Abstract
Background
Minimally invasive techniques have become increasing popular and are expanding into deformity surgery. The lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas anterior column release (ACR) is a newer minimally invasive alternative to posterior osteotomy techniques for correcting and promoting global spinal alignment. This procedure attempts to avoid the potential complications associated with conventional osteotomies, but has its own subset of unique complications to be discussed in depth.
Methods
A retrospective review was performed in all patients who underwent the minimally invasive (MIS) ACR procedure from 2010 to present at our institution. All perioperative and postoperative complications were recorded by an independent reviewer. Demographics, spinopelvic parameters, and operative data were collected. The primary etiologic diagnosis was adult spinal deformity. Spinopelvic parameters were measured based on standing 36-inch scoliosis films.
Results
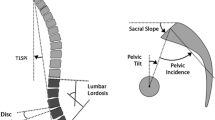
Thirty-one patients underwent a total of 47 MIS-ACRs. The mean age of the cohort was 62. Mean follow up was 12 months (range 3–38 months). The average change from in lumbar lordosis (LL) was 17.6°, in pelvic tilt was 4.3°, coronal Cobb was 13.9 and in SVA was 3.8 cm. Of the 47 MIS-ACR procedures, there were 9 (9/47, 19 %) major complications related to the ACR. Iliopsoas weakness was seen in eight patients and retrograde ejaculation in one patient. Only one patient remained with mild motor deficit at the most recent follow-up. No revision surgeries were required for the anterolateral approach. There was no vascular, visceral, or infectious complications associated with the MIS-ACR.
Conclusion
The MIS-ACR is one of the most technically demanding procedures performed from the lateral transpsoas approach. This procedure has the advantage of maintaining and improving spinal global alignment while minimizing blood loss and excessive tissue dissection. It comes with its own unique set of potentially catastrophic complications and should only be performed by surgeons proficient in both deformity correction and the lateral approach.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lafage V, Schwab F, Patel A, Hawkinson N, Farcy JP (2009) Pelvic tilt and truncal inclination: two key radiographic parameters in the setting of adults with spinal deformity. Spine 34:E599–E606. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181aad219
Cho KJ, Suk SI, Park SR, Kim JH, Kim SS, Choi WK, Lee KY, Lee SR (2007) Complications in posterior fusion and instrumentation for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine 32:2232–2237. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31814b2d3c
Auerbach JD, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Sehn JK, Milby AH, Bumpass D, Crawford CH 3rd, O’Shaughnessy BA, Buchowski JM, Chang MS, Zebala LP, Sides BA (2012) Major complications and comparison between 3-column osteotomy techniques in 105 consecutive spinal deformity procedures. Spine 37:1198–1210. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31824fffde
Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Edwards C, Lenke LG, Iffrig TM, Berra A, Baldus C, Blanke K (2003) Complications and outcomes of pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance. Spine 28:2093–2101. doi:10.1097/01.BRS.0000090891.60232.70
Glassman SD, Hamill CL, Bridwell KH, Schwab FJ, Dimar JR, Lowe TG (2007) The impact of perioperative complications on clinical outcome in adult deformity surgery. Spine 32:2764–2770. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31815a7644
Bianco K, Norton R, Schwab F, Smith JS, Klineberg E, Obeid I, Mundis G Jr, Shaffrey CI, Kebaish K, Hostin R, Hart R, Gupta MC, Burton D, Ames C, Boachie-Adjei O, Protopsaltis TS, Lafage V, International Spine Study G (2014) Complications and intercenter variability of three-column osteotomies for spinal deformity surgery: a retrospective review of 423 patients. Neurosurg Focus 36:E18. doi:10.3171/2014.2.FOCUS1422
