Abstract
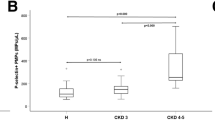
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in Chronic kidney disease patients. This study tries to identify circulating endothelial microparticles {MPs} [such as Cadherin 5 and Anexin V] in CKD patients with and without IHD as potential new risk factors of atherosclerotic vascular disease. This study was carried out in Theodor Bilharz Research Institute [TBRI] on 60 patients with chronic kidney disease on maintenance hemodialysis. They were 41 male and 19 females selected from hemodialysis unit in TBRI. They were further subclassified into the following two groups according to the Echocardiography and Electrocardiogram (ECG) to 25 patients of chronic kidney disease without cardiac complications (17 males, 8 females and ages were 53.5 ± 9.9 years) and 35 patients of chronic kidney disease with cardiac complications (24 males, 11 females and ages were 57.5 ± 7.4 years). Twenty healthy subjects were selected as healthy control, their age 50 ± 9 years. Cadherin 5 & Annexin V Were done by enzyme linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA). The mean cadherin 5 levels in CKD with ischemic HD, CKD without ischemic HD and control group were 86.99 ± 21.51, 33.21 ± 8.65 and 2.63 ± 1.47 respectively which significantly higher in CKD with ischemic HD and CKD without ischemic HD than control group (p < 0.01) and significantly higher in CKD with ischemic HD than CKD without ischemic HD (p < 0.01). As regard to the mean annexin v levels in CKD with ischemic HD, CKD without ischemic HD and control group were 83.73 ± 22.64, 28.51 ± 9.73 and 0.47 ± 0.36 respectively which significantly higher in CKD with ischemic HD and CKD without ischemic HD than control group (p < 0.01) and significantly higher in CKD with ischemic HD than CKD without ischemic HD (p < 0.01). Endothelial dysfunction leading to atherosclerotic vascular disease in patients with CKD can be assessed quantitatively by measurement of plasma levels of endothelial microparticles such as CD144-EMP (Cadherin 5) and Annexin V.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edward M, Laufer PM, Jagat R, Hofstra NL. Annexin 5: an imaging biomarker of cardiovascular risk. Basic Res Cardiol. 2008;103:95–104.
Annuk M, Soveri I, Zilmer M, Lind L, Hulthe J, Fellstrom B. Endothelial function, CRP and oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. J Nephrol. 2005;18(6):721–6.
Stam F, van Guldener C, Becker A, Dekker JM, Heine RG, Bouter LM, et al. Endothelial dysfunction contributes to renal insufficiency: the Hoorn study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(2):537–45.
Suzuki M, Takamisawa I, Suzuki K, Hiuge A, Horio T, Yoshimasa Y, et al. Close association of endothelial dysfunction with insulin resistance and carotid wall thickening in hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17(3):228–32.
Migliacci R, Becattini C, Pesavento R, Davi G, Vedovati MC, Guglielmini G, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in pateints with spontaneous venous thromboembolism. Haematological. 2007;92(6):812–8.
Zoppini G, Targher G, Zamboni C, Venturi C, Cacciatori V, Moghetti P, et al. Effects of moderate-intensity exercise training on plasma biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in older pateints with type 2 diabetes. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006;16(8):543–9.
Takeichi M. Cadherins: a molecular family important in selective cell-cell adhesion. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:237–52.
Soeki T, Tamura Y, Shinohara H, Sakabe K, Onose Y, Fukuda N. Elevated concentration of soluble vascular endothelial cadherin is associated with coronary atherosclerosis. Circ J. 2004;68(1):1–5.
Preston RA, Jy W, Jimenez JJ. Effects of severe hypertension on endothelial and platelet microparticles. Hypertension. 2003;41:211–7.
Werner N, Wassmann S, Ahlers P, Kosiol S, Nickenig G. Circulating CD31/Anexin V apoptotic microparticles correlates with coronary endothelial function in patients with coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(1):112–6.
Kaneko N, Matsudda R, Hosoda S, Kajita T, Ohta Y. Measurement of plasma Annexin V by ELISA in early detection of acute myocardial infarction. Clin Acta Path. 1996;251(1):65–80.
Funakoshi T, Heimark RL, Hendrickson LE, McMullen BA, Fujikawa K. Human placental anticoagulant protein: isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 2001;26:5572–8.
Yao Q, Pecoits-Filho R, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P. Traditional and non-traditional risk factors as contributors to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in end-stage renal disease. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2004;38:405–16.
Dschietzig T, Richter C, Bartsch C, Böhme C, Heinze D, Ott F, et al. Flow-induced pressure differentially regulates endothelin-1, urotensin II, adrenomedullin, and relaxin in pulmonary vascular endothelium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;289(1):245–51.
