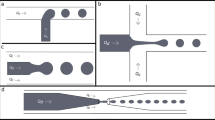
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a cell encapsulation and hydrogel-beads production method using droplet formation in a microchannel. The hydrogel-beads produced by the microfluidic device developed here have smaller diameter and narrower distribution in their diameter compared to the conventional method, such as the droplet extrusion and the emulsification. The effects of the flow velocity and microchannel wall were analyzed based on fluid dynamical analysis. The results revealed that the wall effect of the microchannel strongly affected to the diameter of the droplet and the shape of the hydrogel-beads.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- d :
-
diameter of droplet [m]
- d g :
-
diameter of hydrogel-beads [m]
- F D :
-
drag force [N]
- F S :
-
interfacial tension force [N]
- h :
-
depth of microchannel (50 × 10−6 m) [m]
- L N :
-
peripheral of nozzle exit [m]
- Q i :
-
flow rate [m3/s]
- U i :
-
mean liquid velocity [m/s]
- w :
-
width of microchannel (200 × 10−6 m) [m]
- w n :
-
width of nozzle (50 × 10−6 m) [m]
- γ i :
-
surface tension coefficient [Pa s]
- κ :
-
viscosity ratio between dispersed phase and continuous phase (μ 2/μ 1)
- μ i :
-
viscosity of liquid [Pa s]
- σ :
-
interfacial tension coefficient between alginate solution and oil [N/m]
- i:
-
1: continuous (oil) and 2: dispersed phases (alginate solution)
References
Antonow GN (1907) Sur la tension superficielle a la limite de deux couches. J Chem Phys 5:372–384
Babak VG, Skotnikova EA, Lukina IG, Pelletier S, Hubert P, Dellacherie E (2000) Hydrophobically associating alginate derivatives: surface tension properties of their mixed aqueous solutions with oppositely charged surfactans. J Colloid Interface Sci 225:505–210
Bungay PM, Brenner H (1973) The motion of a closely-fitting sphere in a fluid-filled tube. Int Multiph Flow 1:25–56
Chan LW, Lee HY, Heng PWS (2002) Production of alginate microspheres by internal gelation using an emulsification method. Int J Pharm 242:259–262
Chicheportiche D, Reach G (1988) In vitro kinetics of insulin release by microencapsulated rat islets: effect of the size of the microcapsules. Diabetologia 31:54–57
Hadamard J (1911) Mouvement permanent lent d’une sphere liquide et visqueuse dans un liquid visqueux. Comptes Rendus 152:1735–1738
Duliew C, Poncele D, Neufeld RJ (1999) Encapsulation and immobilization techniques. In: Kühtreiber WM, Lanza RP, Chick WL (eds) Cell encapsulation technology and therapeutics, Boston Kirkhäuser, pp 3–17
Dulong JL, Legallais C (2005) What are the relevant parameters for the geometrical optimization of implantable bioartificial pancreas. J Biomech Eng 127:1054–1061
Effenhauser CS, Bruin GJM, Paulus A, Ehrat M (1997) Integrated capillary electrophoresis on flexible silicone microdevices: analysis of DNA restriction fragments and detection of single DNA molecules on microchips. Anal Chem 69:3451–3457
Hortelano G, Al-Hendy A, Ofosu FA, Chang PL (1996) Delivery of human factor IX in mice by encapsulated recombinant myoblasts: a novel approach towards allogeneic gene therapy of hemophilia B. Blood 87:5095–5103
Meissner HP (1949) Critical constants from parachor and molar refraction. Chem Eng Prog 45(2):149–153
Nisisako T, Torii T, Higuchi T (2002) Droplet formation in a microchannel network. Lab chip 2:24–26
Orive G, Hernández RM, Gascón AR, Calafiore R, Chang TMSC, Vos P, Hortelano G, Hunkeler D, Lacík I, Pedraz L (2004) History, challenges and perspectives of cell microencapsulation. Trends Biotechnol 22(2):87–92
Prakash S, Chang TMS (1996) Microencapsulated genetically engineered live E. coli DH5 cells administered orally to maintain normal plasma urea level in uremic rats. Nat Med 2:883–887
Risso F, Colle-paillot F, Zagzoule M (2006) Experimental investigation of a bioartificial capsule flowing in a narrow tube. J Fluid Mech 547:149–173
Sugiura S, Oda T, Izumida Y, Aoyagi Y, Satake M, Ochiai A, Ohkohchi N, Nakajima M (2005) Size control of calcium alginate beads containing living cells using micro-nozzle array. Biomaterials 26:3327–3331
Sun Y, Ma X, Zhou D, Vacek I, Sun AM (1996) Normalization of diabetes in spontaneously diabetic cynomologus monkeys by xenografts of microencapsulated porcine islets without immunosuppression. J Clin Invest 98:1417–1422
Thorsen T, Roberts RW, Arnold FH, Quake SR (2001) Dynamic pattern formation in a vesicle-generating microfluidic device. Phys Rev Lett 86(18):4163–4166
Acknowledgments
This study is supported in part by grant-in-aids for JSPS Research Fellowships for Young Scientists (No. 16001152) and Center of Excellence for Re-search and Education on Complex Functional Mechanical Systems (COE program) of MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shintaku, H., Kuwabara, T., Kawano, S. et al. Micro cell encapsulation and its hydrogel-beads production using microfluidic device. Microsyst Technol 13, 951–958 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0291-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0291-z