Kelly MP, Lenke LG, Shaffrey CI, Ames CP, Carreon LY, Lafage V, Smith JS, Shimer AL (2014) Evaluation of complications and neurological deficits with three-column spine reconstructions for complex spinal deformity: a retrospective Scoli-RISK-1 study. Neurosurg Focus 36:E17. doi:10.3171/2014.2.FOCUS1419
Dorward IG, Lenke LG, Stoker GE, Cho W, Koester LA, Sides BA (2014) Radiographic and clinical outcomes of posterior column osteotomies in spinal deformity correction. Spine. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000000302
Smith JS, Sansur CA, Donaldson WF 3rd, Perra JH, Mudiyam R, Choma TJ, Zeller RD, Knapp DR Jr, Noordeen HH, Berven SH, Goytan MJ, Boachie-Adjei O, Shaffrey CI (2011) Short-term morbidity and mortality associated with correction of thoracolumbar fixed sagittal plane deformity: a report from the Scoliosis Research Society Morbidity and Mortality Committee. Spine 36:958–964. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181eabb26
Sansur CA, Smith JS, Coe JD, Glassman SD, Berven SH, Polly DW Jr, Perra JH, Boachie-Adjei O, Shaffrey CI (2011) Scoliosis research society morbidity and mortality of adult scoliosis surgery. Spine 36:E593–E597. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182059bfd
Al-Khouja LT, Baron EM, Johnson JP, Kim TT, Drazin D (2014) Cost-effectiveness analysis in minimally invasive spine surgery. Neurosurg Focus 36:E4. doi:10.3171/2014.4.FOCUS1449
O’Toole JE, Eichholz KM, Fessler RG (2009) Surgical site infection rates after minimally invasive spinal surgery. J Neurosurg Spine 11:471–476. doi:10.3171/2009.5.SPINE08633
Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Sansur CA, Berven SH, Fu KM, Broadstone PA, Choma TJ, Goytan MJ, Noordeen HH, Knapp DR Jr, Hart RA, Donaldson WF 3rd, Polly DW Jr, Perra JH, Boachie-Adjei O, Scoliosis Research Society Morbidity and Mortality Committee (2011) Rates of infection after spine surgery based on 108,419 procedures: a report from the Scoliosis Research Society Morbidity and Mortality Committee. Spine 36:556–563. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181eadd41
Uribe JS, Deukmedjian AR, Mummaneni PV, Fu KM, Mundis GM Jr, Okonkwo DO, Kanter AS, Eastlack R, Wang MY, Anand N, Fessler RG, La Marca F, Park P, Lafage V, Deviren V, Bess S, Shaffrey CI, International Spine Study G (2014) Complications in adult spinal deformity surgery: an analysis of minimally invasive, hybrid, and open surgical techniques. Neurosurg Focus 36:E15. doi:10.3171/2014.3.FOCUS13534
Deukmedjian AR, Dakwar E, Ahmadian A, Smith DA, Uribe JS (2012) Early outcomes of minimally invasive anterior longitudinal ligament release for correction of sagittal imbalance in patients with adult spinal deformity. Sci World J 2012:789698. doi:10.1100/2012/789698
Deukmedjian AR, Le TV, Baaj AA, Dakwar E, Smith DA, Uribe JS (2012) Anterior longitudinal ligament release using the minimally invasive lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach: a cadaveric feasibility study and report of four clinical cases. J Neurosurg Spine 17:530–539. doi:10.3171/2012.8.SPINE12432
Manwaring JC, Bach K, Ahmadian AA, Deukmedjian AR, Smith DA, Uribe JS (2014) Management of sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity with minimally invasive anterolateral lumbar interbody fusion: a preliminary radiographic study. J Neurosurg Spine 20:515–522. doi:10.3171/2014.2.SPINE1347
Deukmedjian AR, Ahmadian A, Bach K, Zouzias A, Uribe JS (2013) Minimally invasive lateral approach for adult degenerative scoliosis: lessons learned. Neurosurg Focus 35:E4. doi:10.3171/2013.5.FOCUS13173
Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, Farcy JP, Lafage V (2010) Adult spinal deformity-postoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine 35:2224–2231. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181ee6bd4
Dakwar E, Cardona RF, Smith DA, Uribe JS (2010) Early outcomes and safety of the minimally invasive, lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach for adult degenerative scoliosis. Neurosurg Focus 28:E8. doi:10.3171/2010.1.FOCUS09282