Sarnak MJ, Levey AS. Cardiovascular disease and chronic renal disease: a new paradigm. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;35(4 suppl 1):S117–31.
Ross R. Atherosclerosis-an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:115–26.
Widlansky ME, Gokce N, Keaney Jr JF, Vita JA. The clinical implications of endothelial dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:1149–60.
Leroyer A, Mallat Z, Nguyen C, Boddaert J, London GM, Tedgui A, et al. Circulating endothelial microparticles are associated with vascular dysfunction in patients with end-stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:3381–8.
Modena MG, Bonetti L, Coppi F, Bursi F, Rossi R. Prognostic role of reversible endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive postmenopausal women. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40:505–10.
Nozaki T, Sugiyama S, Koga H, Sugamura K, Ohba K, Matsuzawa Y, et al. Significance of a multiple biomarkers strategy including endothelial dysfunction to improve risk stratification for cardiovascular events in patients at high risk for coronary heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(7):601–8.
Amabile N, Heiss C, Real WM, Minasi P, McGlothlin D, Rame EJ, et al. Circulating endothelial microparticle levels predict hemodynamic severity of pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:1268–75.
Jimenez JJ, Jy W, Mauro LM, Soderland C, Horstman LL, Ahn YS. Endothelial cells release phenotypically and quantitatively distinct microparticles in activation and apoptosis. Thromb Res. 2003;109:175–80.
Bulut D, Tüns H, Mügge A. CD31+/Annexin V+ microparticles in healthy offsprings of patients with coronary artery disease. Eur J Clin Investig. 2008;39(1):17–22.
Bernard S, Loffroy R, Sérusclat A, Boussel L, Bonnefoy E, Thévenon C, et al. Increased levels of endothelial microparticles CD144 (VE-Cadherin) positives in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary noncalcified plaques evaluated by multidetector computed tomography (MDCT). Atherosclerosis. 2009;203(2):429–35.
Faure V, Dou L, Sabatier F, Cerini C, Sampol J, Berland Y, et al. Elevation of circulating endothelial microparticles in patients with chronic renal failure. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:566–73.
Ravassa S, Bennaghmouch A, Kenis H, Lindhout T, Hackeng T, Narula J, et al. Annexin A5 down-regulates surface expression of tissue factor: a novel mechanism of regulating the membrane receptor repertoire. J Biol Chem. 2009;280:6028–35.
Tits LJ, Graaf J, Toenhake H, Heerde W, Stalenhoef A. C-reactive protein and annexin A5 bind to distinct sites of negatively charged phospholipids present in oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:717–22.
Aikawa M, Libby P. The vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque: pathogenesis and therapeutic approach. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2004;13:125–38.
Cederholm A, Svenungsson E, Jensen-Urstad K, Trollmo C, Ulfgren AK, Swedenborg J, et al. Decreased binding of annexin V to endothelial cells: a potential mechanism in atherothrombosis of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;25:198–203.
Jy W, Jimenez JJ, Mauro LM, Horstman LL, Cheng P, Ahn ER, et al. Endothelial microparticles induce formation of platelet aggregates via a von Willebrand factor/ristocetin dependent pathway, rendering them resistant to dissociation. Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:1301–8.
Zoccali C. Arterial pressure components and cardiovascular risk in end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18:249–52.
Boulanger CM, Amabile N, Tedqui A. Circulating microparticles: Potential prognostic marker for atherosclerotic vascular disease. Hypertension. 2006;29:156–213.
Nakajimi T, Schulte S, Warrington KJ. T-cell mediated lysis of endothelial cells in acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2002;105:570–5.
Krane V, Wanner C. Dyslipidaemia in chronic kidney disease. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2007;59(3):299–316.
Zamboli P, De Nicola, Mioutolo R (2007) Heart failure in chronic kidney disease from epidemiology to therapy. G Ital Nefrol Nov–Dec 24 (6):574–83.
Ix JH, Shlipak MG, Liu HH, Schiller NB, Whooley MA. Association between renal insufficiency and inducible ischemia in patients with coronary artery disease: the heart and soul study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(12):3233–8.
Nardi E, Cottone S, Mulè G, Palermo A, Cusimano P, Cerasola G. Influence of chronic renal insufficiency on left ventricular diastolic function in hypertensives without left ventricular hypertrophy. J Nephrol. 2007;20(3):320–8.
Kimura T, Iio K, Obi Y, Hayashi T. Left ventricular hypertrophy in predialysis chronic kidney disease: impact of cardiomuscular stress markers. Nippon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2007;49(8):1007–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shehata, M., El Abd, D., El Shanawani, F. et al. Cadherin 5 and Annexin V as Circulating Endothelial Microparticles: Markers for Atherosclerotic Vascular Lesions in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure. Kidney 19, 307–315 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00596-010-0176-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00596-010-0176-0