Abstract
Aims
Besides energy supply, β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) acts as a bioactive molecule to play multiple protective roles, even in diabetes and its complications. The aim of this study was to investigate the antagonizing effects of BHB against diabetic glomerulosclerosis and the underlying mechanism.
Methods
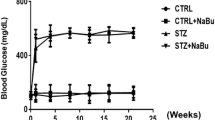
Male Sprague–Dawley rats were intraperitoneally injected with streptozotocin to induce diabetes and then treated with different concentrations of β-hydroxybutyrate. After 10 weeks, body weight, blood glucose, serum creatinine and 24-h urine protein were examined. Glomerular morphological changes and the contents of collagen type IV (COL IV) were evaluated. Then, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β/Smad3 contents and matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) generation were detected. Moreover, the total contents of trans-activating histone H3K9 β-hydroxybutyrylation (H3K9bhb) and the contents of H3K9bhb in the Mmp-2 promoter were measured.
Results
It was firstly confirmed that BHB treatments reduced renal biochemical indicators and attenuated glomerular morphological changes of the diabetic rats, with COL IV content decreased in a concentration-dependent manner. Then, BHB treatments were found to up-regulate renal MMP-2 generation of the diabetic rats significantly, while not affecting the increased TGF-β/Smad3 contents. Furthermore, the contents of H3K9bhb in the Mmp-2 promoter were elevated significantly for the middle and high concentrations of BHB treatments, up-regulating MMP-2 generation.
Conclusion
BHB treatments could up-regulate MMP-2 generation via causing elevated H3K9bhb in its promoter to antagonize glomerulosclerosis in the diabetic rats.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flyvbjerg A (2017) The role of the complement system in diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 13:311–318
Ibarra-Gonzalez I, Cruz-Bautista I, Bello-Chavolla OY et al (2018) Optimization of kidney dysfunction prediction in diabetic kidney disease using targeted metabolomics. Acta Diabetol 55:1151–1161
Xu JL, Gan XX, Ni J et al (2018) SND p102 promotes extracellular matrix accumulation and cell proliferation in rat glomerular mesangial cells via the AT1R/ERK/Smad3 pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39:1513–1521
Chen F, Zhu X, Sun Z et al (2018) Astilbin inhibits high glucose-induced inflammation and extracellular matrix accumulation by suppressing the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathway in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Front Pharmacol 9:1187
Cavaleri F, Bashar E (2018) Potential synergies of beta-hydroxybutyrate and butyrate on the modulation of metabolism, inflammation, cognition, and general health. J Nutr Metab 2018:7195760
Lee BS, Woo DC, Woo CW et al (2018) Exogenous beta-hydroxybutyrate treatment and neuroprotection in a suckling rat model of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Dev Neurosci 40:73–83
Zhang J, Li X, Ren Y et al (2018) Intermittent fasting alleviates the increase of lipoprotein lipase expression in brain of a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease: possibly mediated by beta-hydroxybutyrate. Front Cell Neurosci 12:1
Han YM, Bedarida T, Ding Y et al (2018) beta-Hydroxybutyrate prevents vascular senescence through hnRNP A1-mediated upregulation of Oct4. Mol Cell 71:1064–1078
Klos M, Morgenstern S, Hicks K et al (2019) The effects of the ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate on isolated rat ventricular myocyte excitation-contraction coupling. Arch Biochem Biophys 662:143–150
Min SH, Oh TJ, Baek SI et al (2018) Degree of ketonaemia and its association with insulin resistance after dapagliflozin treatment in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab 44:73–76
Trotta MC, Maisto R, Guida F et al (2019) The activation of retinal HCA2 receptors by systemic beta-hydroxybutyrate inhibits diabetic retinal damage through reduction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and the NLRP3 inflammasome. PLoS ONE 14:e211005
Uchihashi M, Hoshino A, Okawa Y et al (2017) Cardiac-specific bdh1 overexpression ameliorates oxidative stress and cardiac remodeling in pressure overload-induced heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 10:e004417
Li Y, Zhong Y, Gong W et al (2018) C-peptide prevents SMAD3 binding to alpha promoters to inhibit collagen type IV synthesis. J Mol Endocrinol 61:47–56
Yoon JJ, Park JH, Kim HJ et al (2019) Dianthus superbus improves glomerular fibrosis and renal dysfunction in diabetic nephropathy model. Nutrients 11:E553
Adamidis KN, Kopaka ME, Petraki C et al (2019) Glomerular expression of matrix metalloproteinases in systemic lupus erythematosus in association with activity index and renal function. Ren Fail 41:229–237
Mulder H (2011) Matrix metalloproteinases: keys to healthier blood vessels in diabetes? J Endocrinol 210:1–2
Santos S, Porto AE, Ribeiro LM et al (2017) Hyperglycemic condition during puberty increases collagen fibers deposition in the prostatic stroma and reduces MMP-2 activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 493:1581–1586
Shamsara J (2018) Identification of non-zinc binding inhibitors of MMP-2 through virtual screening and subsequent rescoring. Drug Res (Stuttg) 68:529–535
Poteryaeva ON, Russkikh GS, Zubova AV et al (2018) Changes in activity of matrix metalloproteinases and serum concentrations of proinsulin and C-peptide depending on the compensation stage of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Bull Exp Biol Med 164:730–733