Dorward IG, Lenke LG (2010) Osteotomies in the posterior-only treatment of complex adult spinal deformity: a comparative review. Neurosurg Focus 28:E4. doi:10.3171/2009.12.FOCUS09259
Chen IH, Chien JT, Yu TC (2001) Transpedicular wedge osteotomy for correction of thoracolumbar kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis: experience with 78 patients. Spine 26:E354–E360
Yang BP, Ondra SL, Chen LA, Jung HS, Koski TR, Salehi SA (2006) Clinical and radiographic outcomes of thoracic and lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy for fixed sagittal imbalance. J Neurosurg Spine 5:9–17. doi:10.3171/spi.2006.5.1.9
Hu SS (2004) Blood loss in adult spinal surgery. Eur Spine J 13(Suppl 1):S3–S5. doi:10.1007/s00586-004-0753-x
Shaffrey E, Smith JS, Lenke LG, Polly DW Jr, Chen CJ, Coe JD, Broadstone PA, Glassman SD, Vaccaro AR, Ames CP, Shaffrey CI (2014) Defining rates and causes of mortality associated with spine surgery: comparison of two data collection approaches through the Scoliosis Research Society. Spine 39:579–586. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000000201
Shen J, Liang J, Yu H, Qiu G, Xue X, Li Z (2014) Risk factors for delayed infections after spinal fusion and instrumentation in patients with scoliosis. J Neurosurg Spine 21:648–652. doi:10.3171/2014.6.SPINE13636
Ahmadian A, Deukmedjian AR, Abel N, Dakwar E, Uribe JS (2013) Analysis of lumbar plexopathies and nerve injury after lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach: diagnostic standardization. J Neurosurg Spine 18:289–297. doi:10.3171/2012.11.SPINE12755
Buchowski JM, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Kuhns CA, Lehman RA Jr, Kim YJ, Stewart D, Baldus C (2007) Neurologic complications of lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy: a 10-year assessment. Spine 32:2245–2252. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31814b2d52
Assina R, Majmundar NJ, Herschman Y, Heary RF (2014) First report of major vascular injury due to lateral transpsoas approach leading to fatality. J Neurosurg Spine 21:794–798. doi:10.3171/2014.7.SPINE131146
Wang MY, Mummaneni PV, Fu KM, Anand N, Okonkwo DO, Kanter AS, La Marca F, Fessler R, Uribe J, Shaffrey CI, Lafage V, Haque RM, Deviren V, Mundis GM Jr, Minimally Invasive Surgery Section of the International Spine Study G (2014) Less invasive surgery for treating adult spinal deformities: ceiling effects for deformity correction with 3 different techniques. Neurosurgical Focus 36:E12. doi:10.3171/2014.3.FOCUS1423
Haque RM, Mundis GM Jr, Ahmed Y, El Ahmadieh TY, Wang MY, Mummaneni PV, Uribe JS, Okonkwo DO, Eastlack RK, Anand N, Kanter AS, La Marca F, Akbarnia BA, Park P, Lafage V, Terran JS, Shaffrey CI, Klineberg E, Deviren V, Fessler RG, International Spine Study G (2014) Comparison of radiographic results after minimally invasive, hybrid, and open surgery for adult spinal deformity: a multicenter study of 184 patients. Neurosurg Focus 36:E13. doi:10.3171/2014.3.FOCUS1424
Anand N, Baron EM, Khandehroo B (2014) Limitations and ceiling effects with circumferential minimally invasive correction techniques for adult scoliosis: analysis of radiological outcomes over a 7-year experience. Neurosurg Focus 36:E14. doi:10.3171/2014.3.FOCUS13585
Conflict of interest
Dr. Uribe is a consultant to NuVasive, Inc. No funding was provided for any portion of this research product. All other authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials and methods used in this study or findings specified in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murray, G., Beckman, J., Bach, K. et al. Complications and neurological deficits following minimally invasive anterior column release for adult spinal deformity: a retrospective study. Eur Spine J 24 (Suppl 3), 397–404 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3894-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3894-1