Abstract
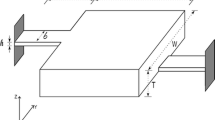
An acceleration sensor from polymer has been developed which balances a proof mass by magnetic forces. The sensor is fabricated from a polyimide membrane with conductor paths from gold patterned by photolithography and etching, a frame manufactured by ultrasonic hot embossing, and permanent magnets fixed to the frame. Except the conductor path and permanent magnets, all components are made of polymers on a planar substrate, and then the frame is kinked forming the desired three-dimensional structure. In a first try, a sensitivity of 0.46 V/(m/s²) was achieved, and cross axis sensitivity error was less than 3 %.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour-Sani E, Huang RS, Kwok CY (1994a) A novel electromagnetic accelerometer. Electron Device Lett IEEE 15(8):272–273. doi:10.1109/55.296213
Abbaspour-Sani E, Huang RS, Kwok CY (1994b) A linear electromagnetic accelerometer. Sens Actuators A 44:103–109. doi:10.1016/0924-4247(94)00792-6
Beeby S, Ensell G, Kraft M, White N (2004) MEMS mechanical sensors. Artech House, Boston London, p 177
Elwenspoek M, Wiegerink R (2001) Mechanical microsensors. Springer, Berlin, p 143
Goodenough F (1991) Airbags boom when IC accelerometer sees 50 g. Electron Design 39(15):45–56
Henrion W, DISanza L, Ip M, Terry S, Jerman H (1990) Wide dynamic range direct digital accelerometer. IEEE Solid-State Sens Actuator Workshop 4:153–157. doi:10.1109/SOLSEN.1990.109842
Khuntontong P, Blaser T, and Schomburg WK (2008) Ultrasonic micro hot embossing of thermoplastic polymers. In: Proceedings of the 24th Annual Meeting of the Polymer Processing Society, Salerno, Italy, pp 364
Khuntontong P, Blaser T, Schomburg WK (2009) Fabrication of molded interconnection devices by ultrasonic hot embossing on thin polymer films. IEEE T Electron Pack 32:152–156
Partridge A, Reynolds JK, Chui BW, Chow EM, Fitzgerld AM, Zhang L, Cooper SR, Kenny TW (2000) A high performance planar piezoresistive accelerometer. J Microelectromech Syst 9(1):58–66. doi:10.1109/84.825778
Roylance LM, Angell JB (1979) A batch-fabricated silicon accelerometer. Electron Device Lett IEEE ED 26:1911–1917. doi: 10.1109/T-ED.1979.19795
Rudolf F, Jornod A, Bergqvist J, Leuthold H (1990) Precision accelerometers with μg resolution. Sens Actuators A 21–23:297–302. doi:10.1016/0924-4247(90)85059-D
Schomburg WK (2011) Introduction to microsystem design. Springer, Berlin, pp 65–81
Schomburg WK, Burlage K, Gerhardy C (2011) Ultrasonic hot embossing. Micromachines 2(2):157–166. doi:10.3390/mi2020157
Sherman SJ, Tsang WK, Core TA, Payne RS, Quinn DE, Chau KH-L, Farash JA, Baum SK (1992) A low cost monolithic accelerometer; product/technology update. In: Tech. dig. International electron devices meeting 1992 (IEDM ‘92), 13–16:501–504. doi:10.1109/IEDM.1992.307410
Touwslager FJ, Willard NP, Leeuw DM (2002) I-line lithography of poly-(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) electrodes and application in all-polymer integrated circuits. Appl Phys Lett 8:4556–4558. doi:10.1063/1.1524031
van Nierop JH (1981) A low-cost linear accelerometer. J Phys E Sci Instrum 14:880–882. doi:10.1088/00223735/14/7/023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Schomburg, W.K. Electromagnetically force balanced polymer accelerometer. Microsyst Technol 19, 219–226 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1558-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1558-1