Abstract.
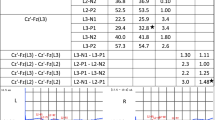
The study was conducted to assess the possible impact of spine deformity in patients with idiopathic scoliosis (IS) on tibial nerve somatosensory evoked potentials (t-SSEPs) and the influence of spine correction upon postoperative SSEP recordings. In 61 consecutive patients undergoing 64 spinal instrumentations, 129 pre- and postoperative SSEPs were analyzed. The degree of spine deformity was assessed by the pre-operative Cobb angle of the major scoliotic curve. In a control group, reference values of t-SSEP latencies were established with respect to body height. In a cohort study, IS patients were compared with healthy controls with respect to t-SSEP latency, amplitude, configuration and interside difference. The results of the analysis showed that preoperative-body-height-corrected t-SSEP latencies were prolonged in 61% of patients, with a pathological interside difference in 23.4% of them. The impairment of t-SSEPs was not related to the extent of spine deformity as assessed by the Cobb angle. Even without occurrence of postoperative neurological deficits, postoperative t-SSEPs showed significantly increased latencies without changes in t-SSEP configuration. The prolongation of t-SSEP latencies was related to the surgical procedure (combined ventro-dorsal approach), but not to the extent of spine correction, level of instrumentation, or number of fused segments. The analysis of preoperative t-SSEPs was of no predictive value for intra- or postoperative neurological complications. t-SSEPs are significantly affected in IS patients, although these patients show no obvious clinical neurological deficits. The extent of t-SSEP impairment is not related to the severity of scoliosis. Even in clinically uneventful surgery, the postoperative t-SSEPs can be deteriorated depending on the surgical approach. This indicates a subclinical impact of spine surgery upon spinal cord function.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hausmann, O., Min, K., Böni, T. et al. SSEP analysis in surgery of idiopathic scoliosis: the influence of spine deformity and surgical approach. Eur Spine J 12, 117–123 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-002-0398-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-002-0398-6