Abstract.
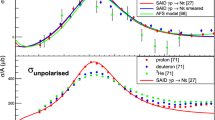
Four-nucleon states in the continuum are studied through exact microscopic calculations based on the solution of the AGS equations for four nonrelativistic quantum particles. Our studies include calculations of cross sections and analyzing powers for all two-body reactions of interest, but here we only show results for n 3He → n 3He. The NN interactions we use are Bonn-CD, Nijmegen II, and Bonn-B. Compared to existing quality data, one finds large discrepancies and some sensitivity to the choice of NN force model. The calculated n + 3He elastic phase shifts show a very strong inelastic resonance at about 0.3 MeV which is not supported by the total cross-section data. This result is due to the existence of a 3 P 0 (0−) resonance in isospin I = 0 at this energy and the undesirable coincidence of n + 3He and p + 3H thresholds in our calculation due to lack of Coulomb repulsion between protons. This interpretation is supported by R-matrix analyses of the data on the basis of coincident thresholds. Calculated 0+ and 0− states are compared with modified R-matrix analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received October 30, 2001; accepted for publication November 7, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fonseca, A., Hale, G. & Haidenbauer, J. Four-Nucleon States in the Continuum: A Means to Probe the Nucleon-Nucleon Interaction. Few-Body Systems 31, 139–144 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s006010200012
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s006010200012