Abstract
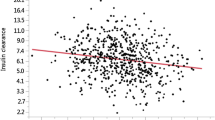
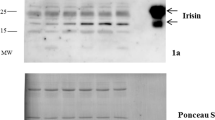
Irisin, a novel myokine, was proposed to be able to regulate glucose homeostasis and obesity in mice. Whether irisin levels are associated with cardio-metabolic variables, insulin sensitivity, and vascular atherosclerosis in humans remain unsettled. To determine the associations between circulating irisin levels, cardio-metabolic variables, insulin sensitivity, and common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT), an indicator of vascular atherosclerosis, a cross-sectional evaluation of circulating irisin levels and cardio-metabolic variables in 192 White adults was conducted. Insulin sensitivity and insulin clearance were assessed by euglycemic–hyperinsulinemic clamp. Common carotid IMT was measured by ultrasound. After adjusting for age and gender, irisin levels were positively correlated with body fat mass (r = 0.12, P < 0.05), fasting (r = 0.17, P < 0.01), 2 h post-load insulin (r = 0.15, P < 0.02) levels, and IMT (r = 0.29, P < 0.0001) and were negatively correlated with insulin-stimulated glucose disposal (r = −0.18, P = 0.007), Matsuda index (r = −0.13, P < 0.04), disposition index (r = −0.278, P < 0.0001), and insulin clearance (r = −0.26, P < 0.0001). After adjusting for age, gender, and BMI, individuals in the highest tertile of irisin levels exhibited higher body fat mass (P < 0.01), fasting (P < 0.05), 2 h post-load (P < 0.01) insulin levels, carotid IMT (P < 0.001), lower insulin-stimulated glucose disposal (P < 0.001), Matsuda index (P < 0.01), disposition index (P < 0.01), and insulin clearance (P < 0.001) as compared with subjects in the lowest tertile of circulating irisin levels. Irisin is inversely associated with insulin sensitivity and positively associated with carotid IMT in humans, suggesting either increased release by adipose/muscle tissue in response to deterioration of insulin sensitivity or a compensatory increase in irisin to overcome an underlying irisin resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM (2012) Prevalence of obesity in the United States, 2009–2010. NCHS Data Brief 82:1–8
Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM et al (2009) Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 120:1640–1645
Prospective Studies Collaboration, Whitlock G, Lewington S et al (2009) Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet 73:1083–1096
Meigs JB, Wilson PW, Fox CS et al (2006) Body mass index, metabolic syndrome, and risk of type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:2906–2912
Arnlöv J, Ingelsson E, Sundström J, Lind L (2010) Impact of body mass index and the metabolic syndrome on the risk of cardiovascular disease and death in middle-aged men. Circulation 121(2):230–236
Ford ES (2005) Risks for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes associated with the metabolic syndrome: a summary of the evidence. Diabetes Care 28:1769–1778
Reaven G (1988) Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37:1595–1607
Tuomilehto J, Lindström J, Eriksson JG et al (2001) Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 344:1343–1350
Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA (2012) Muscles, exercise and obesity: skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8:457–465
Boström P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP et al (2012) A PGC1-a-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 481:463–468
Timmons JA, Baar K, Davidsen PK, Atherton PJ (2012) Is irisin a human exercise gene? Nature 488:E9–E10
Huh JY, Panagiotou G, Mougios V et al (2012) FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism 61:1725–1738
Hee Park K, Zaichenko L, Brinkoetter M et al (2013) Circulating irisin in relation to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:4899–4907
Stengel A, Hofmann T, Goebel-Stengel M, Elbelt U, Kobelt P, Klapp BF (2013) Circulating levels of irisin in patients with anorexia nervosa and different stages of obesity–correlation with body mass index. Peptides 39:125–130
Liu JJ, Wong MD, Toy WC et al (2013) Lower circulating irisin is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complicat 27:365–369
Moreno-Navarrete JM, Ortega F, Serrano M et al (2013) Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:E769–E778
Choi YK, Kim MK, Bae KH et al (2013) Serum irisin levels in new-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 100:96–101
Staiger H, Böhm A, Scheler M et al (2013) Common genetic variation in the human FNDC5 locus, encoding the novel muscle-derived ‘browning’ factor irisin, determines insulin sensitivity. PLoS One 25(8):e61903
