Abstract
Purpose
To investigate a prognostic score for stage II–III colorectal cancer (CRC) based on post-CEA and pT4 levels.
Methods
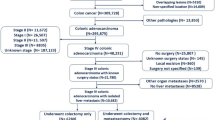
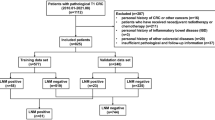
Two cohorts of stage II–III CRC patients who underwent curative surgery between 2011 and 2017 were included. The prognostic score (T-CEA score) was calculated as follows: T-CEA-0, post-CEA ≤ 5 ng/mL and pT1–3; T-CEA-1, post-CEA > 5 ng/mL or pT4; T-CEA-2, post-CEA > 5 ng/mL and pT4.
Results
The T-CEA scores of the 587 patients were as follows: T-CEA-0 (n = 436; 74%), T-CEA-1 (n = 129; 22%), and T-CEA-2 (n = 10; 2%). The 5-year recurrence-free survival (RFS) rates of the T-CEA-0, 1, and 2 groups were 80.3%, 54.8%, and 0%, respectively (P < 0.01), and the 5-year overall survival (OS) rates were 90.9%, 74.2%, and 0%, respectively (T-CEA-0 vs T-CEA-1: P < 0.01, T-CEA-1 vs T-CEA-2: P = 0.04). Multivariate analysis revealed that an elevated T-CEA score of 1 or 2 was a significant risk factor for poor RFS (HR: 2.89, P < 0.01) and OS (HR: 2.85, P < 0.01).
Conclusion
The T-CEA score is a reliable and convenient prognostic score for stage II–III CRC.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All authors are available for the raw data of this study.
References
Hashiguchi Y, Muro K, Saito Y, Ito Y, Ajioka Y, Hamaguchi T, et al. Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (JSCCR) guidelines 2019 for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2000;25(1):1–42.
Chiba S, Okayama H, Noda M, Saito K, Nakajima T, Aoto K, et al. Stromal VCAN expression as a potential prognostic biomarker for disease recurrence in stage II–III colon cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2016;37(9):878–87.
Ujiie D, Okayama H, Saito K, Ashizawa M, Min AKT, Endo E, et al. KRT17 as a prognostic biomarker for stage II colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2020;41(5):591–9.
Weiser MR, Landmann RG, Kattan MW, Gonen M, Shia J, Chou J, et al. Individualized prediction of colon cancer recurrence using a nomogram. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:380–5.
Weiser MR, Gönen M, Chou JF, Kattan MW, Schrag D. Predicting survival after curative colectomy for cancer: individualizing colon cancer staging. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4796–802.
Kanemitsu Y, Shida D, Tsukamoto S, Ueno H, Ishiguro M, Ishihara S, et al. Nomograms predicting survival and recurrence in colonic cancer in the era of complete mesocolic excision. BJS Open. 2019;3:539–48.
Sonoda H, Yamada T, Matsuda A, Ohta R, Shinji S, Yokoyama Y, et al. Elevated serum carcinoembryonic antigen level after curative surgery is a prognostic biomarker of stage II–III colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2021;47(11):2880–7.
Snaebjornsson P, Coupe VMH, Jonasson L, Meijer GA, van Grieken NC, Jonasson JG. pT4 stage II and III colon cancers carry the worst prognosis in a nationwide survival analysis. Shepherd’s local peritoneal involvement revisited. Int J Cancer. 2014;135:467–78.
Park JH, Fuglestad AJ, Køstner AH, Oliwa A, Graham J, Horgan PG, et al. Systemic inflammation and outcome in 2295 patients with stage I-III colorectal cancer from Scotland and Norway: first results from the Scotscan colorectal cancer group. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27:2784–94.
Takagi K, Buettner S, Ijzermans JNM. Prognostic significance of the controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score in patients with colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2020;78:91–6.
Song W, Wang K, Zhang RJ, Zou SB. Prognostic value of the lymphocyte monocyte ratio in patients with colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(49): e5540.
Zhang J, Zhang HY, Li J, Shao XU, Zhang CX. The elevated NLR, PLR and PLT may predict the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(40):68837–46.
Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Yamamoto A, Shigemori T, Ide S, Kitajima T, et al. Lymphocyte-C-reactive protein ratio as promising new marker for predicting surgical and oncological outcomes in colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2020;272:342–51.
Ito K, Hibi K, Ando H, Hidemura K, Yamazaki T, Akiyama S, et al. Usefulness of analytical CEA doubling time and half-life time for overlooked synchronous metastases in colorectal carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2002;32(2):54–8.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Clinical practice guidelines in oncology: colon cancer. Version 4.2020. Fort Washington: NCCN; 2020.
Argiles G, Tabernero J, Labianca R, Hochhauser D, Salazar R, Iveson T, et al. Localized colon cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2020;31(10):1291–305.
Gill S, Loprinzi CL, Sargent DJ, Thomé SD, Alberts SR, Haller DG, et al. Pooled analysis of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy for stage II and III colon cancer: who benefits and by how much? J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(10):1797–806.
Merkel S, Wein A, Günther K, Papadopoulos T, Hohenberger W, Hermanek P. High-risk groups of patients with Stage II colon carcinoma. Cancer. 2001;92:1435–43.
Gunderson LL, Jessup JM, Sargent DJ. Revised TN categorization for colon cancer based on national survival outcome data. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(2):264–71.
Tie J, Wang Y, Tomasetti C, Li L, Springer S, Kinde I, et al. Circulating tumor DNA analysis detects minimal residual disease and predicts recurrence in patients with stage II colon cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(346):346ra92.
Tie J, Cohen JD, Wang Y, Christie M, Simons K, Lee M, et al. Circulating tumor DNA analyses as markers of recurrence risk and benefit of adjuvant therapy for stage III colon cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5(12):1710–7.
Reinert T, Henriksen TV, Christensen E, Sharma S, Salari R, Sethi H, et al. Analysis of plasma cell-free DNA by ultradeep sequencing in patients with stages I to III colorectal cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5(8):1124–31.
Iwai T, Yamada T, Takahashi G, Takeda K, Koizumi M, Shinji S, et al. Circulating cell-free long DNA fragments predict post-hepatectomy recurrence of colorectal liver metastases. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2020;46(1):108–14.
Lonardi S, Montagut C, Pietrantonio F, Elez E, Sartore-Bianchi A, Tarazona N, et al. The PEGASUS trial: Post-surgical liquid biopsy-guided treatment of stage III and high-risk stage II colon cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(15):suppl.TPS124.
Shirasu H, Taniguchi H, Matsuhashi N, Kotaka M, Nakamura Y, Oki E, et al. A randomized, double-blind, phase III study comparing trifluridine/tipiracil hydrochloride therapy versus placebo in resected colorectal cancer patients who are positive for blood circulating tumor DNA after standard adjuvant therapy (EPOC 1905): ALTAIR trial in CIRCULATE-Japan (trial in progress). J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(4):suppl.TPS215.
Moretto R. Exploiting circulating tumour DNA to intensify the postoperative treatment resected colon cancer patients (ERASE-CRC). ClinicalTrials.gov NCT05062889.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. Steven D. Aird for preliminary English language editing.
Funding
This research did not receive any grants from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or non-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sonoda, H., Yamada, T., Matsuda, A. et al. The T-CEA score: a useful prognostic indicator based on postoperative CEA and pathological T4 levels for patients with stage II–III colorectal cancer. Surg Today 53, 890–898 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-023-02644-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-023-02644-6