Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to identify, during total knee arthroplasty surgery, the effect on patellar kinematics of different patellar component designs in the same patients.
Methods
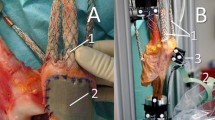
This study enrolled 84 patients with osteoarthritis. Intraoperative X-rays were used to measure internal rotation angle, flexion angle and lateral tilt were at different knee flexion angles with dome-type or anatomic-type patellar components (ATTUNE®, DePuy).
Results
Significant differences from baseline between the two types of components occurred at 120° of the knee flexion in the internal rotation angle, at 90° and 120° of the knee flexion in the flexion angle, and at 60° of the knee flexion in the lateral tilt.
Conclusion
This study revealed that the difference in patellar component design affects patellar kinematics. Therefore, the difference in patellar component design may affect patellar stability.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merkow RL, Soudry M, Insall JN (1985) Patellar dislocation following total knee replacement. J Bone Jt Surg Am 67:1321–1327
Roffman M, Hirsh DM, Mendes DG (1980) Fracture of the resurfaced patella in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 148:112–116
Clayton ML, Thirupathi R (1982) Patellar complications after total condylar arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 170:152–155
Healy WL, Wasilewski SA, Takei R, Oberlander M (1995) Patellofemoral complications following total knee arthroplasty. Correlation with implant design and patient risk factors. J Arthroplasty 10:197–201
Figgie HE 3rd, Goldberg VM, Heiple KG, Moller HS 3rd, Gordon NH (1986) The influence of tibial-patellofemoral location on function of the knee in patients with the posterior stabilized condylar knee prosthesis. J Bone Jt Surg Am 68:1035–1040
Aglietti P, Buzzi R, Gaudenzi A (1988) Patellofemoral functional results and complications with the posterior stabilized total condylar knee prosthesis. J Arthroplasty 3:17–25
Boyd AD Jr, Ewald FC, Thomas WH, Poss R, Sledge CB (1993) Long-term complications after total knee arthroplasty with or without resurfacing of the patella. J Bone Jt Surg Am 75:674–681
Dalury DF, Dennis DA (2003) Extensor mechanism problems following total knee replacement. J Knee Surg 16:118–122
Fehring TK, Odum S, Griffin WL, Mason JB, Nadaud M (2001) Early failures in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:315–318
Abraham W, Buchanan JR, Daubert H, Greer RB 3rd, Keefer J (1998) Should the patella be resurfaced in total knee arthroplasty? Efficacy of patellar resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 236:128–134
Ewald FC, Jacobs MA, Miegel RE, Walker PS, Poss R, Sledge CB (1984) Kinematic total knee replacement. J Bone Jt Surg Am 66:1032–1040
Saffarini M, Zaffagnini S, Bignozzi S, Colle F, Marcacci M, Dejour D (2015) Does patellofemoral geometry in TKA affect patellar position in mid-flexion? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23:1799–1807
Brilhault J, Ries MD (2010) Measuring patellar height using the lateral active flexion radiograph: effect of total knee implant design. Knee 17:148–151
Yoshii I, Whiteside LA, Anouchi YS (1992) The effect of patellar button placement and femoral component design on patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 275:211–219
Chew JT, Stewart NJ, Hanssen AD, Luo ZP, Rand JA, An KN (1997) Differences in patellar tracking and knee kinematics among three different total knee designs. Clin Orthop Relat Res 345:87–98
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1957) Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 16:494–502
Hsu HC, Luo ZP, Rand JA, An KN (1996) Influence of patellar thickness on patellar tracking and patellofemoral contact characteristics after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 11:69–80
Fitzpatrick CK, Baldwin MA, Clary CW, Wright A, Laz PJ, Rullkoetter PJ (2012) Identifying alignment parameters affecting implanted patellofemoral mechanics. J Orthop Res 30:1167–1175
Abo-Alhol TR, Fitzpatrick CK, Clary CW, Cyr AJ, Maletsky LP, Laz PJ et al (2014) Patellar mechanics during simulated kneeling in the natural and implanted knee. J Biomech 47:1045–1051
Huang CH, Hsu LI, Chang TK, Chuang TY, Shih SL, Lu YC et al (2017) Stress distribution of the patellofemoral joint in the anatomic V-shape and curved dome-shape femoral component: a comparison of resurfaced and unresurfaced patellae. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25:263–271
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TM, KI and KO designed the research. TM and RH participated in the operations and data collection. KY performed the statistical analysis. KI and KO participated in the editing and submission of the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mochizuki, T., Yano, K., Ikari, K. et al. Effect on patellar kinematics of the different patellar component designs in total knee arthroplasty: intraoperative measurement of dome type versus anatomic type. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 30, 419–424 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-019-02586-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-019-02586-1