Staiger H, Stančáková A, Zilinskaite J et al (2008) A candidate type 2 diabetes polymorphism near the HHEX locus affects acute glucose-stimulated insulin release in European populations: results from the EUGENE2 study. Diabetes 57:514–517
Stancáková A, Pihlajamäki J, Kuusisto J et al (2008) SNP rs7754840 of CDKAL1 is associated with impaired insulin secretion in non-diabetic offspring of type 2 diabetic subjects (the EUGENE2 study) and in a large sample of men with normal glucose tolerance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:1924–1930
Marini MA, Succurro E, Frontoni S et al (2012) Insulin sensitivity, β-cell function, and incretin effect in individuals with elevated 1-h postload plasma glucose levels. Diabetes Care 35:868–872
Marini MA, Frontoni S, Mineo D et al (2003) The Arg972 variant in insulin receptor substrate-1 is associated with an atherogenic profile in offspring of type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:3368–3371
Succurro E, Marini MA, Arturi F et al (2009) Elevated one-hour post-load plasma glucose levels identifies subjects with normal glucose tolerance but early carotid atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 207:245–249
Marini MA, Frontoni S, Succurro E et al (2013) Insulin clearance is associated with carotid artery intima–media thickness. Atherosclerosis 229:453–458
Abdul-Ghani MA, Matsuda M, Balas B, DeFronzo RA (2007) Muscle and liver insulin resistance indexes derived from the oral glucose tolerance test. Diabetes Care 30:89–94
The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus (2003) Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 26:3160–3167
Faber OK, Christensen K, Kehlet H, Madsbad S, Binder C (1981) Decreased insulin removal contributes to hyperinsulinemia in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 53:618–621
Marini MA, Frontoni S, Succurro E et al (2013) Decreased insulin clearance in individuals with elevated 1-h post-load plasma glucose levels. PLoS One 8:e77440
Mittelman SD, Van Citters GW, Kim SP et al (2000) Longitudinal compensation for fat-induced insulin resistance includes reduced insulin clearance and enhanced β cell response. Diabetes 49:2116–2125
O’Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr (1999) Carotid artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med 340:14–22
Nigro J, Osman N, Dart AM, Little PJ (2006) Insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. Endocr Rev 27:242–259
Madonna R, Pandolfi A, Massaro M, Consoli A, De Caterina R (2004) Insulin enhances vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human cultured endothelial cells through a pro-atherogenic pathway mediated by p38 mitogen activated protein-kinase. Diabetologia 47:532–536
Madonna R, De Caterina R (2009) Prolonged exposure to high insulin impairs the endothelial PI3-kinase/Akt/nitric oxide signalling. Thromb Haemost 101:345–350
Koh YJ, Park BH, Park JH, Han J, Lee IK, Park JW, Koh GY (2009) Activation of PPARγ induces profound multilocularization of adipocytes in adult mouse white adipose tissues. Exp Mol Med 41:880–895
Daniele G, Guardado Mendoza R et al (2014) The inflammatory status score including IL-6, TNF-α, osteopontin, fractalkine, MCP-1 and adiponectin underlies whole-body insulin resistance and hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol 51:123–131
Tripathy D, Daniele G, Fiorentino TV et al (2013) Pioglitazone improves glucose metabolism and modulates skeletal muscle TIMP-3–TACE dyad in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, mechanistic study. Diabetologia 56:2153–2163
Conflict of interest
G. Sesti, F. Andreozzi, T. V. Fiorentino, G. C. Mannino, A. Sciacqua, M. A. Marini and F. Perticone declare they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights disclosure
All procedures followed were approved by approved Institutional Ethics Committee of the University of Rome Tor Vergata and Catanzaro and in accordance with the ethical of the Helsinki declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.
Informed consent disclosure
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Managed by Antonio Secchi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sesti, G., Andreozzi, F., Fiorentino, T.V. et al. High circulating irisin levels are associated with insulin resistance and vascular atherosclerosis in a cohort of nondiabetic adult subjects. Acta Diabetol 51, 705–713 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0576-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0576-0