Abstract
Background
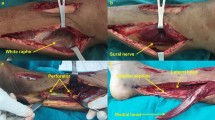
Open proximal tibial fractures accompanied by soft tissue loss are substantially challenging to accomplish both bony consolidation and wound healing. The authors retrospectively delineated the utility of the various forms of the gastrocnemius muscle in fix & flap regimen for management of such complicated injuries.
Methods
Thirty-one patients with open fracture accompanied by soft tissue loss of proximal tibia were managed by the protocol of fix & gastrocnemius flap. The collected data included implant for fixation, form of the gastrocnemius flap, postoperative complications, union time, and clinical assessment.
Results
According to fixation devices, lateral anatomical locking compression plates were selected in 28 cases, dual plates in 1, and interlocking nails in 2. According to the forms of the gastrocnemius flap, medial gastrocnemius flap was utilized in 22 cases, medial hemigastrocnemius flap in 2, medial myocutaneous gastrocnemius flap in 2, lateral gastrocnemius flap in 3, and combined medial and lateral gastrocnemius flaps in 2. All flaps completely survived without any flap-related complications. Fracture consolidation was established in all patients with an average period of 19.9 weeks (range 16–26). Surgical site infection occurred in 3 cases, and delayed union in 1. By functional score of Puno, 3 cases were determined to be excellent, 27 to be good, and 1 to be fair.
Conclusion
Concurrent use of internal fixation and gastrocnemius flap reconstruction is a reliable and efficient protocol in managing open fractures with accompanying soft tissue defect of proximal tibia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canton G, Santolini F, Stella M, Moretti A, Surace MF, Murena L (2020) Strategies to minimize soft tissues and septic complications in staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 30(4):671–680
Devkota P, Manandhar HK, Khadka PB, Mainali LP, Khan JA, Acharya BM et al (2014) Less invasive stabilization system for the management of proximal tibia fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24(6):993–998
Shao J, Chang H, Zhu Y, Chen W, Zheng Z, Zhang H et al (2017) Incidence and risk factors for surgical site infection after open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg 41:176–182
Thabet AM, Simson JE, Gerzina C, Dabash S, Adler A, Abdelgawad AA (2018) The impact of acute compartment syndrome on the outcome of tibia plateau fracture. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 28(1):85–93
Nork SE, Barei DP, Schildhauer TA, Agel J, Holt SK, Schrick JL et al (2006) Intramedullary nailing of proximal quarter tibial fractures. J Orthop Trauma 20(8):523–528
Vidyadhara S, Sharath KR (2006) Prospective study of the clinico-radiological outcome of interlocked nailing in proximal third tibial shaft fractures. Injury 37(6):536–542
Wysocki RW, Kapotas JS, Virkus WW (2009) Intramedullary nailing of proximal and distal one-third tibial shaft fractures with intraoperative two-pin external fixation. J Trauma Inj Infect Crit Care 66(4):1135–1139
Breugem CC, Strackee SD (2006) Is there evidence-based guidance for timing of soft tissue coverage of grade III B tibia fractures? Int J Low Extrem Wounds 5(4):261–270
Gopal S, Majumder S, Batchelor AGB, Knight SL, De Boer P, Smith RM (2000) Fix and flap: the radical orthopaedic and plastic treatment of severe open fractures of the tibia. J Bone Jt Surg Ser B 82(7):959–966
Daigeler A, Drücke D, Tatar K, Homann HH, Goertz O, Tilkorn D et al (2009) The pedicled gastrocnemius muscle flap: a review of 218 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 123(1):250–257
Kilic A, Denney B, De La Torre J (2019) Reconstruction of knee defects using pedicled gastrocnemius muscle flap with split–thickness skin grafting: a single surgeon’s experience with 21 patients. J Knee Surg 32(5):463–467
Agarwal P, Dawar R, Yadav P (2011) The segmental gastrocnemius muscles’ flap: a cadaveric study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 64(9):1202–1206
Mayoly A, Mattei JC, Moullot P, Jaloux C, Rochwerger A, Casanova D et al (2018) Gastrocnemius myocutaneous flaps for knee joint coverage. Ann Plast Surg 81(2):208–214