Saejia P, Lirdprapamongkol K, Svasti J et al (2019) Perfluorooctanoic acid enhances invasion of follicular thyroid carcinoma cells through NF-kappaB and matrix metalloproteinase-2 activation. Anticancer Res 39:2429–2435
Huang C, Wang P, Xu X et al (2018) The ketone body metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate induces an antidepression-associated ramification of microglia via HDACs inhibition-triggered Akt-small RhoGTPase activation. Glia 66:256–278
Qiu X, Rong X, Yang J et al (2019) Evaluation of the antioxidant effects of different histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis) on human lens epithelial cells (HLECs) after UVB exposure. BMC Ophthalmol 19:42
Xie Z, Zhang D, Chung D et al (2016) Metabolic regulation of gene expression by histone lysine beta-hydroxybutyrylation. Mol Cell 62:194–206
Newman JC, Verdin E (2017) beta-Hydroxybutyrate: a signaling metabolite. Annu Rev Nutr 37:51–76
Zhao S, Zhang X, Li H (2018) Beyond histone acetylation-writing and erasing histone acylations. Curr Opin Struct Biol 53:169–177
Sleiman SF, Henry J, Al-Haddad R et al (2016) Exercise promotes the expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) through the action of the ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate. Elife 5:e15092
Li Y, Li X, He K et al (2018) C-peptide prevents NF-kappaB from recruiting p300 and binding to the inos promoter in diabetic nephropathy. FASEB J 32:2269–2279
Bae HR, Kim DH, Park MH et al (2016) beta-Hydroxybutyrate suppresses inflammasome formation by ameliorating endoplasmic reticulum stress via AMPK activation. Oncotarget 7:66444–66454
Orhan N, Ugur YC, Ekizoglu O et al (2016) Effects of beta-hydroxybutyrate on brain vascular permeability in rats with traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 1631:113–126
Ren W, Zhao C, Wang Y et al (2019) Ramipril can alleviate the accumulation of renal mesangial matrix in rats with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting insulin-like growth factor-11. Acta Cir Bras 34:e631258489
Margolis LM, O'Fallon KS (2020) Utility of ketone supplementation to enhance physical performance: a systematic review. Adv Nutr 11:412–419
Soto-Mota A, Vansant H, Evans RD et al (2019) Safety and tolerability of sustained exogenous ketosis using ketone monoester drinks for 28 days in healthy adults. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 109:104506
Stekovic S, Hofer SJ, Tripolt N et al (2019) Alternate day fasting improves physiological and molecular markers of aging in healthy, non-obese humans. Cell Metab 30:462–476.e6
Kimura Y, Kuno A, Tanno M et al (2019) Canagliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, normalizes renal susceptibility to type 1 cardiorenal syndrome through reduction of renal oxidative stress in diabetic rats. J Diabetes Investig 10:933–946
Karolak MJ, Guay JA, Oxburgh L (2018) Inactivation of MAP3K7 in FOXD1-expressing cells results in loss of mesangial PDGFRBeta and juvenile kidney scarring. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 315:F336–F344
Cui N, Hu M, Khalil RA (2017) Biochemical and biological attributes of matrix metalloproteinases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 147:1–73
Kim DH, Park MH, Ha S et al (2019) Anti-inflammatory action of beta-hydroxybutyrate via modulation of PGC-1alpha and FoxO1, mimicking calorie restriction. Aging (Albany NY) 11:1283–1304
Zambrano S, Moller-Hackbarth K, Li X et al (2019) GPRC5b modulates inflammatory response in glomerular diseases via NF-kappaB pathway. J Am Soc Nephrol 30:1573–1586
Yürük Yıldırım Z, Yılmaz A, Pehlivanoğlu C et al (2019) Urine levels of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 11:157–163
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81600384 and 81470595) and the Hebei Natural Science Foundation (H2015206101).
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81600384 and 81470595) and the Hebei Natural Science Foundation (H2015206101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WL, YY, HW, MH and CX conducted the experiments. KL and YW analyzed the data. WL and YL wrote the manuscript. YL and JQ convinced the whole project and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethics Review Committee for Animal Experimentation of Hebei Medical University.
Informed consent
A verbal informed consent was obtained from each study subject for publication.
Availability of data and material
All data will be available upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to the topical collection diabetic nephropathy, managed by Giuseppe Pugliese.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
592_2020_1552_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Effects of β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) on the binding of NF-κB to the Mmp-2 promoter. a The protein content of NF-κB p65 was detected and calculated. b After DNA pull-down, the protein contents of NF-κB p65 were detected. c The ratios of pull-down NF-κB p65 to its input (nuclear NF-κB p65) were calculated to show the relative bound contents. **p < 0.01 or *p < 0.05, vs control (Con) group (n = 3). DM, diabetes mellitus; BHB1, DM + low concentration BHB; BHB2, DM + middle concentration BHB; BHB3, DM + high concentration BHB (TIF 702 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, W., Yu, Y., Wang, H. et al. Up-regulation of MMP-2 by histone H3K9 β-hydroxybutyrylation to antagonize glomerulosclerosis in diabetic rat. Acta Diabetol 57, 1501–1509 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-020-01552-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-020-01552-2