao H, Quan X, Chen J (2016) An electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polypyrrole/graphene quantum dots composite for detection of bisphenol A in water samples. Sensors Actuators B Chem 233:599–606
Huang N, Liu ML, Li HT, Zhang YY, Yao SZ (2015) Synergetic signal amplification based on electrochemical reduced graphene oxide-ferrocene derivative hybrid and gold nanoparticles as an ultra-sensitive detection platform for bisphenol A. Anal Chim Acta 853:249–257
Zhu L, Cao Y, Cao G (2014) Electrochemical sensor based on magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles at surfactant modified magnetic electrode for determination of bisphenol A. Biosens Bioelectron 54:258–261
Wang X, Reisberg S, Serradji N, Anquetin G, Pham MC, Wu W, Dong CZ, Piro B (2014) Biosens Bioelectron 53:214–219
Ma Y, Liu J, Li H (2017) E-assay concept: detection of bisphenol A with a label-free electrochemical competitive immunoassay. Biosens Bioelectron 92:21–25
Shi R, Liang J, Zhao Z, Liu A, Tian Y (2017) An electrochemical bisphenol A sensor based on one step electrochemical reduction of cuprous oxide wrapped graphene oxide nanoparticles modified electrode. Talanta 169:37–43
Xu X, Zheng Q, Bai G, Sang L, Yao Y, Cao X, Liu S, Yao C (2017) Polydopamine induced in-situ growth of Au nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide as an efficient biosensing platform for ultrasensitive detection of bisphenol A. Electrochim Acta 242:56–65
Cui H, Wu J, Eda S, Chen J, Chen W, Zheng L (2015) Rapid capacitive detection of femtomolar levels of bisphenol A using an aptamer-modified disposable microelectrode array. Microchim Acta 182:2361–2367
Dadkhah S, Ziaei E, Mehdinia A, Kayyal TB, Jabbari A (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with amino-functionalized graphene oxide and molecularly imprinted polymer for electrochemical sensing of bisphenol A. Microchim Acta 183:1933–1941
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Research Council of Isfahan University of Technology (IUT), the Center of Excellence in Sensor and Green Chemistry and the Iranian Nanotechnology Initiative Council for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 188 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ensafi, A.A., Amini, M. & Rezaei, B. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical aptasensor for the attomolar detection of bisphenol A. Microchim Acta 185, 265 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2810-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2810-x