Abstract
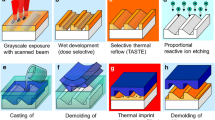
We succeeded in achieving inclined sidewalls in a positive-tone photoresist structure by adjusting the focus offsets in a projection ultraviolet (UV) lithography system. In our experiments, highly precise patterns on Ni-electroformed mold were replicated from a photoresist master. The practicality of the mold was then evaluated by thermal nanoimprint experiments on polycarbonate (PC). When the focus offsets became small by moving the UV image plane (defined by wafer surface) closer to the lens the inclined angles of the photoresist walls increased. In this work, the release force was measured using a desktop nanoimprint system equipped with a load cell that measured not only the compression power but also the tensile force in the de-molding process. Starting from the glass transition temperature T g (144°C) of PC, the heating temperature in the molding process was changed by increments of 10°C resulting in T g + 10, T g + 20, and T g + 30°C. The result showed that the release force decreased with increasing incline angles. It was observed that the more inclined the sidewalls of the mold pattern were, further small the release forces became, and the mold pattern became to be defended from deformation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker EW, Ehrfeld W, Hagmann P, Maner A, Münchmeyer D (1986) Fabrication of microstructures with high aspect ratios and great structural heights by synchrotron radiation lithography, galvanoforming, and plastic moulding (LIGA process). Microelectron Eng 4:35–56. doi:10.1016/0167-9317(86)90004-3
Chou SY, Krauss PR, Renstrom PJ (1995) Imprint of sub-25 nm vias and trenches in polymers. Appl Phys Lett 67:3114–3116. doi:10.1063/1.114851
Colburn M, Johnson SC, Stewart MD, Damle S, Bailey TC, Choi B, Wedlake M, Michaelson T, Sreenivasan SV, Ekerdt J, Wilson CG (1999) Step and flash imprint lithography: a new approach to high-resolution pattering. Proc SPIE 3676:379–389. doi:10.1117/12.3511550
Däschner W, Long P, Stein R, Wu C, Lee SH (1997) Cost-effective mass fabrication of multilevel diffractive optical elements by use a single optical exposure with a gray scale mask on high-energy beam-sensitive glass. Appl Opt 36:4675–4680. doi:10.1364/AO.36.004675
Gauthier MM (1995) Engineered materials handbook. ASM International Handbook Committee, Ohio
Guo Y, Liu G, Zhu X, Tian Y (2007) Analysis of the demolding forces during hot embossing. Microsyst Technol 13:411–415. doi:10.1007/s00542-006-0225-9
Haisma J, Verheijen M, Van den Heuvel K, Van den Berg J (1996) Mold-assisted nanolithography: a process for reliable pattern replication. J Vac Sci Technol B 14:4124–4128. doi:10.1116/1.588604
Herzing HP (1997) Micro-optics, elements, systems and applications. Taylor & Francis, London
Hirai Y, Harada S, Kikuta H, Tanaka Y (2002) Imprint lithography for curved cross-sectional structure using replicated Ni mold. J Vac Sci Technol B 20:2867–2871. doi:10.1116/1.1515305
Hirai Y, Yoshida S, Nobuyuki Takagi (2003) Defect analysis in thermal nano-imprint lithography. J Vac Sci Technol B 21:2765–2770. doi:10.1116/1.1629289
Horade M, Khumouang S, Fujioka K, Sugiyama S (2007) Mask design compensation for sloped sidewall structures fabricated by X-ray lithography. Microsyst Technol 13:215–219. doi:10.1007/s00542-006-0219-7
Kley E, Cumme M, Wittig L, Wu C (1999) Adapting existing e-beam writers to write HEBS-glass gray-scale masks. Proc SPIE 3633:35–45. doi:10.1117/12.349333
Lee KC, Lee SS (2005) Deep X-ray lithography using mask with integrated electrothermal actuator. Microsyst Technol 11:358–364. doi:10.1007/s00542-004-0455-7
McCord MA, Rooks MJ (2000) SPIE handbook of microlithography, micromachining and microfabrication. SPIE, Bellingham
Mekaru H, Takahashi M (2009) Ultrasonic nano-imprint on engineering plastics. J Vac Sci Technol A 27:785–792. doi:10.1116/1.3153278
Mekaru M, Utsumi Y, Hattori T (2002) Quasu-3D microstructure fabrication technique utilizing hard X-ray lithography of synchrotron radiation. Microsyst Technol 9:36–40. doi:10.1007/s00542-002-0210-x
Mekaru H, Takano T, Awazu K, Takahashi M, Maeda R (2007) Fabrication of a needle array using a Si gray mask for X-ray lithography. J Vac Sci Technol B 25:2196–2201. doi:10.1116/1.2794314
Mekaru H, Takano T, Awazu K, Takahashi M, Maeda R (2008) Fabrication and evaluation of a grayscale mask for X-ray lithography using MEMS technology. J Micro/Nanolith MEMS MOEMS 7: 013009-1-013009-9. doi: 10.1117/12.800753
Menz W, Mohr J, Paul O (2001) Microsystem technology. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Nakajima H (2004) Optics design using excel. Advanced Communication Media Co. Ltd Tokyo (in Japanese)
Nathanson HC, Newell WE, Wickstrom RA, Davis JR (1967) The resonant gate transistor. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 14:117–133
Nicolas S, Dufoure-Gergan E, Bosseboeuf A, Bourouina T, Gilles JP, Grandchamp JP (1998) Fabrication of a gray-tone mask and pattern transfer in thick photoreists. J Micromech Microeng 8:95–98. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/8/2/013
Reimer K, Hofmann U, Jürss M, Pilz W, Quenzer HJ, Wangner B (1997) Fabrication of microrelief surfaces using a one-step lithography process. Proc SPIE 3226:2–10. doi:10.1117/12.284557
Spears DL, Smith HI (1972) X-ray lithography: a new high resolution replication process. Solid State Technol 15:21–26
Tabata O, Matsuzaka N, Yamaji Y, Uemura S, Yamamoto K (2002) 3D fabrication by moving mask deep X-ray lithography (M2DXL) with multiple stages. In: Proceedings of IEEE 15th International Annual Conference on Micro Electronic Mechanical System, pp. 180–183
Takahashi M, Goto H, Meda R, Maruyama O (2006) Desktop nano-imprint system––Prototype and performance. In: Proceedings of Japan Society Precision Engineering Conference, pp. 737–738 (in Japanese)
Tanaka T, Namura T, Funabiki Y, Kitadani T, Idei K, Yamashita K, Noda D, Hattori T (2006) Fabrication of a tapered structure by means of exposure to diffracted UV light. In: Proceedings of 2006 International Symposium on Micro-Nano Mechatronics Human Science, 5–8
Tuner R, Desta Y, Kelly K, Zhang J, Geiger S, Cortez S, Mancini D (2003) Tapered LIGA HARMS. J Micromech Microeng 13:367–372. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/13/3/303
van Kan JA, Bettiol AA, Watt F (2003) Three-dimensional nanolithography using proton beam writing. Appl Phys Lett 83:1629–1631. doi:10.1063/1.1604468
Wang W, Soper SA (2006) Bio-MEMS technologies and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mekaru, H., Koizumi, O., Ueno, A. et al. Inclination of mold pattern’s sidewalls by combined technique with photolithography at defocus-positions and electroforming. Microsyst Technol 16, 1323–1330 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-009-0983-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-009-0983-2