Puno RM, Grossfeld SL, Henry SL, Seligson D, Harkess J, Tsai TM (1996) Functional outcome of patients with salvageable limbs with grades III-B and III-C open fractures of the tibia. Microsurgery 17(3):167–173
Godina M, Lister G (1986) Early microsurgical reconstruction of complex trauma of the extremities. Plast Reconstr Surg 78:285–292
Gopal S, Giannoudis PV, Murray A, Matthews SJ, Smith RM (2004) The functional outcome of severe, open tibial fractures managed with early fixation and flap coverage. J Bone Jt Surg Ser Br vol 86(6):861–867
Tielinen L, Lindahl JE, Tukiainen EJ (2007) Acute unreamed intramedullary nailing and soft tissue reconstruction with muscle flaps for the treatment of severe open tibial shaft fractures. Injury 38(8):906–912
Naique SB, Pearse M, Nanchahal J (2006) Management of severe open tibial fractures: the need for combined orthopaedic and plastic surgical treatment in specialist centres. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88(3):351–357
Jitprapaikulsarn S, Patamamongkonchai C, Gromprasit A, Thremthakanpon W (2021) Simultaneous internal fixation and soft tissue coverage by soleus muscle flap and variances: a reproducible strategy for managing open fractures of tibial shaft. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 31(2):365–373
Wood T, Sameem M, Avram R, Bhandari M (2012) A systematic review of early versus delayed wound closure in patients with open fractures requiring flap coverage. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 72(4):1078–1085
Chou YC, Wu CC, Chan YS, Chang CH, Hsu YH, Huang YC (2010) Medial gastrocnemius muscle flap for treating wound complications after double-plate fixation via two-incision approach for complex tibial plateau fractures. J Trauma Inj Infect Crit Care 68(1):138–145
Franke J, Hohendorff B, Alt V, Thormann U, Schnettler R (2016) Suprapatellar nailing of tibial fractures–Indications and technique. Injury 47(2):495–501
McConnell T, Tornetta P, Tilzey J, Casey D (2001) Tibial portal placement: the radiographic correlate of the anatomic safe zone. J Orthop Trauma 15(3):207–209
Shahulhameed A, Roberts CS, Ojike NI (2011) Technique for precise placement of poller screws with intramedullary nailing of metaphyseal fractures of the femur and the tibia. Injury 42(2):136–139
Stinner DJ, Mir H (2014) Techniques for intramedullary nailing of proximal tibia fractures. Orthop Clin North Am 45(1):33–45
Smith TO, Hedges C, Schankat K, Hing CB (2010) A systematic review of the clinical and radiological outcomes of LISS plating for proximal tibial fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 20(2):141–150
Mahadeva D, Costa ML, Gaffey A (2008) Open reduction and internal fixation versus hybrid fixation for bicondylar/severe tibial plateau fractures: A systematic review of the literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128(10):1169–1175
Jitprapaikulsarn S, Benjawongsathien K, Patamamongkonchai C, Gromprasit A, Thremthakanpon W (2021) Combined medial gastrocnemius and hemisoleus flap: a reproducible alternative for open tibial fractures complicated with large or double soft tissue defects. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 31(2):413–420
Funding
There was no source of funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SJ was involved in drafting and revising the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content, study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, as well as acquisition of the data. KS, CP, AG and WT were involved in revising the manuscript for content and analysis and interpretation of data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
S. Jitprapaikulsarn, K Sukha, C Patamamongkonchai, A. Gromprasit and W. Thremthakanpon declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study has been approved by the ethical committees of Buddhachinaraj Hospital in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jitprapaikulsarn, S., Sukha, K., Patamamongkonchai, C. et al. Utilizing the various forms of the gastrocnemius muscle in fix & flap protocol: a reliable remedy for open proximal tibial fractures with accompanying soft tissue defect. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 32, 505–513 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03013-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03013-0