Abstract
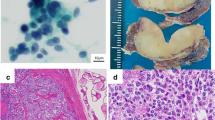
A thyroid nodule with elevated plasma levels of calcitonin is usually suggestive of a medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC); however, thyroid and extrathyroid conditions have been reported with elevated plasma calcitonin levels in the absence of MTC. We report the case of a patient with a thyroid nodule and an elevated basal plasma calcitonin level of 315 pg/ml (normal value <100 pg/ml) who underwent a left hemithyroidectomy. Interestingly, histopathological examination revealed a Hürthle-cell carcinoma with positive neuroendocrine (NE) markers such as calcitonin and synapthophysin, but not with chromogranin staining. Thus, we discuss the phenomenon of non-NE tumors showing positivity for NE markers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munitiz, V., Martinez-Barba, E., Riquelme, J. et al. Elevated Basal Calcitonin Levels in a Patient with a Hürthle-Cell Carcinoma of the Thyroid and Neuroendocrine Differentiation: Report of a Case. Surg Today 35, 404–406 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-004-2928-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-004-2928-9