Abstract
Background
Congenital patellar dislocation is a rarely encountered condition and is readily treated in childhood to prevent lasting disability, knee pain, decreased range of motion and ambulation problems. This condition is very rarely seen in skeletally mature patients, and the treatment of the condition represents a challenge to the orthopedic surgeon.
Surgical technique and methods
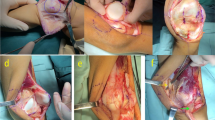
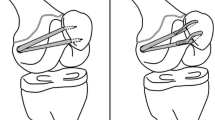
Patients were treated with soft tissue reconstruction and tibial tubercle transfer with or without a prior medial close-wedge distal femoral osteotomy, depending on the degree of valgus deformity. We, then, searched the database of our orthopedics center for cases of congenital patellar dislocation in skeletally mature patients who were surgically treated. We collected a total of five knees and analyzed the cases according to the type of surgery performed and difference between pre- and postoperative functions.
Results
Five knees with congenital patellar dislocation were treated. The mean age of the patients was 29.6 years, and mean follow-up time was 4.3 years. Mean preoperative range of motion was 65°, and it increased to a mean of 105.5° after surgical treatment. The mean preoperative Kujala score was 29.2 and increased to 67.2 after surgical treatment.
Discussion
Congenital patellar dislocations that are allowed to proceed to adulthood are difficult to treat, and surgical treatment depends on the degree of deformity of the patella and of the knee joint. This study shows that surgical treatment is able to correct the deformity and provide better knee function.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eilert RE (2001) Congenital dislocation of the patella. Clin Orthop Relat Res 389:22–29
Ghanem I, Wattincourt L, Seringe R (2000) Congenital dislocation of the patellaPart I: pathologic anatomy. J Pediatr Orthop 20:812–816
Stanisavljevic S, Zemenick G, Miller D (1976) Congenital, irreducible, permanent lateral dislocation of the patella. Clin Orthop Relat Res 116:190–199
Kumagi M, Ikeda S, Uchida K, Ono T, Tsumara H (2007) Total knee replacement for osteoarthritis of the knee with congenital dislocation of the patella. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89(11):1522–1524
Marmor L (1988) Total knee arthroplasty in a patient with congenital dislocation of the patella. Case report. Clin Orthop Relat Res 226:129–133
Noda M, Saegusa Y, Kashiwagi N, Seto Y (2011) Surgical treatment for permanent dislocation of the patella in adults. Orthopedics 34(12):e948–e951
Kwon JH, Kim JI, Seo DH, Kang KW, Nam JH, Nha KW (2013) Patellar dislocation with genu valgum treated by DFO. Orthopedics 36(6):840–843
Eilert RE (2001) Congenital dislocation of the patella. Clin Orthop Relat Res 389:22–29
Hudson J, Reddy VR, Krikler SJ (2003) Total knee arthroplasty for neglected permanent post-traumatic patellar dislocation–case report. Knee 10(2):207–212
Matsushita T, Kuroda R, Araki D, Kubo S, Matsumoto T, Kurosaka M (2013) Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction with lateral soft tissue release in adult patients with habitual patellar dislocation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(3):726–730
Avikainen VJ, Nikku RK, Seppänen-Lehmonen TK (1993) Adductor magnus tenodesis for patellar dislocation. Technique and preliminary results. Clin Orthop Relat Res 297:12–16
Beasley LS, Vidal AF (2004) Traumatic patellar dislocation in children and adolescents: treatment update and literature review. Curr Opin Pediatr 16(1):29–36
Winell J, Burke SW (2003) Sports participation of children with Down syndrome. Orthop Clin North Am 34(3):439–443
Bullek DD, Scuderi GR, Insall JN (1996) Management of the chronic irreducible patellar dislocation in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 11(3):339–345
Sternheim A, Garbedian S, Backstein D (2011) Distal femoral varus osteotomy: unloading the lateral compartment: long-term follow-up of 45 medial closing wedge osteotomies. Orthopedics 34(9):e488–e490
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshvin, S., Southern, E.P. & Wang, Y. Surgical treatment of congenital patellar dislocation in skeletally mature patients: surgical technique and case series. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 25, 1081–1086 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1619-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1619-0