Abstract
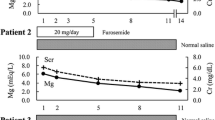
We report a case of hypermagnesemia in a hospitalized patient after prolonged laxative use; due to preexisting impaired consciousness and digestive problems, the hypermagnesemia was difficult to detect until it almost became fatal. A 64-year-old man who was a patient at another hospital for treatment of head injury and gastric ulcer had developed circulatory collapse and was transferred to our hospital. Hypermagnesemia (serum magnesium concentration 11.0 mg·dl−1) was thought to be the cause of the circulatory collapse and treatments were successful. A magnesium laxative had been administered for more than a month at the previous hospital, but the patient's serum magnesium level was never measured. Care should be taken when a magnesium laxative is administered to patients who already have impaired consciousness and digestive problems that are early symptoms of hypermagnesemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R Behzad S Douglas (2000) ArticleTitleHypermagnesemia–induced multiorgan failure Am J Med 108 686–687 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9343(00)00403-4
MC Garcia RP Byrd SuffixJr TM Roy (2002) ArticleTitleLethal iatrogenic hypermagnesemia Tenn Med 95 334–336 Occurrence Handle12174756
T Qureshi TK Melonakos (1996) ArticleTitleAcute hypermagnesemia after laxative use Ann Emerg Med 28 552–555 Occurrence Handle8909278 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0196-0644(96)70120-8 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiD28rnvFM%3D
SA McLaughlin PE McKinney (1998) ArticleTitleAntacid-induced hypermagnesemia in a patient with normal renal function and bowel obstruction Ann Pharmacother 32 312–315 Occurrence Handle9533062 Occurrence Handle10.1345/aph.17284 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7psVamtA%3D%3D
N Hashizume M Mori (1990) ArticleTitleAn analysis of hypermagnesemia and hypomagnesemia Jpn J Med 29 368–372 Occurrence Handle2273620 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6C3cbgsVE%3D
JM Brand FR Greer (1990) ArticleTitleHypermagnesemia and intestinal perforation following antacid administration in a premature infant Pediatrics 85 121–124 Occurrence Handle2296480 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BC3MrhslA%3D
CA Weber RM Santiago (1989) ArticleTitleHypermagnesemia—a potential complication during treatment of theophyline intoxication with oral activated charcoal and magnesium-containing cathartics Chest 95 56–59 Occurrence Handle2909356 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaD2sfgvFY%3D
M Kotani A Hara S Ohta T Ikeda (2005) ArticleTitleHypermagnesemia induced by massive cathartic ingestion in an elderly woman without pre-existing renal dysfunction Intern Med 44 448–452 Occurrence Handle10.2169/internalmedicine.44.448
J Golzarian HW Scott SuffixJr WO Richards (1994) ArticleTitleHypermagnesemia-induced paralytic ileus Dig Dis Sci 39 1138–1142 Occurrence Handle8174429 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02087570 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuB38fovVw%3D
JR Schelling (2000) ArticleTitleFatal hypermagnesemia Clin Nephrol 53 61–65 Occurrence Handle10661484 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7isFWhtA%3D%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
So, M., Ito, H., Sobue, K. et al. Circulatory collapse caused by unnoticed hypermagnesemia in a hospitalized patient. J Anesth 21, 273–276 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-006-0492-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-006-0492-8